In economics and finance, arbitrage is the practice of taking advantage of a price difference between two or more markets: striking a combination of matching deals that capitalize upon the imbalance, the profit being the difference between the market prices at which the unit is traded. When used by academics, an arbitrage is a transaction that involves no negative cash flow at any probabilistic or temporal state and a positive cash flow in at least one state; in simple terms, it is the possibility of a risk-free profit after transaction costs. For example, an arbitrage opportunity is present when there is the possibility to instantaneously buy something for a low price and sell it for a higher price.

In finance, a derivative is a contract that derives its value from the performance of an underlying entity. This underlying entity can be an asset, index, or interest rate, and is often simply called the "underlying". Derivatives can be used for a number of purposes, including insuring against price movements (hedging), increasing exposure to price movements for speculation, or getting access to otherwise hard-to-trade assets or markets. Some of the more common derivatives include forwards, futures, options, swaps, and variations of these such as synthetic collateralized debt obligations and credit default swaps. Most derivatives are traded over-the-counter (off-exchange) or on an exchange such as the Chicago Mercantile Exchange, while most insurance contracts have developed into a separate industry. In the United States, after the financial crisis of 2007–2009, there has been increased pressure to move derivatives to trade on exchanges.
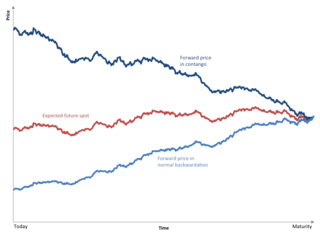
Normal backwardation, also sometimes called backwardation, is the market condition where the price of a commodity's forward or futures contract is trading below the expected spot price at contract maturity. The resulting futures or forward curve would typically be downward sloping, since contracts for further dates would typically trade at even lower prices. In practice, the expected future spot price is unknown, and the term "backwardation" may refer to "positive basis", which occurs when the current spot price exceeds the price of the future.

Contango is a situation where the futures price of a commodity is higher than the expected spot price of the contract at maturity. In a contango situation, arbitrageurs or speculators are "willing to pay more [now] for a commodity [to be received] at some point in the future than the actual expected price of the commodity [at that future point]. This may be due to people's desire to pay a premium to have the commodity in the future rather than paying the costs of storage and carry costs of buying the commodity today." On the other side of the trade, hedgers are happy to sell futures contracts and accept the higher-than-expected returns. A contango market is also known as a normal market, or carrying-cost market.
In finance, an interest rate swap (IRS) is an interest rate derivative (IRD). It involves exchange of interest rates between two parties. In particular it is a "linear" IRD and one of the most liquid, benchmark products. It has associations with forward rate agreements (FRAs), and with zero coupon swaps (ZCSs).

In finance, a futures contract is a standardized legal agreement to buy or sell something at a predetermined price at a specified time in the future, between parties not known to each other. The asset transacted is usually a commodity or financial instrument. The predetermined price the parties agree to buy and sell the asset for is known as the forward price. The specified time in the future—which is when delivery and payment occur—is known as the delivery date. Because it is a function of an underlying asset, a futures contract is a derivative product.

In finance, a forward contract or simply a forward is a non-standardized contract between two parties to buy or sell an asset at a specified future time at a price agreed on at the time of conclusion of the contract, making it a type of derivative instrument. The party agreeing to buy the underlying asset in the future assumes a long position, and the party agreeing to sell the asset in the future assumes a short position. The price agreed upon is called the delivery price, which is equal to the forward price at the time the contract is entered into.

A hedge is an investment position intended to offset potential losses or gains that may be incurred by a companion investment. A hedge can be constructed from many types of financial instruments, including stocks, exchange-traded funds, insurance, forward contracts, swaps, options, gambles, many types of over-the-counter and derivative products, and futures contracts.

A swap, in finance, is an agreement between two counterparties to exchange financial instruments or cashflows or payments for a certain time. The instruments can be almost anything but most swaps involve cash based on a notional principal amount.
Rational pricing is the assumption in financial economics that asset prices will reflect the arbitrage-free price of the asset as any deviation from this price will be "arbitraged away". This assumption is useful in pricing fixed income securities, particularly bonds, and is fundamental to the pricing of derivative instruments.
In finance, a single-stock future (SSF) is a type of futures contract between two parties to exchange a specified number of stocks in a company for a price agreed today with delivery occurring at a specified future date, the delivery date. The contracts are traded on a futures exchange. The party agreeing to take delivery of the underlying stock in the future, the "buyer" of the contract, is said to be "long", and the party agreeing to deliver the stock in the future, the "seller" of the contract, is said to be "short". The terminology reflects the expectations of the parties - the buyer hopes or expects that the stock price is going to increase, while the seller hopes or expects that it will decrease. Because entering the contract itself costs nothing, the buy/sell terminology is a linguistic convenience reflecting the position each party is taking - long or short.
Covered interest arbitrage is an arbitrage trading strategy whereby an investor capitalizes on the interest rate differential between two countries by using a forward contract to cover exchange rate risk. Using forward contracts enables arbitrageurs such as individual investors or banks to make use of the forward premium to earn a riskless profit from discrepancies between two countries' interest rates. The opportunity to earn riskless profits arises from the reality that the interest rate parity condition does not constantly hold. When spot and forward exchange rate markets are not in a state of equilibrium, investors will no longer be indifferent among the available interest rates in two countries and will invest in whichever currency offers a higher rate of return. Economists have discovered various factors which affect the occurrence of deviations from covered interest rate parity and the fleeting nature of covered interest arbitrage opportunities, such as differing characteristics of assets, varying frequencies of time series data, and the transaction costs associated with arbitrage trading strategies.
The forward exchange rate is the exchange rate at which a bank agrees to exchange one currency for another at a future date when it enters into a forward contract with an investor. Multinational corporations, banks, and other financial institutions enter into forward contracts to take advantage of the forward rate for hedging purposes. The forward exchange rate is determined by a parity relationship among the spot exchange rate and differences in interest rates between two countries, which reflects an economic equilibrium in the foreign exchange market under which arbitrage opportunities are eliminated. When in equilibrium, and when interest rates vary across two countries, the parity condition implies that the forward rate includes a premium or discount reflecting the interest rate differential. Forward exchange rates have important theoretical implications for forecasting future spot exchange rates. Financial economists have put forth a hypothesis that the forward rate accurately predicts the future spot rate, for which empirical evidence is mixed.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to finance:
In finance, a spread trade is the simultaneous purchase of one security and sale of a related security, called legs, as a unit. Spread trades are usually executed with options or futures contracts as the legs, but other securities are sometimes used. They are executed to yield an overall net position whose value, called the spread, depends on the difference between the prices of the legs. Common spreads are priced and traded as a unit on futures exchanges rather than as individual legs, thus ensuring simultaneous execution and eliminating the execution risk of one leg executing but the other failing.
Spot–future parity is a parity condition whereby, if an asset can be purchased today and held until the exercise of a futures contract, the value of the future should equal the current spot price adjusted for the cost of money, dividends, "convenience yield" and any carrying costs. That is, if a person can purchase a good for price S and conclude a contract to sell it one month later at a price of F, the price difference should be no greater than the cost of using money less any expenses from holding the asset; if the difference is greater, the person has an opportunity to buy and sell the "spots" and "futures" for a risk-free profit, i.e. an arbitrage. Spot–future parity is an application of the law of one price; see also Rational pricing and #Futures.
A foreign exchange derivative is a financial derivative whose payoff depends on the foreign exchange rates of two currencies. These instruments are commonly used for currency speculation and arbitrage or for hedging foreign exchange risk.
Iran Mercantile Exchange (IME) is a commodities exchange located in Tehran, Iran.
The forward curve is a function graph in finance that defines the prices at which a contract for future delivery or payment can be concluded today. For example, a futures contract forward curve is prices being plotted as a function of the amount of time between now and the expiry date of the futures contract. The forward curve represents a term structure of prices.
In finance, a zero coupon swap (ZCS) is an interest rate derivative (IRD). In particular it is a linear IRD, that in its specification is very similar to the much more widely traded interest rate swap (IRS).

