
Arroyo Seco is an American Viticultural Area (AVA) in Monterey County, California, southeast of Monterey Bay. The appellation encompasses 18,240 acres (29 sq mi) in the valley adjacent to the Arroyo Seco Creek with approximately 8,500 acres (3,440 ha) of cultivation. The region's proximity to the Pacific Ocean produces the maritime climate, and is best suited for those cool climate grape varieties.

Willamette Valley is an American Viticultural Area (AVA) which lies in the Willamette Valley of Oregon. The AVA is the wine growing region which encompasses the drainage basin of the Willamette River. It stretches from the Columbia River in the north to just south of Eugene in the south, where the Willamette Valley ends; and from the Oregon Coast Range in the west to the Cascade Mountains in the east. At 5,360 square miles, it is the largest AVA in the state, and contains most of the state's wineries; approximately 908 as of 2021.
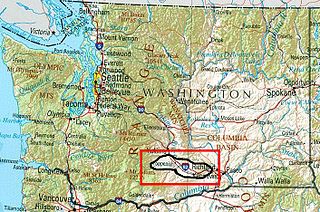
Yakima Valley is the first American Viticultural Area (AVA) established within Washington state, gaining the recognition on May 4, 1983. Within the vast Columbia Valley AVA, Yakima Valley appellation cultivates more than 53,000 acres (21,448 ha) giving the region the largest concentration of wineries and vineyards in the state. The most widely planted varietals in the area are Chardonnay, Riesling, Merlot, Cabernet Sauvignon, Pinot gris, and Syrah. Nearly 40% of Washington's annual wine production is made from Yakima Valley grapes. In addition to grapes, the Yakima Valley is also home to several fruit orchards growing apples, cherries, nectarines, peaches, pears and plums. Around the town of Zillah, there is the Zillah Fruit Loop driving tour through the area's orchards and vineyards. The area is also home to nearly 80% of the US hop production.

Horse Heaven Hills is an American Viticultural Area (AVA) in southeastern Washington lying in portions of Klickitat, Yakima, and Benton counties, north and west of the Columbia River and south of the Yakima Valley and lies within the vast Columbia Valley appellation. Horse Heaven Hills was established by the Alcohol and Tobacco Tax and Trade Bureau {TTB), Treasury on June 30, 2005 after reviewing the petition filed by Paul D. Lucas on behalf of regional wine grape growers. Horse Heaven Hills viticultural area is about 60 miles (97 km) long and 22 miles (35 km) wide located 115 miles (185 km) east from Vancouver, Washington. The appellation encompasses 570,000 acres (891 sq mi) with about 6,400 acres (2,590 ha) under vine.

Santa Maria Valley is an American Viticultural Area (AVA) which straddles the boundary of Santa Barbara and San Luis Obispo counties in California's multi-county Central Coast AVA. It was established on August 5, 1981, by the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms and Explosives (ATF) as California's second oldest AVA. A portion of the AVA crosses the Cuyama River into the southernmost corner of San Luis Obispo County. The east–west orientation of the 152.3 square miles with a wide, open valley and rolling hills means cool winds and fog flow in freely from the Pacific Ocean, settling most noticeably in lower-lying areas. The result is a mild Mediterranean climate that lengthens the growing season and contributes to the eventual sugar/acid balance in the grapes from Santa Maria Valley's 7,500 acres (3,000 ha) cultivated vineyards. On January 28, 2011, the AVA was granted an 29.4 square miles expansion to its southern boundary.

Temecula Valley is an American Viticultural Area (AVA) in the Temecula Valley, located in southwestern Riverside County, California against the eastern slopes of the Santa Ana Mountains. It was initially established by the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco and Firearms (ATF), Treasury as "Temecula" on October 23, 1984 based on submitted petitions from by the Rancho Califomia/Temecula Winegrowers Association and Callaway Vineyard and Winery, Temecula, California in 1982. It was renamed "Temecula Valley" by the Alcohol and Tobacco Tax and Trade Bureau (TTB) in 2004, approving the 2001 petition by Temecula Valley Winegrowers Association. The petition stated the name change would provide a more accurate description of the Temecula geography and greater clarity as to its location for wine consumers and the public. The petition did not request any change to the established AVA boundaries. This was the first American Viticultural Area to change its name after the initial approval. Temecula Valley encompasses 33,000 acres (52 sq mi) and 5,000 acres (8 sq mi) is located in a "protected" area referred to as the Citrus/Vineyard Zone. This area is generally located in and around the Rancho California Road area with Riverside County. County guidelines strictly enforce the number of acres needed to build a winery, lodging and other limited housing and commercial ventures.

Paso Robles is the third American Viticultural Area (AVA) located in San Luis Obispo (SLO) County, California. It was established by the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco and Firearms (ATF), Treasury on November 3, 1983 based on a petition submitted by Martin Brothers Winery. The area encompasses 609,673 acres (953 sq mi) with approximately 18,500 acres (7,487 ha) cultivated with wine grapes known for their heritage varietal Zinfandel, Cabernet Sauvignon, and Rhône-style wines.
Arroyo Grande Valley is an American Viticultural Area (AVA) located in San Luis Obispo County, California approximately 12 miles (19 km) southeast of the county seat San Luis Obispo. Arroyo Grande Valley was recognized on February 5, 1990 by the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms and Explosives (ATF) as the state's 60th AVA based on the petition filed in 1987 by Don Talley of Talley Vineyards and William S. Greenough of Saucelito Canyon Vineyard for the establishment of the "Arroyo Grande Valley" viticultural area in San Luis Obispo County. The 16 miles (26 km) long, approximately 67 square miles valley appellation benefits from its east-northeast orientation allowing the breeze from the Pacific Ocean to moderate the climate of the area. The valley is divided by a fog line produced by the cool maritime layer where Zinfandel, Petite Sirah and Rhône varietals are grown on the higher elevations near Lopez Lake and the cooler mid-valley vineyards being home to Chardonnay and Pinot noir. On April 8, 2022, the Alcohol and Tobacco Tax and Trade Bureau (TTB) approved the designation of the expansive San Luis Obispo (SLO) Coast AVA overlapping the boundaries of Edna Valley and Arroyo Grande Valley viticultural areas because they share common features. However, these two previously established areas still have unique characteristics to retain their viticultural area distinctions within SLO Coast. Edna Valley lies immediately to the northwest, the Los Padres National Forest straddles the north leg boundary, the Santa Maria Valley AVA lies to the southeast of Arroyo Grande Valley, and the Pacific Ocean communities of Oceano, Grover City and Arroyo Grande abut its southwestern border.

Lake County wine designates wine made from grapes grown mostly in Lake County, California. The region is located north of Napa County and east of Mendocino County. Although each region within Lake County has unique viticultural attributes, many are influenced by Clear Lake, the largest inland body of water in California.

Red Hills Lake County is an American Viticultural Area (AVA) located in Lake County, California and was established by the Alcohol and Tobacco Tax and Trade Bureau (TTB) on September 10, 2004. Part of the Mayacamas Range, the region lies along the southeastern shores of Clear Lake, separating Excelsior Valley to the east from Big Valley to the west. The hills lie at the foot of Mount Konocti, a volcano which last erupted 11,000 years ago, but which is still regarded as active. The terrain is rolling hills with elevations between 1,400 feet (430 m) and 3,000 feet (910 m) above sea level. Red Hills receives an average of 25 to 40 inches (635–1,016 mm) of rainfall annually.

The Santa Ynez Valley AVA is an American Viticultural Area located in Santa Barbara County, California established on May 16, 1983 by the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco and Firearms (ATF), Treasury after approving a petition submitted by Firestone Vineyard, a bounded winery in Los Olivos, California. It is part of the larger Central Coast AVA, and contains the greatest concentration of wineries in Santa Barbara County. The valley is formed by the Purisima Hills and San Rafael Mountains to the north and the Santa Ynez Mountains to the south creating a long, east-west corridor with very cool temperatures on the coast that become progressively warmer inland. The Santa Ynez River flows east to west on the valley floor toward the Pacific Ocean. As of 2021, the Santa Ynez Valley contains four other established viticultural areas: Sta. Rita Hills on its western boundary; Ballard Canyon and Los Olivos District occupying the center region; and Happy Canyon on the eastern border. Chardonnay is the most planted grape variety in the cooler, western portion of the valley while Rhône varieties thrive in the eastern locales.

Lake Chelan is an American Viticultural Area (AVA) in Washington state. The appellation lies about 112 miles (180 km) northeast of Seattle located in north-central Washington's Lake Chelan Valley and is a sub-appellation of the vast Columbia Valley AVA. It lies east of the Puget Sound viticultural area and north or west of the other Washington State viticultural areas. It borders the Columbia Valley viticultural area on is eastern side and does not include any portion of other Washington viticultural areas except the Columbia Valley AVA.
The Happy Canyon of Santa Barbara is an American Viticultural Area (AVA) located in Santa Barbara County, California. It was officially designated by the Alcohol and Tobacco Tax and Trade Bureau (TTB), Treasury on November 9, 2009 and is the smallest AVA in Santa Barbara County when measured by land under vine, covering 37 square miles with 492 acres (199 ha) of planted vine. The area comprises canyon terrain, hills, and river and creek basins to the east and south of the San Rafael Mountains, northwest of Lake Cachuma and north of the Santa Ynez River. According to the petitioner and USGS maps, the "Happy Canyon" name applies to a specific canyon within the area. Elevations within the AVA range from 500 feet (150 m) in the southwest corner to 3,430 feet (1,050 m) in the northeast corner, in the foothills of the San Rafael Range. It is home to six major vineyards and one active winery.

Eagle Foothills is the second American Viticultural Area (AVA) in the state of Idaho located in the southwestern region in Gem and Ada Counties. The area lies southeast of Emmett, north of Eagle and approximately 10 miles (16 km) northwest of the city of Boise. It was established on December 28, 2015 by the Alcohol and Tobacco Tax and Trade Bureau (TTB), Treasury as the first sub-appellation in the vast Snake River Valley viticultural area and the first appellation entirely within Idaho’s state borders. It does not overlap with any existing or proposed AVA. Eagle Foothills lies at the north bank of Ancient Lake Idaho with its elevations ranging from 2,490 to 3,412 feet (759–1,040 m). The area encompasses 49,815 acres (78 sq mi) with nearly 70 acres (28 ha) under vine with plans to add 472 acres (191 ha) and seven vineyards. Its USDA plant hardiness zones are 7a and 7b. Vineyard elevations are below 3,000 feet (914 m). The majority of viticulture activity is at 3 Horse Ranch Vineyards with its 46 acres (19 ha) in center of the appellation. The cool climate and relatively short growing season are suitable for growing early to mid-season varietals such as Chardonnay, Pinot Gris and Riesling.
Laurelwood District is an American Viticultural Area (AVA) located west of the city of Portland and lies entirely within the northern end of Willamette Valley AVA with the Chehalem Mountains AVA covering its northern slopes including the towns of Cornelius, Scholls and Sherwood in Washington County. The district was established on May 13, 2020, by the Alcohol and Tobacco Tax and Trade Bureau (TTB) after reviewing the petition submitted by Luisa Ponzi, president of Ponzi Vineyards, Maria Ponzi, winemaker of Ponzi Vineyards, and Kevin Johnson, winemaker of Dion Vineyards, on behalf of themselves and other local grape growers and vintners, proposing the establishment of the “Laurelwood” AVA. However, at the request of TTB, the petitioners agreed to add the word “District” to the proposed name, in order to avoid a potential impact on current label holders who are using “Laurelwood” as a brand name or fanciful name on their wine labels. Its coverage is approximately 33,600 acres (53 sq mi) and contains 25 wineries and approximately 70 commercially-producing vineyards that plant approximately 975 acres (395 ha). The distinguishing feature of the Laurelwood District is the predominance of the Laurelwood soil that predominates in the area. The district contains the highest concentration of the namesake soil in Oregon.

Tualatin Hills is an American Viticultural Area (AVA) located due west of Portland and just east from the Oregon Coast Range in the upland hills of the Tualatin River watershed and encompasses elevations between 200 and 1,000 feet. It was established on May 13, 2020 by the Alcohol and Tobacco Tax and Trade Bureau (TTB) after reviewing the petition from Rudolf Marchesi, president of Montinore Estate, Alfredo Apolloni, owner and winemaker of Apolloni Vineyards, and Mike Kuenz, general manager of David Hill Vineyard and Winery, on behalf of themselves and other local grape growers and vintners, proposing the establishment of the "Tualatin Hills" viticultural area in portions of Multnomah and Washington Counties. It lies entirely within the northernmost location of the Willamette Valley AVA in and around towns like Gaston, Forest Grove, Sherwood and Cornelius. To the south and southeast are the Chehalem Mountains with elevations of over 1,000 feet (300 m) and considered to be a separate, distinct landform from the uplands within Tualatin Hills. The region stretches over approximately 144,000 acres (225 sq mi) and contains 21 wineries with 33 commercially-producing vineyards that covers approximately 860.5 acres (348 ha). The distinguishing features of Tualatin Hills are its soils, elevation, and climate.
Los Olivos District AVA is an American Viticultural Area located in Santa Barbara County, California established on January 20, 2016, by the Alcohol and Tobacco Tax and Trade Bureau (TTB). It straddles the Santa Ynez Valley, formed by the Santa Ynez River, between the Purisima Hills above Solvang. The area encompasses the townships of Los Olivos, Ballard, Santa Ynez and Solvang. State Route 154, known locally as the San Marcos Pass Road or Chumash Highway, bisects the region accessing many of the wineries and vineyards as it traverses toward its destination in Santa Barbara.

Santa Barbara County wine is an appellation that designates wine made from grapes grown mostly in Santa Barbara County, California which is located approximately 50 miles (80 km) north of Los Angeles County. County names in the United States automatically qualify as legal appellations of origin for wine produced from grapes grown in that county and do not require registration with the Alcohol and Tobacco Tax and Trade Bureau (TTB) of the Treasury Department. TTB was created in January 2003, when the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco and Firearms, or ATF, was extensively reorganized under the provisions of the Homeland Security Act of 2002.

Monterey County wine is a appellation that designates wine made from grapes grown in Monterey County, California which lies entirely within the expansive multi-county Central Coast viticultural area. County names in the United States automatically qualify as legal appellations of origin for wine produced from grapes grown in that county and do not require registration with the Alcohol and Tobacco Tax and Trade Bureau (TTB). TTB was created in January 2003, when the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco and Firearms, or ATF, was extensively reorganized under the provisions of the Homeland Security Act of 2002.

Goose Gap is the 19th American Viticultural Area (AVA) in Washington, United States. It encompasses the local region surrounding Goose Mountain in Benton County between Kiona to the west, and Richland along the Columbia River to the east. The viticultural area was formally established on August 2, 2021, by the Alcohol and Tobacco Tax and Trade Bureau (TTB), Treasury after reviewing the petition submitted by geologist/vintner, Alan Busacca, on behalf of the Goose Gap Wine Grower's Association, proposing the viticultural area "Goose Gap". The area is a sub-appellation entirely within the Yakima Valley and the expansive Columbia Valley AVAs sandwiched on a northwest–southeast axis between neighboring viticultural areas Red Mountain and the minute Candy Mountain.
















