
Vaccinium is a common and widespread genus of shrubs or dwarf shrubs in the heath family (Ericaceae). The fruits of many species are eaten by humans and some are of commercial importance, including the cranberry, blueberry, bilberry (whortleberry), lingonberry (cowberry), and huckleberry. Like many other ericaceous plants, they are generally restricted to acidic soils.

Vaccinium vitis-idaea is a short evergreen shrub in the heath family that bears edible fruit, native to boreal forest and Arctic tundra throughout the Northern Hemisphere from Europe and Asia to North America. Lingonberries are picked in the wild and used to accompany a variety of dishes in Northern Baltoscandia, Russia, Canada and Alaska. Commercial cultivation is undertaken in the U.S. Pacific Northwest and in many other regions of the world.

Bilberries, or occasionally European blueberries, are a primarily Eurasian species of low-growing shrubs in the genus Vaccinium, bearing edible, dark blue berries. The species most often referred to is Vaccinium myrtillus L., but there are several other closely related species.

Vaccinium macrocarpon is a North American species of cranberry of the subgenus Oxycoccus and genus Vaccinium.
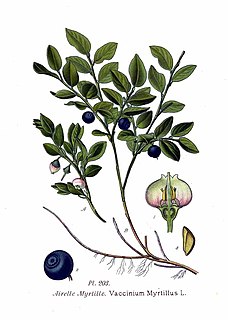
Vaccinium myrtillus is a species of shrub with edible fruit of blue color, commonly called "bilberry", "wimberry", "whortleberry", or European blueberry. It has much in common with the American blueberry. It is more precisely called common bilberry or blue whortleberry, to distinguish it from other Vaccinium relatives. Regional names include blaeberry, urts or hurts, hurtleberry, huckleberry, myrtleberry, wimberry, whinberry, winberry, blueberry, and fraughan. Chromosome count is 2n =24.

Vaccinium myrtilloides is a shrub with common names including common blueberry, velvetleaf huckleberry, velvetleaf blueberry, Canadian blueberry, and sourtop blueberry. It is common in much of North America, reported from all 10 Canadian provinces plus Nunavut and Northwest Territories, as well as from the northeastern and Great Lakes states in the United States. It is also known to occur in Montana and Washington.

Vaccinium arboreum is a species of Vaccinium native to the southeastern and south-central United States, from southern Virginia west to southeastern Nebraska, south to Florida and eastern Texas, and north to Illinois.

Amsterdam Beach State Park is a 199-acre (0.81 km2) undeveloped state park on the Atlantic Ocean in the Town of East Hampton just east of Montauk, New York. The land is also known as the Amsterdam Beach Preserve.
Vaccinium bissei is a species of plant in the family Ericaceae. It is endemic to Cuba.
Vaccinium whitmorei is a species of plant in the family Ericaceae. It is endemic to Peninsular Malaysia. It is threatened by habitat loss.

Blueberries are perennial flowering plants with blue or purple berries. They are classified in the section Cyanococcus within the genus Vaccinium. Vaccinium also includes cranberries, bilberries, huckleberries and Madeira blueberries. Commercial blueberries—both wild (lowbush) and cultivated (highbush)—are all native to North America. The highbush varieties were introduced into Europe during the 1930s.

Hemaris gracilis, the slender clearwing or graceful clearwing, is a moth of the family Sphingidae. The species was first described by Augustus Radcliffe Grote and Coleman Townsend Robinson in 1865. It is found in North America from Nova Scotia to central Florida along the East Coast and west through New England to Michigan to Saskatchewan. The species is listed as threatened in Connecticut.

Lycaena epixanthe, the bog copper or cranberry-bog copper, is a North American butterfly in the family Lycaenidae. Adults like to sip drops of dew clinging to leaves and almost exclusively nectar on their host plant, cranberries. Because of this, bog coppers will spend their entire lives within the area of a single acid bog. Even though their flight is weak and close to the ground, bog coppers are hard to catch because of the habitat in which they live. Also, 85% of the bog coppers life span is spent in the egg. It is listed as a species of special concern in the US state of Connecticut.

Psectraglaea is a monotypic moth genus of the family Noctuidae described by George Hampson in 1906. Its only species, Psectraglaea carnosa, the pink sallow, described by Augustus Radcliffe Grote in 1877, is native to North America. It is listed as threatened in Connecticut, and as a species of special concern in Massachusetts.

Huckleberry is a name used in North America for several plants in the family Ericaceae, in two closely related genera: Vaccinium and Gaylussacia. The huckleberry is the state fruit of Idaho.
Drasteria occulta, the occult drasteria moth, is a moth of the family Erebidae. The species was first described by Henry Edwards in 1881. It is found in North America, where it has been recorded from coastal areas in Maine, New Jersey, Pennsylvania and Texas. It is listed as a species of special concern and believed extirpated in the US state of Connecticut.
Sympistis dentata, the toothed apharetra moth, is a moth of the family Noctuidae described by Augustus Radcliffe Grote in 1875. It is found from Yukon, the Northwest Territories, and British Columbia to Newfoundland and the northern United States, south in the east to New Jersey. It is listed as threatened in the US state of Connecticut. The habitat consists of acidic spruce bogs and swamps, pine-oak barrens on sandplains, rocky summits and ridges.
Digrammia equivocata, the equivocal looper, is a species of moth native to North America. It is listed as historic in the US state of Massachusetts, and as a species of special concern in Connecticut. The larval host plant is Tephrosia virginiana. It was described by Douglas C. Ferguson in 2008.
Speranza austrinata is a species of geometrid moth in the family Geometridae. It was described by Douglas C. Ferguson in 2008 and is found in Central and North America.












