Related Research Articles

The geography of Mozambique consists mostly of coastal lowlands with uplands in its center and high plateaus in the northwest. There are also mountains in the western portion. The country is located on the east coast of southern Africa, directly west of the island of Madagascar. Mozambique has a tropical climate with two seasons, a wet season from October to March and a dry season from April to September.

The Limpopo River rises in South Africa and flows generally eastward through Mozambique to the Indian Ocean. The term Limpopo is derived from Rivombo (Livombo/Lebombo), a group of Tsonga settlers led by Hosi Rivombo who settled in the mountainous vicinity and named the area after their leader. The river has been called Vhembe by local Venda communities of the area where now that name has been adopted by the South African government as its District Municipality in the north, a name that was also suggested in 2002 as a possible name to be adopted for the Province but was voted against. The river is approximately 1,750 kilometres (1,087 mi) long, with a drainage basin 415,000 square kilometres (160,200 sq mi) in size. The mean discharge measured over a year is 170 m3 per second at its mouth. The Limpopo is the second largest river in Africa that drains to the Indian Ocean, after the Zambezi River.

South Africa occupies the southern tip of Africa, its coastline stretching more than 2,850 kilometres from the desert border with Namibia on the Atlantic (western) coast southwards around the tip of Africa and then northeast to the border with Mozambique on the Indian Ocean. The low-lying coastal zone is narrow for much of that distance, soon giving way to a mountainous escarpment that separates the coast from the high inland plateau. In some places, notably the province of KwaZulu-Natal in the east, a greater distance separates the coast from the escarpment. Although much of the country is classified as semi-arid, it has considerable variation in climate as well as topography. The total land area is 1,220,813 km2 (471,359 sq mi). It has the 23rd largest Exclusive Economic Zone of 1,535,538 km2 (592,875 sq mi).

The Drakensberg is the eastern portion of the Great Escarpment, which encloses the central Southern African plateau. The Great Escarpment reaches its greatest elevation – 2,000 to 3,482 metres within the border region of South Africa and Lesotho.

The Province of the Transvaal, commonly referred to as the Transvaal, was a province of South Africa from 1910 until 1994, when a new constitution subdivided it following the end of apartheid. The name "Transvaal" refers to the province's geographical location to the north of the Vaal River. Its capital was Pretoria, which was also the country's executive capital.

MzilikaziMoselekatse, Khumalo was a Southern African king who founded the Ndebele Kingdom now called Matebeleland which is now part of Zimbabwe. His name means "the great river of blood". He was born the son of Mashobane kaMangethe near Mkuze, Zululand, and died at Ingama, Matabeleland. Many consider him to be the greatest Southern African military leader after the Zulu king, Shaka. In his autobiography, David Livingstone referred to Mzilikazi as the second most impressive leader he encountered on the African continent.
The following lists events that happened during 1895 in South Africa.

Gazaland is the historical name for the region in southeast Africa, in modern-day Mozambique and Zimbabwe, which extends northward from the Komati River at Delagoa Bay in Mozambique's Maputo Province to the Pungwe River in central Mozambique.
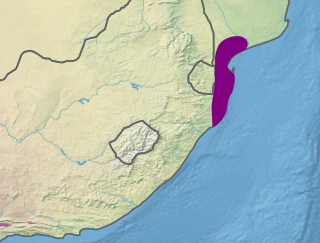
The Maputaland coastal forest mosaic is a subtropical moist broadleaf forest ecoregion on the Indian Ocean coast of Southern Africa. It covers an area of 29,961 square kilometres (11,568 sq mi) in southern Mozambique, Eswatini, and the KwaZulu-Natal Province of South Africa. Mozambique's capital Maputo lies within the ecoregion.
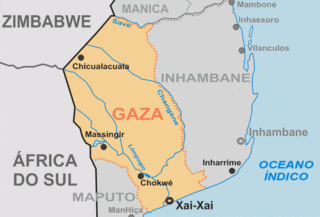
The Gaza Empire (1824–1895) was an African empire established by general Soshangane and was located in southeastern Africa in the area of southern Mozambique and southeastern Zimbabwe. The Gaza Empire, at its height in the 1860s, covered all of Mozambique between the Zambezi and Limpopo rivers, known as Gazaland.
King Mzila Nxumalo, Mzila kaSoshangane Nxumalo, Umzila, Muzila, or Nyamende was the son of Soshangane kaZikode, the founder of the Gaza empire, which at the height of its power stretched from southern Mozambique to the Limpopo River. He defeated his brother Mawewe kaSoshangane in 1861 to ascend to the Gaza throne which he ruled from 1861 to 1885. He was father of King Ngungunyane Nxumalo Gungunhana|Ndungazwe who was deposed by the Portuguese invasion Portuguese Empire.
In South Africa, as elsewhere in the world, the railways played a huge part in development and growth on nearly all terrains in the country. Conversely, events in South Africa and its neighbours over the years had a huge influence on the development of railways.
Lubimbi people are scattered all over Africa, mostly found in Southern Africa. Notable countries being South Africa, Zimbabwe, Mozambique, Zambia, Democratic Republic of Congo, Tanzania and Uganda.

Pretoria–Maputo railway, also called Delagoa Bay railway, Iron railway and Eastern railway, is a railway that connects the city of Maputo, Mozambique, to the city of Pretoria, in South Africa. It is 567 km long, in 1067 mm gauge. The Mozambican section, between Maputo and Ressano Garcia, is managed by the state-owned Mozambique Ports and Railways (CFM) company, and it is officially known in Mozambique as the Ressano Garcia Line; in turn, on the South African stretch, between the town of Komatipoort and city of Pretoria, the administration is done by the company Transnet Freight Rail.

Delagoa is a marine ecoregion along the eastern coast of Africa. It extends along the coast of Mozambique and South Africa from the Bazaruto Archipelago to Lake St. Lucia in South Africa in South Africa's Kwazulu-Natal province. It adjoins the Bight of Sofala/Swamp Coast ecoregion to the north, and the Natal ecoregion to the south. It has Africa's southernmost tropical coral reefs and mangrove forests. It is the southernmost Indo-Pacific ecoregion, marking the transition from the tropical Indo-Pacific to Temperate Southern Africa.
References
- ↑ Australian Birth Index 1788-1922 www.ancestry.com
- ↑ see Burke's Peerage "Earl of Buchan"
- ↑ "Anna Maria Erskine (Spode)". Geni.com. 4 January 1822. Retrieved 2 September 2019.
- ↑ Daughter of 8d. Herman Jan Reindeers http://www.nikhef.nl/~louk/REIN/generation8.html
- ↑ Journal of the RGS Vol 39 (1869) pp 233-276 JSTOR 1798552
- ↑ Journal of the RGS Vol 45 page 45 JSTOR 1798705
- ↑ Proceedings of the RGS Vol 22 No. 2. 1877-1878 JSTOR 1799716
- ↑ Campbell Collections of the University of Natal; Reference KC611.35/75 ERSK http://campbell.ukzn.ac.za/?q=taxonomy/term/349
- ↑ Published Cape Town 1923 at pages 187 - 199
- ↑ http://www.national.archsrch.gov.za/sm300cv/smws/sm300dl - NASA Archives
- ↑ http://www.rgs.org/OurWork/Collections/Catalogue+search/Catalogue+search.htm - RGS Archives
- ↑ http://www.nationalarchives.gov.uk/A2A/advanced-search.aspx?tab=1. - and click on RGS