
The RABDe 500, is a Swiss high speed passenger train which was introduced in 2000, in time for Expo.02 held in western Switzerland in 2002. Its maximum speed is 200 km/h (120 mph), which can be reached on the Mattstetten–Rothrist new line; as of 2018 the RABDe 500 uses the branch to Solothurn only; the ICNs reach 200 km/h in the new Gotthard Base Tunnel. The train sets were a joint development by Bombardier, Swiss Federal Railways and Alstom, with an aerodynamic body designed by Pininfarina, bogies and tilting mechanism designed by the then SIG, Schweizerische Industrie Gesellschaft.

The term solar panel is used colloquially for a photo-voltaic (PV) module.

The Mildura Solar Concentrator Power Station was a proposed 100 megawatts (130,000 hp) concentrated photovoltaic (CPV) solar PV system to be built at Carwarp, near Mildura, Victoria, Australia. It was proposed by Solar Systems in 2006, which was acquired by Silex Systems in 2010. A 1.5 MW demonstration plant was completed in April 2013. Construction of the larger facility was expected to commence in 2014 and be completed in 2017. However, the expansion plan was abandoned in August 2014 due to a number of factors, including low wholesale electricity prices, a lack of commitment to clean energy by the Australian government and uncertainty surrounding the Renewable Energy Target (RET) in Australia.
Lobosillo Solar Park is a 12.7 MW-peak photovoltaic power plant located in Lobosillo, Murcia, Spain, making it at the time the third largest photovoltaic (PV) power plant in the world.

A photovoltaic system, also PV system or solar power system, is a power system designed to supply usable solar power by means of photovoltaics. It consists of an arrangement of several components, including solar panels to absorb and convert sunlight into electricity, a solar inverter to convert the output from direct to alternating current, as well as mounting, cabling, and other electrical accessories to set up a working system. It may also use a solar tracking system to improve the system's overall performance and include an integrated battery solution, as prices for storage devices are expected to decline. Strictly speaking, a solar array only encompasses the ensemble of solar panels, the visible part of the PV system, and does not include all the other hardware, often summarized as balance of system (BOS). As PV systems convert light directly into electricity, they are not to be confused with other solar technologies, such as concentrated solar power or solar thermal, used for heating and cooling.
The nominal power is the nameplate capacity of photovoltaic (PV) devices, such as solar cells, modules and systems, and is determined by measuring the electric current and voltage in a circuit, while varying the resistance under precisely defined conditions. The nominal power is important for designing an installation in order to correctly dimension its cabling and converters.

Solon SE was a German solar energy company with headquarters in Berlin. Solon SE produced photovoltaic modules at its production sites in Greifswald, Steinach in Tirol, Carmignano di Brenta, Tucson and Berlin. Solon also offered turn-key solar power plants, projected by SOLON Inverstments and Inverters, developed and produced by SOLON Inverters AG.

SMA Solar Technology AG is a German solar energy equipment supplier founded in 1981 and headquartered in Niestetal, Northern Hesse, Germany. SMA is a producer and manufacturer of solar inverters for photovoltaics systems with grid connection, off-grid power supply and backup operations.
IBC Solar is a Germany based photovoltaics specialist, offering solutions for sunlight-generated power. The company, established in 1982, offers tailored solutions, project management, consultation and planning of the photovoltaic installation.
Gehrlicher Solar AG is a German photovoltaics corporation with its registered office in Neustadt near Coburg and its administrative headquarters in Dornach near Munich. Gehrlicher Solar AG acts as a system integrator, planning, building, financing, maintaining and operating photovoltaic systems on open areas and roofs. In addition, the corporation acts as a wholesaler for solar modules, inverters and complete photovoltaic systems as well as offering its own developed components from the „GehrTec“ family of products.

A rooftop photovoltaic power station, or rooftop PV system, is a photovoltaic (PV) system that has its electricity-generating solar panels mounted on the rooftop of a residential or commercial building or structure. The various components of such a system include photovoltaic modules, mounting systems, cables, solar inverters and other electrical accessories.

A photovoltaic power station, also known as a solar park, solar farm, or solar power plant is a large-scale photovoltaic system designed for the supply of merchant power into the electricity grid. They are differentiated from most building-mounted and other decentralised solar power applications because they supply power at the utility level, rather than to a local user or users. The generic expression utility-scale solar is sometimes used to describe this type of project.
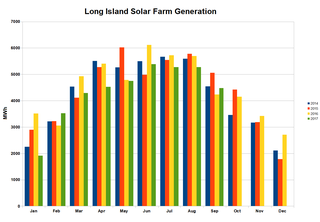
The 32 megawatt AC Long Island Solar Farm (LISF), located in Upton, New York, is the largest photovoltaic array in the eastern U.S. The LISF is made up of 164,312 solar panels from BP Solar which provide enough electricity for roughly 4,500 households. The project will cause the abatement of more than 30,000 metric tons of carbon dioxide emissions per year. LISF is co-owned by BP Solar and MetLife through Long Island Solar Farm LLC. Municipal utility Long Island Power Authority (LIPA) buys the 37-megawatt (49,600 hp) power plant's output, which is estimated at 44 GWh annually, under a 20-year power purchase agreement (PPA). Payments over that time are expected to total $298 million. The project was engineered by Blue Oak Energy and construction subcontracted to Hawkeye LLC from Hauppauge, New York. The plant earned the Best Photovoltaic Project of Year Award from the New York Solar Energy Industries Association. The panels are mounted at a fixed tilt angle of 35°, with the rows spaced approximately 18 ft 4 in (5.59 m) apart.

The Lauingen Energy Park is a 25.7–megawatt (MW) photovoltaic power station, located in Bavarian Swabia, Germany. It covers an area of 63 hectares and was commissioned in June 2010.
The Fraunhofer Institute for Solar Energy Systems ISE is an institute of the Fraunhofer-Gesellschaft. Located in Freiburg, Germany, The Institute performs applied scientific and engineering research and development for all areas of solar energy. Fraunhofer ISE has three external branches in Germany which carry out work on solar cell and semiconductor material development: the Laboratory and Service Center (LSC) in Gelsenkirchen, the Technology Center of Semiconductor Materials (THM) in Freiberg, and the Fraunhofer Center for Silicon Photovoltaics (CSP) in Halle. Since 2006, Prof. Dr. Eicke R. Weber is the director of Fraunhofer ISE. With over 1,100 employees, Fraunhofer ISE is the largest institute for applied solar energy research in Europe. The 2012 Operational Budget including investments is 74.3 million euro.

Solarpark Meuro is a 166 megawatt (MW) photovoltaic power station located in Meuro and Schipkau, Germany. The plant was built on a former lignite mine and is the country's largest solar park. It was named POWER-GEN International solar project of the year in 2012.
In 2018 Chile produced about 7% of its electricity from solar power. As of year end, it had 2137 MW of solar PV capacity. In July 2020 installed solar capacity had risen to 3104 MW, with another 2801 MW under construction.
Meyer Burger, headquartered in Thun, (Switzerland), is a globally active mechanical engineering company, which is primarily known for its production facilities in the photovoltaic industry. Meyer Burger develops and produces systems with which solar cellss can be manufactured and electrically connected for use in solar modules. The focus is on heterojunction technology (HJT) and the exclusive SmartWire Connection Technology (SWCT). High-precision measuring systems for silicon wafers, solar cells and modules are also offered. From spring 2021, the company will produce solar cells and solar modules itself at two locations in Germany.

The Bison Solar Plant, also known as the Rawhide Flats Solar Plant, is a 30 megawatt (MWAC) photovoltaic power station in Larimer County, Colorado located about 10 miles (16 km) north of the town of Wellington. The plant is notable for being one of the first in the U.S. built to a 1500 Volt system specification. The electricity is being sold to the Platte River Power Authority (PRPA) under a 25-year power purchase agreement.

At the time of commissioning in 2003, the 500 kW Chevron Solarmine solar photovoltaic (PV) system was the world's largest thin-film amorphous silicon solar PV system and one of the largest solar PV systems in the United States. Located at the Midway-Sunset Oil Field, Solarmine was the first solar PV system in California to power oil field operations.
















