
In biology, mating is the pairing of either opposite-sex or hermaphroditic organisms for the purposes of sexual reproduction. Fertilization is the fusion of two gametes. Copulation is the union of the sex organs of two sexually reproducing animals for insemination and subsequent internal fertilization. Mating may also lead to external fertilization, as seen in amphibians, fishes and plants. For most species, mating is between two individuals of opposite sexes. However, for some hermaphroditic species, copulation is not required because the parent organism is capable of self-fertilization (autogamy); for example, banana slugs.
The Coolidge effect is a biological phenomenon seen in animals, whereby males exhibit renewed sexual interest whenever a new female is introduced, even after sex with prior but still available sexual partners. To a lesser extent, the effect is also seen among females with regard to their mates.

The insect order Zoraptera, commonly known as angel insects, contains small and soft bodied insects with two forms: winged with wings sheddable as in termites, dark and with eyes (compound) and ocelli (simple); or wingless, pale and without eyes or ocelli. They have a characteristic nine-segmented beaded (moniliform) antenna. They have mouthparts adapted for chewing and are mostly found under bark, in dry wood or in leaf litter.

Sperm competition is the competitive process between spermatozoa of two or more different males to fertilize the same egg during sexual reproduction. Competition can occur when females have multiple potential mating partners. Greater choice and variety of mates increases a female's chance to produce more viable offspring. However, multiple mates for a female means each individual male has decreased chances of producing offspring. Sperm competition is an evolutionary pressure on males, and has led to the development of adaptations to increase males' chance of reproductive success. Sperm competition results in a sexual conflict of interest between males and females. Males have evolved several defensive tactics including: mate-guarding, mating plugs, and releasing toxic seminal substances to reduce female re-mating tendencies to cope with sperm competition. Offensive tactics of sperm competition involve direct interference by one male on the reproductive success of another male, for instance by physically removing another male's sperm prior to mating with a female. For an example, see Gryllus bimaculatus.

A spermatophore or sperm ampulla is a capsule or mass containing spermatozoa created by males of various animal species, especially salamanders and arthropods, and transferred in entirety to the female's ovipore during reproduction. Spermatophores may additionally contain nourishment for the female, in which case it is called a nuptial gift, as in the instance of bush crickets. In the case of the toxic moth Utetheisa ornatrix, the spermatophore includes sperm, nutrients, and pyrrolizidine alkaloids which prevent predation because it is poisonous to most organisms. However, in some species such as the Edith's checkerspot butterfly, the "gift" provides little nutrient value. The weight of the spermatophore transferred at mating has little effect on female reproductive output.

Internal fertilization is the union of an egg and sperm cell during sexual reproduction inside the female body. Internal fertilization, unlike its counterpart, external fertilization, brings more control to the female with reproduction. For internal fertilization to happen there needs to be a method for the male to introduce the sperm into the female's reproductive tract.

Heliconius charithonia, the zebra longwing or zebra heliconian, is a species of butterfly belonging to the subfamily Heliconiinae of the family Nymphalidae. It was first described by Carl Linnaeus in his 1767 12th edition of Systema Naturae. The boldly striped black and white wing pattern is aposematic, warning off predators.

An aedeagus is a reproductive organ of male arthropods through which they secrete sperm from the testes during copulation with a female. It can be thought of as the insect equivalent of a mammal's penis, though the comparison is fairly loose given the greater complexity of insect reproduction. The term is derived from Ancient Greek αἰδοῖα and ἀγός. It is pronounced or.

Sexual conflict or sexual antagonism occurs when the two sexes have conflicting optimal fitness strategies concerning reproduction, particularly over the mode and frequency of mating, potentially leading to an evolutionary arms race between males and females. In one example, males may benefit from multiple matings, while multiple matings may harm or endanger females, due to the anatomical differences of that species. Sexual conflict underlies the evolutionary distinction between male and female.

Teleogryllus oceanicus, commonly known as the Australian, Pacific or oceanic field cricket, is a cricket found across Oceania and in coastal Australia from Carnarvon in Western Australia and Rockhampton in north-east Queensland

Traumatic insemination, also known as hypodermic insemination, is the mating practice in some species of invertebrates in which the male pierces the female's abdomen with his aedeagus and injects his sperm through the wound into her abdominal cavity (hemocoel). The sperm diffuses through the female's hemolymph, reaching the ovaries and resulting in fertilization.

Deinacrida fallai or the Poor Knights giant wētā is a species of insect in the family Anostostomatidae. It is endemic to the Poor Knights Islands off northern New Zealand. D. fallai are commonly called giant wētā due to their large size. They are one of the largest insects in the world, with a body length measuring up to 73 mm. Their size is an example of island gigantism. They are classified as vulnerable by the IUCN due to their restricted distribution.
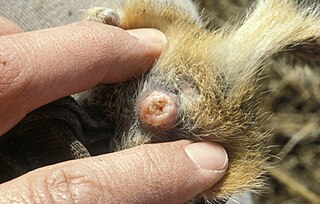
A mating plug, also known as a copulation plug, sperm plug, vaginal plug, or sphragis, is gelatinous secretion used in the mating of some species. It is deposited by a male into a female genital tract, such as the vagina, and later hardens into a plug or glues the tract together. While females can expel the plugs afterwards, the male's sperm still gets a time advantage in getting to the egg, which is often the deciding factor in fertilization.
An intromittent organ is any external organ of a male organism that is specialized to deliver sperm during copulation. Intromittent organs are found most often in terrestrial species, as most non-mammalian aquatic species fertilize their eggs externally, although there are exceptions. For many species in the animal kingdom, the male intromittent organ is a hallmark characteristic of internal fertilization.

The study of the genitalia of Lepidoptera is important for Lepidoptera taxonomy in addition to development, anatomy and natural history. The genitalia are complex and provide the basis for species discrimination in most families and also in family identification. The genitalia are attached onto the tenth or most distal segment of the abdomen. Lepidoptera have some of the most complex genital structures in the insect groups with a wide variety of complex spines, setae, scales and tufts in males, claspers of different shapes and different modifications of the ductus bursae in females.
A nuptial gift is a nutritional gift given by one partner in some animals' sexual reproduction practices.

Sexual selection in amphibians involves sexual selection processes in amphibians, including frogs, salamanders and newts. Prolonged breeders, the majority of frog species, have breeding seasons at regular intervals where male-male competition occurs with males arriving at the waters edge first in large number and producing a wide range of vocalizations, with variations in depth of calls the speed of calls and other complex behaviours to attract mates. The fittest males will have the deepest croaks and the best territories, with females making their mate choices at least partly based on the males depth of croaking. This has led to sexual dimorphism, with females being larger than males in 90% of species, males in 10% and males fighting for groups of females.

The mating of gastropods is a vast and varied topic, because the taxonomic class Gastropoda is very large and diverse, a group comprising sea snails and sea slugs, freshwater snails and land snails and slugs. Gastropods are second only to the class Insecta in terms of total number of species. Some gastropods have separate sexes, others are hermaphroditic. Some hermaphroditic groups have simultaneous hermaphroditism, whereas some sequential hermaphroditism. In addition, numerous very different mating strategies are used within different taxa.

In zoology, copulation is animal sexual behavior in which a male introduces sperm into the female's body, especially directly into her reproductive tract. This is an aspect of mating. Many animals that live in water use external fertilization, whereas internal fertilization may have developed from a need to maintain gametes in a liquid medium in the Late Ordovician epoch. Internal fertilization with many vertebrates occurs via cloacal copulation, known as cloacal kiss, while mammals copulate vaginally, and many basal vertebrates reproduce sexually with external fertilization.

Teleopsis dalmanni, synonym Cyrtodiopsis dalmanni, also known as the Malaysian stalk-eyed fly, is a species of fly in the family Diopsidae. T. dalmanni flies possess lateral elongations on their head capsules called eyestalks. These eyestalks play an important role in mate selection and as a result physical characteristic of the fly has been the subject of several studies on sexual selection, natural selection, and mating behavior.














