Related Research Articles

Sodium hydroxide, also known as lye and caustic soda, is an inorganic compound with the formula NaOH. It is a white solid ionic compound consisting of sodium cations Na+
and hydroxide anions OH−
.

Sodium carbonate, Na2CO3, (also known as washing soda, soda ash and soda crystals) is the inorganic compound with the formula Na2CO3 and its various hydrates. All forms are white, water-soluble salts. All forms have a strongly alkaline taste and give moderately alkaline solutions in water. Historically it was extracted from the ashes of plants growing in sodium-rich soils. Because the ashes of these sodium-rich plants were noticeably different from ashes of wood (once used to produce potash), sodium carbonate became known as "soda ash". It is produced in large quantities from sodium chloride and limestone by the Solvay process.
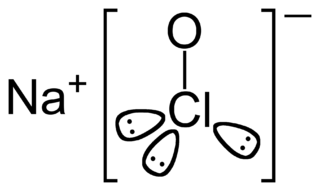
Sodium hypochlorite is a chemical compound with the formula NaOCl or NaClO, comprising a sodium cation and a hypochlorite anion. It may also be viewed as the sodium salt of hypochlorous acid. The anhydrous compound is unstable and may decompose explosively. It can be crystallized as a pentahydrate NaOCl·5H
2O, a pale greenish-yellow solid which is not explosive and is stable if kept refrigerated.

Potassium hydroxide is an inorganic compound with the formula KOH, and is commonly called caustic potash.

Ethylene oxide, called oxirane by IUPAC, is an organic compound with the formula C
2H
4O. It is a cyclic ether and the simplest epoxide: a three-membered ring consisting of one oxygen atom and two carbon atoms. Ethylene oxide is a colorless and flammable gas with a faintly sweet odor. Because it is a strained ring, ethylene oxide easily participates in a number of addition reactions that result in ring-opening. Ethylene oxide is isomeric with acetaldehyde and with vinyl alcohol. Ethylene oxide is industrially produced by oxidation of ethylene in the presence of silver catalyst.
The Bayer process is the principal industrial means of refining bauxite to produce alumina (aluminium oxide) and was developed by Carl Josef Bayer. Bauxite, the most important ore of aluminium, contains only 30–60% aluminium oxide (Al2O3), the rest being a mixture of silica, various iron oxides, and titanium dioxide. The aluminium oxide must be purified before it can be refined to aluminium metal.
Red oil is defined as a substance of varying composition formed when an organic solution, typically tri-n-butyl phosphate and its diluent, comes in contact with concentrated nitric acid at a temperature above 120 °C.

Sodium sulfate (also known as sodium sulphate or sulfate of soda) is the inorganic compound with formula Na2SO4 as well as several related hydrates. All forms are white solids that are highly soluble in water. With an annual production of 6 million tonnes, the decahydrate is a major commodity chemical product. It is mainly used for the manufacture of detergents and in the kraft process of paper pulping.

The chloralkali process is an industrial process for the electrolysis of sodium chloride solutions. It is the technology used to produce chlorine and sodium hydroxide, which are commodity chemicals required by industry. 35 million tons of chlorine were prepared by this process in 1987. Industrial scale production began in 1892.

The kraft process (also known as kraft pulping or sulfate process) is a process for conversion of wood into wood pulp, which consists of almost pure cellulose fibers, the main component of paper. The kraft process entails treatment of wood chips with a hot mixture of water, sodium hydroxide (NaOH), and sodium sulfide (Na2S), known as white liquor, that breaks the bonds that link lignin, hemicellulose, and cellulose. The technology entails several steps, both mechanical and chemical. It is the dominant method for producing paper. In some situations, the process has been controversial because kraft plants can release odorous products and in some situations produce substantial liquid wastes.

Flue-gas desulfurization (FGD) is a set of technologies used to remove sulfur dioxide from exhaust flue gases of fossil-fuel power plants, and from the emissions of other sulfur oxide emitting processes such as waste incineration.
Industrial wastewater treatment describes the processes used for treating wastewater that is produced by industries as an undesirable by-product. After treatment, the treated industrial wastewater may be reused or released to a sanitary sewer or to a surface water in the environment.
Sodium methoxide is a chemical compound with the formula CH3ONa. This white solid, which is formed by the deprotonation of methanol, is a widely used reagent in industry and the laboratory. It is also a dangerously caustic base.
Merox is an acronym for mercaptan oxidation. It is a proprietary catalytic chemical process developed by UOP used in oil refineries and natural gas processing plants to remove mercaptans from LPG, propane, butanes, light naphthas, kerosene and jet fuel by converting them to liquid hydrocarbon disulfides.
Wet oxidation is a form of hydrothermal treatment. It is the oxidation of dissolved or suspended components in water using oxygen as the oxidizer. It is referred to as "Wet Air Oxidation" (WAO) when air is used. The oxidation reactions occur in superheated water at a temperature above the normal boiling point of water (100 °C), but below the critical point (374 °C).
A carbon dioxide scrubber is a piece of equipment that absorbs carbon dioxide (CO2). It is used to treat exhaust gases from industrial plants or from exhaled air in life support systems such as rebreathers or in spacecraft, submersible craft or airtight chambers. Carbon dioxide scrubbers are also used in controlled atmosphere (CA) storage. They have also been researched for carbon capture and storage as a means of combating global warming.
This article presents the industrial and laboratory methods to prepare elemental chlorine.

Wood ash is the residue powder left after the combustion of wood, such as burning wood in a home fireplace or an industrial power plant. It is used traditionally by gardeners as a good source of potash.
In situ chemical oxidation (ISCO), a form of advanced oxidation processes and advanced oxidation technology, is an environmental remediation technique used for soil and/or groundwater remediation to reduce the concentrations of targeted environmental contaminants to acceptable levels. ISCO is accomplished by injecting or otherwise introducing strong chemical oxidizers directly into the contaminated medium to destroy chemical contaminants in place. It can be used to remediate a variety of organic compounds, including some that are resistant to natural degradation.
References
- Suarez, F. "Pluses and Minuses of Caustic Treating", Hydrocarbon Processing, pp 117–123, Oct 1996.
- Maugans, C.; Ellis, C. "Age Old Solution for Today's SO2 and NOx", Pollution Engineering, April 2004.
- Carlos T.; Maugans, C. "Wet Air Oxidation of Refinery Spent Caustic: A Refinery Case Study", NPRA Conference, San Antonio, TX, September 2000. WAO for Refinery Spent Caustic
- Kumfer, B.; Felch, C.; Maugans, C. "Wet Air Oxidation of Spent Caustic in Petroleum Refineries", NPRA, March 2010, San Antonio, TX. WAO for Spent Caustic in Petroleum Refineries