Related Research Articles

Tides are the rise and fall of sea levels caused by the combined effects of the gravitational forces exerted by the Moon and are also caused by the Earth and Moon orbiting one another.

Hydrography is the branch of applied sciences which deals with the measurement and description of the physical features of oceans, seas, coastal areas, lakes and rivers, as well as with the prediction of their change over time, for the primary purpose of safety of navigation and in support of all other marine activities, including economic development, security and defense, scientific research, and environmental protection.

A radiosonde is a battery-powered telemetry instrument carried into the atmosphere usually by a weather balloon that measures various atmospheric parameters and transmits them by radio to a ground receiver. Modern radiosondes measure or calculate the following variables: altitude, pressure, temperature, relative humidity, wind, cosmic ray readings at high altitude and geographical position (latitude/longitude). Radiosondes measuring ozone concentration are known as ozonesondes.

A nautical chart or hydrographic chart is a graphic representation of a sea region or water body and adjacent coasts or banks. Depending on the scale of the chart, it may show depths of water (bathymetry) and heights of land (topography), natural features of the seabed, details of the coastline, navigational hazards, locations of natural and human-made aids to navigation, information on tides and currents, local details of the Earth's magnetic field, and human-made structures such as harbours, buildings, and bridges. Nautical charts are essential tools for marine navigation; many countries require vessels, especially commercial ships, to carry them. Nautical charting may take the form of charts printed on paper or computerized electronic navigational charts. Recent technologies have made available paper charts which are printed "on demand" with cartographic data that has been downloaded to the commercial printing company as recently as the night before printing. With each daily download, critical data such as Local Notices to Mariners are added to the on-demand chart files so that these charts are up to date at the time of printing.

The knot is a unit of speed equal to one nautical mile per hour, exactly 1.852 km/h. The ISO standard symbol for the knot is kn. The same symbol is preferred by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), while kt is also common, especially in aviation, where it is the form recommended by the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO). The knot is a non-SI unit. The knot is used in meteorology, and in maritime and air navigation. A vessel travelling at 1 knot along a meridian travels approximately one minute of geographic latitude in one hour.

A navigator is the person on board a ship or aircraft responsible for its navigation. The navigator's primary responsibility is to be aware of ship or aircraft position at all times. Responsibilities include planning the journey, advising the ship's captain or aircraft commander of estimated timing to destinations while en route, and ensuring hazards are avoided. The navigator is in charge of maintaining the aircraft or ship's nautical charts, nautical publications, and navigational equipment, and they generally have responsibility for meteorological equipment and communications. With the advent of satellite navigation, the effort required to accurately determine one's position has decreased by orders of magnitude, so the entire field has experienced a revolutionary transition since the 1990s with traditional navigation tasks, like performing celestial navigation, being used less frequently. Using multiple independent position fix methods without solely relying on electronic systems subject to failure helps the navigator detect errors. Professional mariners are still proficient in traditional piloting and celestial navigation.
The lunitidal interval measures the time lag from lunar culmination to the next high tide at a given location. It is also called the high water interval (HWI). Sometimes a term is not used for the time lag, but instead the terms age or establishment of the tide are used for the entry that is in tide tables.

Wynyard (/ˈwɪnjɚd/) wi-nyuhd) is a rural town located on the North West coast of Tasmania, Australia. Wynyard is situated 17 kilometres (11 mi) west of Burnie. As of the 2021 census, Wynyard has an estimated population of 6,296 The town is a regional hub servicing the surrounding rural areas, the adjacent Burnie Wynyard Airport provides commercial flights to Melbourne and other districts. The main council offices for the Waratah-Wynyard local government area are located in Wynyard.
Slack tide or slack water is the short period in a body of tidal water when the water is completely unstressed, and there is no movement either way in the tidal stream. It occurs before the direction of the tidal stream reverses. Slack water can be estimated using a tidal atlas or the tidal diamond information on a nautical chart. The time of slack water, particularly in constricted waters, does not occur at high and low water, and in certain areas, such as Primera Angostura, the ebb may run for up to three hours after the water level has started to rise. Similarly, the flood may run for up to three hours after the water has started to fall. In 1884, Thornton Lecky illustrated the phenomenon with an inland basin of infinite size, connected to the sea by a narrow mouth. Since the level of the basin is always at mean sea level, the flood in the mouth starts at half tide, and its velocity is at its greatest at the time of high water, with the strongest ebb occurring conversely at low water.

The ultraviolet index, or UV index, is an international standard measurement of the strength of the sunburn-producing ultraviolet (UV) radiation at a particular place and time. It is primarily used in daily and hourly forecasts aimed at the general public. The UV index is designed as an open-ended linear scale, directly proportional to the intensity of UV radiation, and adjusting for wavelength based on what causes human skin to sunburn. The purpose of the UV index is to help people effectively protect themselves from UV radiation, which has health benefits in moderation but in excess causes sunburn, skin aging, DNA damage, skin cancer, immunosuppression, and eye damage, such as cataracts.
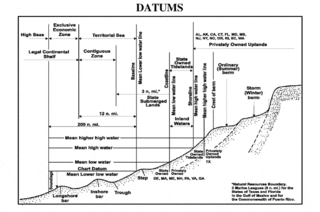
A chart datum is the water level surface serving as origin of depths displayed on a nautical chart and for reporting and predicting tide heights. A chart datum is generally derived from some tidal phase, in which case it is also known as a tidal datum. Common chart datums are lowest astronomical tide (LAT) and mean lower low water (MLLW). In non-tidal areas, e.g. the Baltic Sea, mean sea level (MSL) is used. A chart datum is a type of vertical datum and must not be confused with the horizontal datum for the chart.

Tide tables, sometimes called tide charts, are used for tidal prediction and show the daily times and levels of high and low tides, usually for a particular location. Tide heights at intermediate times can be approximated by using the rule of twelfths or more accurately calculated by using a published tidal curve for the location. Tide levels are typically given relative to a low-water vertical datum, e.g. the mean lower low water (MLLW) datum in the US.

The Australian Height Datum was introduced in 1971 as the official vertical datum for Australia, and thereby serves as the benchmark to which all height measurements are referred. The Australian Height Datum is an amalgamation of decades of spirit levelling work conducted by numerous state and territory authorities across the country, and was corrected to align with the mean sea level observations of thirty tide gauges positioned around the entire coastline. While it remains the published vertical datum for all surveying and engineering operations performed throughout Australia, newer technologies have uncovered numerous deficiencies, offsets and distortions within the Australian Height Datum, leading to discussions about defining a new Australian vertical datum.

Sailing Directions are written directions that describe the routes to be taken by boats and ships during coastal navigation and port approaches. There are also products known as Sailing Directions, which are books written by various Hydrographic Offices throughout the world. They are known as Pilot Books, because they provide local knowledge of routes and landmarks, which would typically be provided by a local marine pilot. As such, they are used frequently by naval and government vessels, who are exempted from 'Compulsory Pilotage' in many ports.

Head of tide, tidal limit or tidehead is the farthest point upstream where a river is affected by tidal fluctuations, or where the fluctuations are less than a certain amount. The river section influenced by tides and marine forces but without salinity is a tidal river, while downstream areas are brackish and termed estuaries.
Arthur Thomas Doodson was a British oceanographer.
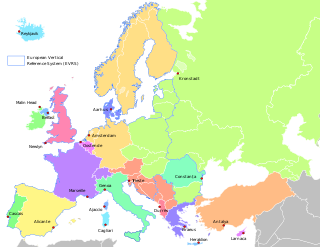
In geodesy, surveying, hydrography and navigation, vertical datum or altimetric datum, is a reference coordinate surface used for vertical positions, such as the elevations of Earth-bound features and altitudes of satellite orbits and in aviation. In planetary science, vertical datums are also known as zero-elevation surface or zero-level reference.
A coastal skipper is a yachtsman or woman who has the ability to skipper a yacht in coastal waters by day or night. There is a shore-based course which provides the background knowledge required, a practical course which teaches the skills and techniques required, and a Certificate of Competence.

The Tuvalu Meteorological Service (TMS) is the principal meteorological observatory of Tuvalu and is responsible for providing weather services to the islands of Tuvalu. A meteorological office was established on Funafuti at the time the islands of Tuvalu were administered as parts of the Gilbert and Ellice Islands colony of the United Kingdom. The meteorological office is now an agency of the government of Tuvalu.
The National Operations Centre Tidal Unit is a group of experts responsible for providing tidal tables and tidal predictions to the Australian Hydrographic Service. Their tidal predictions are also published on the Australian Bureau of Meteorology website.
References
- ↑ Admiralty Tide Tables – ATT. Taunton, UK: UKHO – United Kingdom Hydrographic Office. 2010. p. vi.
- ↑ "Definitions of tidal terms". LINZ – Land Information New Zealand. Retrieved 1 October 2013.
- ↑ "An explanation of tidal information". Cambridge school of navigation. Archived from the original on 4 October 2013. Retrieved 1 October 2013.
- ↑ "About us – Australian National Tidal Center" (PDF). Bureau of Meteorology. Archived from the original (PDF) on 16 October 2013. Retrieved 1 October 2013.
- ↑ "Notes and definitions". Tides. Maritime Safety Queensland. Retrieved 1 October 2013.
- ↑ "Tides". Terrestrial Navigation. www.thenauticalsite.com. Archived from the original on 8 August 2013. Retrieved 1 October 2013.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: bot: original URL status unknown (link)