
The Alps form part of a Cenozoic orogenic belt of mountain chains, called the Alpide belt, that stretches through southern Europe and Asia from the Atlantic all the way to the Himalayas. This belt of mountain chains was formed during the Alpine orogeny. A gap in these mountain chains in central Europe separates the Alps from the Carpathians to the east. Orogeny took place continuously and tectonic subsidence has produced the gaps in between.
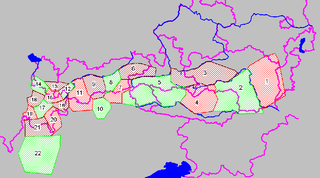
The Central Eastern Alps, also referred to as Austrian Central Alps or just Central Alps, comprise the main chain of the Eastern Alps in Austria and the adjacent regions of Switzerland, Liechtenstein, Italy and Slovenia. South them is the Southern Limestone Alps.

In geology, a nappe or thrust sheet is a large sheetlike body of rock that has been moved more than 2 km (1.2 mi) or 5 km (3.1 mi) above a thrust fault from its original position. Nappes form in compressional tectonic settings like continental collision zones or on the overriding plate in active subduction zones. Nappes form when a mass of rock is forced over another rock mass, typically on a low angle fault plane. The resulting structure may include large-scale recumbent folds, shearing along the fault plane, imbricate thrust stacks, fensters and klippes.

The Periadriatic Seam is a distinct geologic fault in Southern Europe, running S-shaped about 1,000 km (621 mi) from the Tyrrhenian Sea through the whole Southern Alps as far as Hungary. It forms the division between the Adriatic plate and the European plate.

The Helvetic zone, Helvetic system or the Helveticum is a geologic subdivision of the Alps. The Helvetic zone crops out mainly in Switzerland, hence the name. Rocks in the Helvetic zone are sedimentary and were originally deposited at the southern margin of the European plate. The Helvetic zone correlates with the French Dauphinois zone, French geologists often prefer the French name but normally this is considered the same thing.

The Penninic nappes or the Penninicum, commonly abbreviated as Penninic, are one of three nappe stacks and geological zones in which the Alps can be divided. In the western Alps the Penninic nappes are more obviously present than in the eastern Alps, where they crop out as a narrow band. The name Penninic is derived from the Pennine Alps, an area in which rocks from the Penninic nappes are abundant.

The Austroalpine nappes are a geological nappe stack in the European Alps. The Alps contain three such stacks, of which the Austroalpine nappes are structurally on top of the other two. The name Austroalpine means Southern Alpine, because these nappes crop out mainly in the Eastern Alps.

The Aarmassif or Aaremassif is a geologic massif in the Swiss Alps. It contains a number of large mountain chains and parts of mountain chains.

The Adriatic or Apulian Plate is a small tectonic plate carrying primarily continental crust that broke away from the African Plate along a large transform fault in the Cretaceous period. The name Adriatic Plate is usually used when referring to the northern part of the plate. This part of the plate was deformed during the Alpine orogeny, when the Adriatic/Apulian Plate collided with the Eurasian Plate.

The Giudicarie Line is a major geologic fault zone in the Italian Alps, named for the Giudicarie valleys area. It runs from Meran in the northeast more or less straight along the lower part of the Val di Sole, along the Val Rendena and then along the Chiese valley to the Lago d'Idro.

The Lepontine dome or Lepontin dome is a region of tectonic uplift in the Swiss part of the Alps. It is located in the Lepontine Alps and Glarus Alps.

The Molasse basin is a foreland basin north of the Alps which formed during the Oligocene and Miocene epochs. The basin formed as a result of the flexure of the European plate under the weight of the orogenic wedge of the Alps that was forming to the south.
The Helvetic nappes are a series of nappes in the Northern part of the Alps and part of the Helvetic zone. They consist of Mesozoic limestones, shales and marls that were originally deposited on the southern continental margin of the European continent. During the Alpine orogeny they were thrust north over a décollement and at the same time were internally deformed by folding and thrusting.

Fold mountains are formed by the effects of folding on layers within the upper part of the Earth's crust. Before the development of the theory of plate tectonics and before the internal architecture of thrust belts became well understood, the term was used to describe most mountain belts but has otherwise fallen out of use.

The Western Carpathians are an arc-shaped mountain range, the northern branch of the Alpine-Himalayan fold and thrust system called the Alpide belt, which evolved during the Alpine orogeny. In particular, their pre-Cenozoic evolution is very similar to that of the Eastern Alps, and they constitute a transition between the Eastern Alps and the Eastern Carpathians.

The geology of Germany is heavily influenced by several phases of orogeny in the Paleozoic and the Cenozoic, by sedimentation in shelf seas and epicontinental seas and on plains in the Permian and Mesozoic as well as by the Quaternary glaciations.

A longitudinal valley is an elongated valley found between two almost-parallel mountain chains in geologically young fold mountains, such as the Alps, Carpathians, Andes, or the highlands of Central Asia. They are often occupied and shaped by a subsequent stream. The term is frequently used if a mountain range also has prominent transverse valleys, where rivers cut through the mountain chains in so-called water gaps.
The geology of Austria consists of Precambrian rocks and minerals together with younger marine sedimentary rocks uplifted by the Alpine orogeny.

The geology of Croatia has some Precambrian rocks mostly covered by younger sedimentary rocks and deformed or superimposed by tectonic activity.

The geology of Italy includes mountain ranges such as the Alps and the Apennines formed from the uplift of igneous and primarily marine sedimentary rocks all formed since the Paleozoic. Some active volcanoes are located in Insular Italy.











