Related Research Articles

Bioterrorism is terrorism involving the intentional release or dissemination of biological agents. These agents include bacteria, viruses, insects, fungi, and/or toxins, and may be in a naturally occurring or a human-modified form, in much the same way as in biological warfare. Further, modern agribusiness is vulnerable to anti-agricultural attacks by terrorists, and such attacks can seriously damage economy as well as consumer confidence. The latter destructive activity is called agrobioterrorism and is a subtype of agro-terrorism.
Biodefense refers to measures to restore biosecurity to a group of organisms who are, or may be, subject to biological threats or infectious diseases. Biodefense is frequently discussed in the context of biowar or bioterrorism, and is generally considered a military or emergency response term.
Anthrax hoaxes involving the use of white powder or labels to falsely suggest the use of anthrax are frequently reported in the United States and globally. Hoaxes have increased following the 2001 anthrax attacks, after which no genuine anthrax attacks have occurred. The FBI and U.S. postal inspectors have responded to thousands of "white powder events" and targets have included government offices, US embassies, banks and news organizations.

The State Research Center of Virology and Biotechnology VECTOR, also known as the Vector Institute, is a biological research center in Koltsovo, Novosibirsk Oblast, Russia. It has research facilities and capabilities for all levels of Biological Hazard, CDC Levels 1–4. It is one of two official repositories for the now-eradicated smallpox virus, and was part of the system of laboratories known as the Biopreparat.

The United States Army Medical Research Institute of Infectious Diseases is the U.S Army's main institution and facility for defensive research into countermeasures against biological warfare. It is located on Fort Detrick, Maryland, near Washington, D.C. and is a subordinate lab of the U.S. Army Medical Research and Development Command (USAMRDC), headquartered on the same installation.

Michael Thomas Osterholm is an American epidemiologist, Regents Professor, and Director of the Center for Infectious Disease Research and Policy at the University of Minnesota.
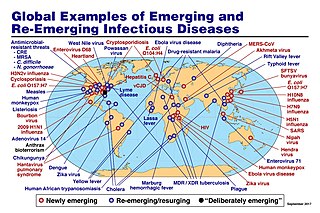
An emerging infectious disease (EID) is an infectious disease whose incidence has increased recently, and could increase in the near future. The minority that are capable of developing efficient transmission between humans can become major public and global concerns as potential causes of epidemics or pandemics. Their many impacts can be economic and societal, as well as clinical. EIDs have been increasing steadily since at least 1940. For every decade since 1940, there has been a consistent increase in the number of EID events from wildlife-related zoonosis. Human activity is the primary driver of this increase, with loss of biodiversity a leading mechanism.
Texas Biomedical Research Institute, located in San Antonio, Texas, is an independent, non-profit biomedical research institution, specializing in genetics and in virology and immunology. Texas Biomed is funded by government and corporate grants and contracts, and donations from the public.

Disease surveillance is an epidemiological practice by which the spread of disease is monitored in order to establish patterns of progression. The main role of disease surveillance is to predict, observe, and minimize the harm caused by outbreak, epidemic, and pandemic situations, as well as increase knowledge about which factors contribute to such circumstances. A key part of modern disease surveillance is the practice of disease case reporting.
The National Biodefense Analysis and Countermeasures Center (NBACC) is a government biodefense research laboratory created by the U.S. Department of Homeland Security (DHS) and located at the sprawling biodefense campus at Fort Detrick in Frederick, MD, USA. The NBACC is the principal U.S. biodefense research institution engaged in laboratory-based threat assessment and bioforensics. NBACC is an important part of the National Interagency Biodefense Campus (NIBC) also located at Fort Detrick for the US Army, National Institutes of Health and the US Department of Agriculture.

The Biomedical Advanced Research and Development Authority(BARDA) is a U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) office responsible for the procurement and development of medical countermeasures, principally against bioterrorism, including chemical, biological, radiological and nuclear (CBRN) threats, as well as pandemic influenza and emerging diseases. BARDA was established in 2006 through the Pandemic and All-Hazards Preparedness Act (PAHPA) and reports to the Office of the Assistant Secretary for Preparedness and Response (ASPR). The office manages Project BioShield, which funds the research, development and stockpiling of vaccines and treatments that the government could use during public health emergencies such as chemical, biological, radiological or nuclear (CBRN) attacks.
Stephen S. Morse is an American epidemiologist, influenza researcher and specialist on emerging infectious diseases, who has served as an adviser on the epidemiology of infectious diseases and on improving disease early warning systems to numerous government and international organizations. As of 2016, he is Professor of Epidemiology at the Mailman School of Public Health of Columbia University. His seminal book Emerging Viruses (1993) was selected by American Scientist for its list of "100 Top Science Books of the 20th Century".
The United States biological defense program—in recent years also called the National Biodefense Strategy—refers to the collective effort by all levels of government, along with private enterprise and other stakeholders, in the United States to carry out biodefense activities.

The National Biodefense Strategy Act of 2016 is a bill introduced in the United States Senate by U.S. Senator Ron Johnson (R-Wisconsin). The bill would amend the Homeland Security Act of 2002 by requiring the government to change its current policy and programs to coordinate and improve biodefense preparedness. Johnson is the current chairman of the Senate Committee on Homeland Security and Governmental Affairs.

The Alliance for Biosecurity is a consortium of companies that develop products to respond to national security threats, including bioterrorism pathogens and emerging infectious diseases. It is headquartered in Washington DC.

The Pandemic and All-Hazards Preparedness and Advancing Innovation Act (PAHPAI) is legislation introduced and passed by the U.S. Congress in 2019 that aims to improve the nation's preparation and response to public health threats, including both natural threats and deliberate man-made threats.
Daniel R. Lucey is an American physician, researcher, senior scholar and adjunct professor of infectious diseases at Georgetown University, and a research associate in anthropology at the Smithsonian National Museum of Natural History, where he has co-organised an exhibition on eight viral outbreaks.

Vickie Sutton is a Lumbee Law professor currently on the faculty of Texas Tech University. Since 2014, Sutton has been on the Texas Task Force on Infectious Disease Preparedness and Response.
Crystal Watson is a senior scholar at the Johns Hopkins Center for Health Security and an assistant professor in the Department of Environmental Health and Engineering. She is an expert in health security, biodefense, and risk assessment and preparedness for emerging infectious diseases. She is currently working on the public health response to the COVID-19 pandemic.
References
- ↑ Wright, Dorothy (October 2004). "Bioterrorism: The New Threat of Infectious Diseases". Science and Technology Newsletter. Bryn Mawr College.
- ↑ "Goss warns of terror threat to U.S." CNN. 2005-02-17.