
A sphere is a geometrical object that is a three-dimensional analogue to a two-dimensional circle. Formally, a sphere is the set of points that are all at the same distance r from a given point in three-dimensional space. That given point is the center of the sphere, and r is the sphere's radius. The earliest known mentions of spheres appear in the work of the ancient Greek mathematicians.

A triangle is a polygon with three corners and three sides, one of the basic shapes in geometry. The corners, also called vertices, are zero-dimensional points while the sides connecting them, also called edges, are one-dimensional line segments. A triangle has three internal angles, each one bounded by a pair of adjacent edges; the sum of angles of a triangle always equals a straight angle. The triangle is a plane figure and its interior is a planar region. Sometimes an arbitrary edge is chosen to be the base, in which case the opposite vertex is called the apex; the shortest segment between base and apex is the height. The area of a triangle equals one-half the product of height and base length.
In mathematics, non-Euclidean geometry consists of two geometries based on axioms closely related to those that specify Euclidean geometry. As Euclidean geometry lies at the intersection of metric geometry and affine geometry, non-Euclidean geometry arises by either replacing the parallel postulate with an alternative, or relaxing the metric requirement. In the former case, one obtains hyperbolic geometry and elliptic geometry, the traditional non-Euclidean geometries. When the metric requirement is relaxed, then there are affine planes associated with the planar algebras, which give rise to kinematic geometries that have also been called non-Euclidean geometry.

Spherical geometry or spherics is the geometry of the two-dimensional surface of a sphere or the n-dimensional surface of higher dimensional spheres.
Elliptic geometry is an example of a geometry in which Euclid's parallel postulate does not hold. Instead, as in spherical geometry, there are no parallel lines since any two lines must intersect. However, unlike in spherical geometry, two lines are usually assumed to intersect at a single point. Because of this, the elliptic geometry described in this article is sometimes referred to as single elliptic geometry whereas spherical geometry is sometimes referred to as double elliptic geometry.

In mathematics, hyperbolic geometry is a non-Euclidean geometry. The parallel postulate of Euclidean geometry is replaced with:
In mathematics, the uniformization theorem states that every simply connected Riemann surface is conformally equivalent to one of three Riemann surfaces: the open unit disk, the complex plane, or the Riemann sphere. The theorem is a generalization of the Riemann mapping theorem from simply connected open subsets of the plane to arbitrary simply connected Riemann surfaces.

In mathematics, hyperbolic space of dimension n is the unique simply connected, n-dimensional Riemannian manifold of constant sectional curvature equal to −1. It is homogeneous, and satisfies the stronger property of being a symmetric space. There are many ways to construct it as an open subset of with an explicitly written Riemannian metric; such constructions are referred to as models. Hyperbolic 2-space, H2, which was the first instance studied, is also called the hyperbolic plane.
A regular polyhedron is a polyhedron whose symmetry group acts transitively on its flags. A regular polyhedron is highly symmetrical, being all of edge-transitive, vertex-transitive and face-transitive. In classical contexts, many different equivalent definitions are used; a common one is that the faces are congruent regular polygons which are assembled in the same way around each vertex.

In spherical geometry, a spherical circle is the locus of points on a sphere at constant spherical distance from a given point on the sphere. It is a curve of constant geodesic curvature relative to the sphere, analogous to a line or circle in the Euclidean plane; the curves analogous to straight lines are called great circles, and the curves analogous to planar circles are called small circles or lesser circles. If the sphere is embedded in three-dimensional Euclidean space, its circles are the intersections of the sphere with planes, and the great circles are intersections with planes passing through the center of the sphere.

In geometry, the Dandelin spheres are one or two spheres that are tangent both to a plane and to a cone that intersects the plane. The intersection of the cone and the plane is a conic section, and the point at which either sphere touches the plane is a focus of the conic section, so the Dandelin spheres are also sometimes called focal spheres.

A gnomonic projection, also known as a central projection or rectilinear projection, is a perspective projection of a sphere, with center of projection at the sphere's center, onto any plane not passing through the center, most commonly a tangent plane. Under gnomonic projection every great circle on the sphere is projected to a straight line in the plane. More generally, a gnomonic projection can be taken of any n-dimensional hypersphere onto a hyperplane.
In mathematics, constant curvature is a concept from differential geometry. Here, curvature refers to the sectional curvature of a space and is a single number determining its local geometry. The sectional curvature is said to be constant if it has the same value at every point and for every two-dimensional tangent plane at that point. For example, a sphere is a surface of constant positive curvature.
Geometry is a branch of mathematics concerned with questions of shape, size, relative position of figures, and the properties of space. Geometry is one of the oldest mathematical sciences.
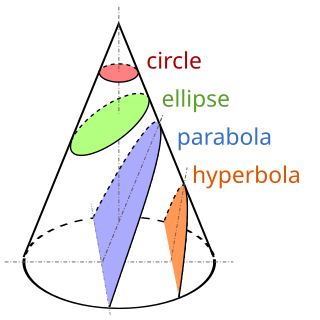
A conic section, conic or a quadratic curve is a curve obtained from a cone's surface intersecting a plane. The three types of conic section are the hyperbola, the parabola, and the ellipse; the circle is a special case of the ellipse, though it was sometimes called as a fourth type. The ancient Greek mathematicians studied conic sections, culminating around 200 BC with Apollonius of Perga's systematic work on their properties.
In mathematics, a plane is a two-dimensional space or flat surface that extends indefinitely. A plane is the two-dimensional analogue of a point, a line and three-dimensional space. When working exclusively in two-dimensional Euclidean space, the definite article is used, so the Euclidean plane refers to the whole space.

Ordinary trigonometry studies triangles in the Euclidean plane . There are a number of ways of defining the ordinary Euclidean geometric trigonometric functions on real numbers, for example right-angled triangle definitions, unit circle definitions, series definitions, definitions via differential equations, and definitions using functional equations. Generalizations of trigonometric functions are often developed by starting with one of the above methods and adapting it to a situation other than the real numbers of Euclidean geometry. Generally, trigonometry can be the study of triples of points in any kind of geometry or space. A triangle is the polygon with the smallest number of vertices, so one direction to generalize is to study higher-dimensional analogs of angles and polygons: solid angles and polytopes such as tetrahedrons and n-simplices.

In differential geometry Dupin's theorem, named after the French mathematician Charles Dupin, is the statement:
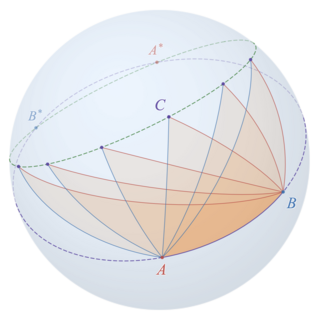
In spherical geometry, Lexell's theorem holds that every spherical triangle with the same surface area on a fixed base has its apex on a small circle, called Lexell's circle or Lexell's locus, passing through each of the two points antipodal to the two base vertices.













