Related Research Articles

Electronic mail is a method of transmitting and receiving messages using electronic devices. It was conceived in the late–20th century as the digital version of, or counterpart to, mail. Email is a ubiquitous and very widely used communication medium; in current use, an email address is often treated as a basic and necessary part of many processes in business, commerce, government, education, entertainment, and other spheres of daily life in most countries.
A Domain Name System blocklist, Domain Name System-based blackhole list, Domain Name System blacklist (DNSBL) or real-time blackhole list (RBL) is a service for operation of mail servers to perform a check via a Domain Name System (DNS) query whether a sending host's IP address is blacklisted for email spam. Most mail server software can be configured to check such lists, typically rejecting or flagging messages from such sites.
A mailing list is a collection of names and addresses used by an individual or an organization to send material to multiple recipients. The term is often extended to include the people subscribed to such a list, so the group of subscribers is referred to as "the mailing list", or simply "the list".
A tarpit is a service on a computer system that purposely delays incoming connections. The technique was developed as a defense against a computer worm, and the idea is that network abuses such as spamming or broad scanning are less effective, and therefore less attractive, if they take too long. The concept is analogous with a tar pit, in which animals can get bogged down and slowly sink under the surface, like in a swamp.
Various anti-spam techniques are used to prevent email spam.

Email spam, also referred to as junk email, spam mail, or simply spam, is unsolicited messages sent in bulk by email (spamming). The name comes from a Monty Python sketch in which the name of the canned pork product Spam is ubiquitous, unavoidable, and repetitive. Email spam has steadily grown since the early 1990s, and by 2014 was estimated to account for around 90% of total email traffic.
Address munging is the practice of disguising an e-mail address to prevent it from being automatically collected by unsolicited bulk e-mail providers. Address munging is intended to disguise an e-mail address in a way that prevents computer software from seeing the real address, or even any address at all, but still allows a human reader to reconstruct the original and contact the author: an email address such as, "no-one@example.com", becomes "no-one at example dot com", for instance.
The Distributed Sender Blackhole List was a Domain Name System-based Blackhole List that listed IP addresses of insecure e-mail hosts. DSBL could be used by server administrators to tag or block e-mail messages that came from insecure servers, which is often spam.
Greylisting is a method of defending e-mail users against spam. A mail transfer agent (MTA) using greylisting will "temporarily reject" any email from a sender it does not recognize. If the mail is legitimate, the originating server will try again after a delay, and if sufficient time has elapsed, the email will be accepted.
Email marketing is the act of sending a commercial message, typically to a group of people, using email. In its broadest sense, every email sent to a potential or current customer could be considered email marketing. It involves using email to send advertisements, request business, or solicit sales or donations. Email marketing strategies commonly seek to achieve one or more of three primary objectives: build loyalty, trust, or brand awareness. The term usually refers to sending email messages with the purpose of enhancing a merchant's relationship with current or previous customers, encouraging customer loyalty and repeat business, acquiring new customers or convincing current customers to purchase something immediately, and sharing third-party ads.
Kontact is a personal information manager and groupware software suite developed by KDE. It supports calendars, contacts, notes, to-do lists, news, and email. It offers a number of inter-changeable graphical UIs all built on top of a common core.
Email harvesting or scraping is the process of obtaining lists of email addresses using various methods. Typically these are then used for bulk email or spam.
spamd is an ISC-licensed lightweight spam-deferral daemon written under the umbrella of the OpenBSD project. spamd works directly with smtp connections, and supports features such as greylisting, minimising false positives compared to a system that does full-body analysis. spamd is designed to work in conjunction with pf(4), and should be fully functional on any POSIX system where pf is available, i.e. OpenBSD, NetBSD, FreeBSD and DragonFly BSD.
Opt-in email is a term used when someone is not initially added to an emailing list and is instead given the option to join the emailing list. Typically, this is some sort of mailing list, newsletter, or advertising. Opt-out emails do not ask for permission to send emails, these emails are typically criticized as unsolicited bulk emails, better known as spam.

Blue Frog was a freely-licensed anti-spam tool produced by Blue Security Inc. and operated as part of a community-based system which tried to persuade spammers to remove community members' addresses from their mailing lists by automating the complaint process for each user as spam is received. Blue Security maintained these addresses in a hashed form in a Do Not Intrude Registry, and spammers could use free tools to clean their lists. The tool was discontinued in 2006.
A challenge–response system is a type of that automatically sends a reply with a challenge to the (alleged) sender of an incoming e-mail. It was originally designed in 1997 by Stan Weatherby, and was called Email Verification. In this reply, the purported sender is asked to perform some action to assure delivery of the original message, which would otherwise not be delivered. The action to perform typically takes relatively little effort to do once, but great effort to perform in large numbers. This effectively filters out spammers. Challenge–response systems only need to send challenges to unknown senders. Senders that have previously performed the challenging action, or who have previously been sent e-mail(s) to, would be automatically
In computer networking, the Composite Blocking List (CBL) is a DNS-based Blackhole List of suspected E-mail spam sending computer infections.
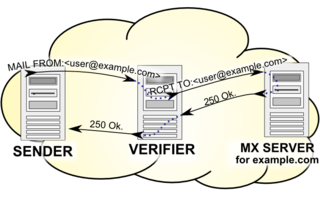
Callback verification, also known as callout verification or Sender Address Verification, is a technique used by SMTP software in order to validate e-mail addresses. The most common target of verification is the sender address from the message envelope. It is mostly used as an anti-spam measure.
Backscatter is incorrectly automated bounce messages sent by mail servers, typically as a side effect of incoming spam.
XRumer is a piece of software made for spamming online forums and comment sections. It is marketed as a program for search engine optimization and was created by BotmasterLabs. It is able to register and post to forums with the aim of boosting search engine rankings. The program is able to bypass security techniques commonly used by many forums and blogs to deter automated spam, such as account registration, client detection, many forms of CAPTCHAs, and e-mail activation before posting. The program utilises SOCKS and HTTP proxies in an attempt to make it more difficult for administrators to block posts by source IP, and features a proxy checking tool to verify the integrity and anonymity of the proxies used.