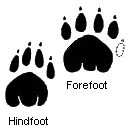
Spoor is a trace or a set of footprints by which the progress of someone or something may be followed. Spoor may include tracks, scents, or broken foliage. Spoor is useful for discovering or surveying what types of animals live in an area, or in animal tracking.
Contents
The word was borrowed into English c. 1823, from Afrikaans spoor, from Middle Dutch spor , which is cognate with Old English spor , 'footprint, track, trace', and modern English spurn (as in 'ankle'). [1] [2] It is cognate also with spur , the metal tool on the heels of riding boots .
By analogy, in politics, "to look carefully on the spoor in the trails" means to investigate what is actually going on in a sensitive situation. [3]