Southern Head is a headland located at the southwestern tip of Grand Manan Island in the Canadian province of New Brunswick.
Both headland and bay are two coastal features that are related and often found on the same coastline. A bay is a body of water—usually seawater and sometimes fresh water— mostly surrounded by land, whereas a headland is surrounded by water on three sides. Headlands are characterized by breaking waves, rocky shores, intense erosion and steep sea cliffs. Bays generally have less wave activity and typically have sandy beaches. Headlands and bays form on discordant coastlines, where the land consists of bands of rock of alternating resistance that run perpendicular to the coast.

Grand Manan Island is a Canadian island, and the largest of the Fundy Islands in the Bay of Fundy. It is the primary island in the Grand Manan Archipelago, sitting at the boundary between the Bay of Fundy and the Gulf of Maine on the Atlantic coast. Grand Manan is jurisdictionally part of Charlotte County in the province of New Brunswick.

Canada is a country in the northern part of North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic to the Pacific and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering 9.98 million square kilometres, making it the world's second-largest country by total area. Canada's southern border with the United States is the world's longest bi-national land border. Its capital is Ottawa, and its three largest metropolitan areas are Toronto, Montreal, and Vancouver. As a whole, Canada is sparsely populated, the majority of its land area being dominated by forest and tundra. Consequently, its population is highly urbanized, with over 80 percent of its inhabitants concentrated in large and medium-sized cities, many near the southern border. Canada's climate varies widely across its vast area, ranging from arctic weather in the north, to hot summers in the southern regions, with four distinct seasons.
Southern Head is an important landmark:
- It forms the southern and westernmost point on Grand Manan Island.
- It forms the northwestern limit of the Bay of Fundy and is opposite the southwestern limit at Brier Island, Nova Scotia.
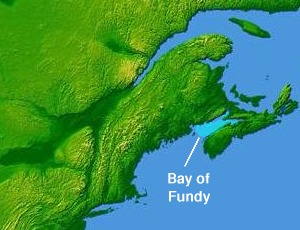
The Bay of Fundy is a bay between the Canadian provinces of New Brunswick and Nova Scotia, with a small portion touching the US state of Maine. It has an extremely high tidal range.

Brier Island is an island in the Bay of Fundy in Digby County, Nova Scotia.

Nova Scotia is one of Canada's three Maritime Provinces, and one of the four provinces that form Atlantic Canada. Its provincial capital is Halifax. Nova Scotia is the second-smallest of Canada's ten provinces, with an area of 55,284 square kilometres (21,300 sq mi), including Cape Breton and another 3,800 coastal islands. As of 2016, the population was 923,598. Nova Scotia is Canada's second-most-densely populated province, after Prince Edward Island, with 17.4 inhabitants per square kilometre (45/sq mi).
The Canadian Coast Guard maintains an automated light station to assist vessels navigating in the thick fog that frequents the area, particularly during the humid summer months.

The Canadian Coast Guard is the coast guard of Canada. Formed in 1962, the coast guard is tasked with marine search and rescue, communication, navigation and transportation issues in Canadian waters, such as navigation aids and icebreaking, marine pollution response and providing support for other Canadian government initiatives. The coast guard operates 119 vessels of varying sizes and 22 helicopters, along with a variety of smaller craft. The Canadian Coast Guard is headquartered in Ottawa, Ontario, and is a Special Operating Agency within Fisheries and Oceans Canada.
Coordinates: 44°35′55″N66°54′20″W / 44.59861°N 66.90556°W

A geographic coordinate system is a coordinate system that enables every location on Earth to be specified by a set of numbers, letters or symbols. The coordinates are often chosen such that one of the numbers represents a vertical position and two or three of the numbers represent a horizontal position; alternatively, a geographic position may be expressed in a combined three-dimensional Cartesian vector. A common choice of coordinates is latitude, longitude and elevation. To specify a location on a plane requires a map projection.