Owner-occupancy or home-ownership is a form of housing tenure in which a person, called the owner-occupier, owner-occupant, or home owner, owns the home in which they live. The home can be a house, such as a single-family house, an apartment, condominium, or a housing cooperative. In addition to providing housing, owner-occupancy also functions as a real estate investment.
Inclusionary zoning (IZ) is municipal and county planning ordinances that require or provide incentives when a given percentage of units in a new housing development be affordable by people with low to moderate incomes. Such housing is known as inclusionary housing. The term inclusionary zoning indicates that these ordinances seek to counter exclusionary zoning practices, which exclude low-cost housing from a municipality through the zoning code. Non-profit affordable housing developers build 100% of their units as affordable, but need significant taxpayer subsidies for this model to work. Inclusionary zoning allows municipalities to have new affordable housing constructed without taxpayer subsidies. In order to encourage for-profit developers to build projects that include affordable units, cities often allow developers to build more total units than their zoning laws currently allow so that there will be enough profit generating market-rate units to offset the losses from the below market-rate units and still allow the project to be financially feasible. Inclusionary zoning can be mandatory or voluntary, though the great majority of units have been built as a result of mandatory programmes. There are variations among the set-aside requirements, affordability levels, and length of time the unit is deed-restricted as affordable housing.

The Home Ownership Scheme (HOS) is a subsidised-sale public housing programme managed by the Hong Kong Housing Authority. It was instituted in the late 1970s as part of the government policy for public housing with two aims – to encourage better-off tenants of rental flats to vacate those flats for re-allocation to families in greater housing need; and also to provide an opportunity for home ownership to families unable to afford to buy in the private sector.

Real estate economics is the application of economic techniques to real estate markets. It aims to describe and predict economic patterns of supply and demand. The closely related field of housing economics is narrower in scope, concentrating on residential real estate markets, while the research on real estate trends focuses on the business and structural changes affecting the industry. Both draw on partial equilibrium analysis, urban economics, spatial economics, basic and extensive research, surveys, and finance.

State housing is a system of public housing in New Zealand, offering low-cost rental housing to residents on low to moderate incomes. Some 69,000 state houses are managed by Kāinga Ora – Homes and Communities, most of which are owned by the Crown. In excess of 31,000 former state houses exist, which are now privately owned after large-scale sell-offs during recent decades. Since 2014, state housing has been part of a wider social housing system, which also includes privately owned low-cost housing.
A real-estate bubble or property bubble is a type of economic bubble that occurs periodically in local or global real estate markets, and it typically follows a land boom. A land boom is a rapid increase in the market price of real property such as housing until they reach unsustainable levels and then declines. This period, during the run-up to the crash, is also known as froth. The questions of whether real estate bubbles can be identified and prevented, and whether they have broader macroeconomic significance, are answered differently by schools of economic thought, as detailed below.

Public housing in Hong Kong is a set of mass housing programmes through which the Government of Hong Kong provides affordable housing for lower-income residents. It is a major component of housing in Hong Kong, with nearly half of the population now residing in some form of public housing. The public housing policy dates to 1954, after a fire in Shek Kip Mei destroyed thousands of shanty homes and prompted the government to begin constructing homes for the poor.

Affordable housing is housing which is deemed affordable to those with a household income at or below the median, as rated by the national government or a local government by a recognized housing affordability index. Most of the literature on affordable housing refers to mortgages and a number of forms that exist along a continuum – from emergency homeless shelters, to transitional housing, to non-market rental, to formal and informal rental, indigenous housing, and ending with affordable home ownership. Demand for affordable housing is generally associated with a decrease in housing affordability, such as rent increases, in addition to increased homelessness.

Build to order (BTO) is a real estate development scheme enacted by the Housing and Development Board (HDB), a statutory board responsible for Singapore's public housing. First introduced in 2001, it consists of a flat allocation system that offers flexibility in timing and location for owners buying new public housing in the country.

Workforce housing is a term that is increasingly used by planners, government, and organizations concerned with housing policy or advocacy. It is gaining cachet with realtors, developers and lenders. Workforce housing can refer to any form of housing, including ownership of single or multi-family homes, as well as occupation of rental units. Workforce housing is generally understood to mean affordable housing for households with earned income that is insufficient to secure quality housing in reasonable proximity to the workplace.

Secondary suites (also known as accessory dwelling units (ADU), in-law apartments, granny flats, granny annexes or garden suites) are self-contained apartments, cottages, or small residential units, that are located on a property that has a separate main, single-family home, duplex, or other residential unit. In some cases, the ADU or in-law is attached to the principal dwelling or is an entirely separate unit, located above a garage, across a carport, or in the backyard on the same property. Reasons for wanting to add a secondary suite to a property may be to receive additional income, provide social and personal support to a family member, or obtain greater security.
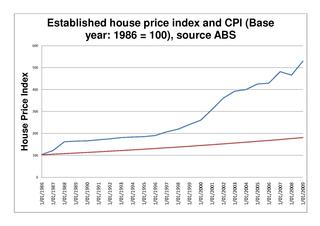
The Australian property bubble is the economic theory that the Australian property market has become or is becoming significantly overpriced and due for a significant downturn. Since the early 2010s, various commentators, including one Treasury official, have claimed the Australian property market is in a significant bubble.
Housing in India varies from palaces of erstwhile maharajas, to modern apartment buildings in big cities, to tiny huts in far-flung villages. The Human Rights Measurement Initiative finds that India is doing 60.9% of what should be possible at its level of income for the right to housing.
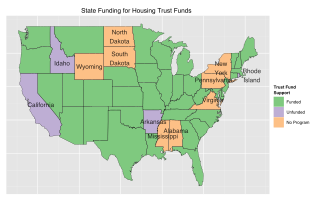
Housing trust funds are established sources of funding for affordable housing construction and other related purposes created by governments in the United States (U.S.). Housing Trust Funds (HTF) began as a way of funding affordable housing in the late 1970s. Since then, elected government officials from all levels of government in the U.S. have established housing trust funds to support the construction, acquisition, and preservation of affordable housing and related services to meet the housing needs of low-income households. Ideally, HTFs are funded through dedicated revenues like real estate transfer taxes or document recording fees to ensure a steady stream of funding rather than being dependent on regular budget processes. As of 2016, 400 state, local and county trust funds existed across the U.S.
Non-profit housing developers build affordable housing for individuals under-served by the private market. The non-profit housing sector is composed of community development corporations (CDC) and national and regional non-profit housing organizations whose mission is to provide for the needy, the elderly, working households, and others that the private housing market does not adequately serve. Of the total 4.6 million units in the social housing sector, non-profit developers have produced approximately 1.547 million units, or roughly one-third of the total stock. Since non-profit developers seldom have the financial resources or access to capital that for-profit entities do, they often use multiple layers of financing, usually from a variety of sources for both development and operation of these affordable housing units.

Affordable housing in Canada refers to living spaces that are deemed financially accessible to households with a median household income. Housing affordability is generally measured based on a shelter-cost-to-income ratio (STIR) of 30% by the Canada Mortgage and Housing Corporation (CMHC), the national housing agency of Canada. It encompasses a continuum ranging from market-based options like affordable rental housing and affordable home ownership, to non-market alternatives such as government-subsidized housing. Canada ranks among the lowest of the most developed countries for housing affordability.

Since about 1970, California has been experiencing an extended and increasing housing shortage, such that by 2018, California ranked 49th among the states of the U.S. in terms of housing units per resident. This shortage has been estimated to be 3-4 million housing units as of 2017. As of 2018, experts said that California needs to double its current rate of housing production to keep up with expected population growth and prevent prices from further increasing, and needs to quadruple the current rate of housing production over the next seven years in order for prices and rents to decline.
KiwiBuild is a real estate development scheme pursued by the Sixth Labour Government of New Zealand. It began in 2018, with the aim of building 100,000 homes by 2028 to increase housing affordability in New Zealand. It comes under the oversight of the Ministry of Housing and Urban Development and the Minister responsible is the Minister of Housing, Megan Woods.

Affordable housing is housing that is deemed affordable to those with a median household income as rated by the national government or a local government by a recognized housing affordability index. A general rule is no more than 30% of gross monthly income should be spent on housing, to be considered affordable as the challenges of promoting affordable housing varies by location.

The Canadian property bubble refers to a significant rise in Canadian real estate prices from 2002 to present. The Dallas Federal Reserve rated Canadian real estate as "exuberant" beginning in 2003. From 2003 to 2018, Canada saw an increase in home and property prices of up to 337% in some cities. In 2016, the OECD warned that Canada's financial stability was at risk due to elevated housing prices, investment and household debt. By 2018, home-owning costs were above 1990 levels when Canada saw its last housing bubble burst. Bloomberg Economics ranked Canada as the second largest housing bubble across the OECD in 2019 and 2021. Toronto scored the highest in the world in Swiss bank UBS' real estate bubble index in 2022, with Vancouver also scoring among the 10 riskiest cities in the world.




![New Multifamily Units Constructed
For Rent
.mw-parser-output figure[typeof="mw:File/Thumb"] .image-key>ol{margin-left:1.3em;margin-top:0}.mw-parser-output figure[typeof="mw:File/Thumb"] .image-key>ul{margin-top:0}.mw-parser-output figure[typeof="mw:File/Thumb"] .image-key li{page-break-inside:avoid;break-inside:avoid-column}@media(min-width:300px){.mw-parser-output figure[typeof="mw:File/Thumb"] .image-key,.mw-parser-output figure[typeof="mw:File/Thumb"] .image-key-wide{column-count:2}.mw-parser-output figure[typeof="mw:File/Thumb"] .image-key-narrow{column-count:1}}@media(min-width:450px){.mw-parser-output figure[typeof="mw:File/Thumb"] .image-key-wide{column-count:3}}
.mw-parser-output .plainlist ol,.mw-parser-output .plainlist ul{line-height:inherit;list-style:none;margin:0;padding:0}.mw-parser-output .plainlist ol li,.mw-parser-output .plainlist ul li{margin-bottom:0}
Under 1,000 ft
1,000 - 1,199 ft
1,200 - 1,399 ft
1,400 - 1,799 ft
1,800+ ft
For Sale
Under 1,000 ft
1,000 - 1,199 ft
1,200 - 1,399 ft
1,400 - 1,799 ft
1,800+ ft New Multifamily Units Constructed.webp](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/1/16/New_Multifamily_Units_Constructed.webp/400px-New_Multifamily_Units_Constructed.webp.png)













