
Faneuil Hall is a marketplace and meeting hall located near the waterfront and today's Government Center, in Boston, Massachusetts. Opened in 1742, it was the site of several speeches by Samuel Adams, James Otis, and others encouraging independence from Great Britain. It is now part of Boston National Historical Park and a well-known stop on the Freedom Trail. It is sometimes referred to as "the Cradle of Liberty", though the building and location have ties to slavery.

Beacon Hill is a historic neighborhood in Boston, Massachusetts, United States. It is also the location of the Massachusetts State House. The term "Beacon Hill" is used locally as a metonym to refer to the state government or the legislature itself, much like Washington, D.C.'s Capitol Hill does at the federal level.

The Custom House Tower is a skyscraper in McKinley Square, in the Financial District neighborhood of Boston, Massachusetts. The original building was constructed in 1837–47 and was designed by Ammi Burnham Young in the Greek Revival style. The tower was designed by Peabody and Stearns and was added in 1913–15. The building is part of the Custom House District, which was added to the National Register of Historic Places in 1973.

The Public Garden, also known as Boston Public Garden, is a large park in the heart of Boston, Massachusetts, adjacent to Boston Common. It is a part of the Emerald Necklace system of parks and is bounded by Charles Street and Boston Common to the east, Beacon Street and Beacon Hill to the north, Arlington Street and Back Bay to the west, and Boylston Street to the south. The Public Garden was the first public botanical garden in America.

James Wallace Black, known professionally as J.W. Black, was an early American photographer whose career was marked by experimentation and innovation.

Long Wharf is a historic American pier in Boston, Massachusetts, built between 1710 and 1721. It once extended from State Street nearly a half-mile into Boston Harbor; today, the much-shortened wharf functions as a dock for passenger ferries and sightseeing boats.

The Bedford Block or Bedford Building is an historic commercial building at 99 Bedford Street Boston, Massachusetts, in an area called Church Green. Built in 1875 to a design by Charles Amos Cummings and Willard T. Sears, it is a rare local example of a style promoted by John Ruskin called Venetian Gothic. The building was added to the National Historic Register in 1979.

Custom House District is a historic district in Boston, Massachusetts, located between the Fitzgerald Expressway and Kilby Street and South Market and High and Batterymarch Streets. Named after the 1849 Boston Custom House located on State Street, the historic district contains about seventy buildings on nearly sixteen acres in Downtown Boston, consisting of 19th-century mercantile buildings along with many early 20th-century skyscrapers, including the 1915 Custom House Tower.

The U.S. Custom House, also known as the Old Post Office and Custom House, is a historic government building at 423 Canal Street in New Orleans, Louisiana. It was designated a National Historic Landmark, receiving this designation in 1974 and noted for its Egyptian Revival columns. Construction on the building, designed to house multiple federal offices and store goods, began in 1848 and didn't finish until 1881 due to redesigns and the American Civil War. The U.S. Customs offices have been located there since the late 19th century.

The United States Customhouse is a historic and active custom house at 2nd and William Streets in New Bedford, Massachusetts. Architect Robert Mills designed the custom house in 1834 in a Greek Revival style. It has been used by the U.S. Customs Service ever since, and today serves as a port of entry.

Federal Street is a street in the Financial District of Boston, Massachusetts. Prior to 1788, it was known as Long Lane. The street was renamed after state leaders met there in 1788 to determine Massachusetts' ratification of the United States Constitution.

Court Street is located in the Financial District of Boston, Massachusetts. Prior to 1788, it was called Prison Lane (1634–1708) and then Queen Street (1708–1788). In the 19th century it extended beyond its current length, to Bowdoin Square. In the 1960s most of Court Street was demolished to make way for the construction of Government Center. The remaining street extends a few blocks, near the Old State House on State Street.

Summer Street in Boston, Massachusetts, extends from Downtown Crossing in the Financial District, over Fort Point Channel, and into the Seaport District to the southeast. In the mid-19th century it was also called Seven Star Lane. Seven Star Lane was named so for "Seven Stars," a tavern once located at the northwest corner of Summer and Hawley streets.
The Custom House in Boston, Massachusetts, was established in the 17th century and stood near the waterfront in several successive locations through the years. In 1849 the U.S. federal government constructed a neoclassical building on State Street; it remains the "Custom House" known to Bostonians today. A tower was added in 1915; the building joined the National Register of Historic Places in 1973 and was designated a Boston Landmark by the Boston Landmarks Commission in 1986.

Cornhill was a street in Boston, Massachusetts, in the 18th, 19th and 20th centuries, located on the site of the current City Hall Plaza in Government Center. It was named in 1829; previously it was known as Market Street (1807–1828). In its time, it comprised a busy part of the city near Brattle Street, Court Street and Scollay Square. In the 19th century, it was the home of many bookstores and publishing companies. As of 1969, Cornhill exists as 144 feet along the edge of City Hall Plaza.

Andrews, Jaques & Rantoul was an American architectural firm founded in Boston, Massachusetts in 1883 and composed of architects Robert Day Andrews, Herbert Jaques and Augustus Neal Rantoul. The firm, with its successors, was in business continuously from 1883 to 1970, for a total of eighty-seven years of architectural practice.

The American House was a hotel in Boston, Massachusetts, located on Hanover Street. Abraham W. Brigham, Lewis Rice (1837–1874), Henry B. Rice (1868–1888), and Allen C. Jones served as proprietors. In 1851 the building was expanded, to a design by Charles A. Alexander. In 1868 it had "the first hotel passenger elevator in Boston." By the 1860s it also had "billiard halls, telegraph office, and cafe." In the late 19th century it was described as "the headquarters of the shoe-and-leather trade" in the city. Guests of the hotel and restaurant included John Brown, Ralph Waldo Emerson, William Whitwell Greenough, Charles Savage Homer, Zadoc Long, and George Presbury Rowell. Many groups held meetings there, among them: Granite Cutters' International Association of America, Letter Carriers' Association, National Electric Light Association, and New England Shorthand Reporters' Association. The hotel closed in 1916, and re-opened under new management in 1918. It permanently closed on August 8, 1935, and the building was shortly afterwards demolished to make room for a parking lot. The John F. Kennedy Federal Building now occupies the site.
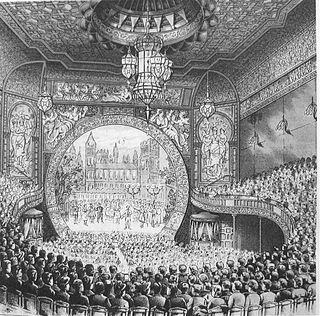
The Bijou Theatre (1882–1943) in Boston, Massachusetts, occupied the second floor of 545 Washington Street near today's Theatre District. Architect George Wetherell designed the space, described by a contemporary reviewer as "dainty." Proprietors included Edward Hastings, George Tyler, and B.F. Keith. Around the 1900s, it featured a "staircase of heavy glass under which flowed an illuminated waterfall." The Bijou "closed 31 December 1943 and was razed in 1951." The building's facade still exists. It is currently a pending Boston Landmark by the Boston Landmarks Commission.

Central Wharf is a historic pier in Boston, Massachusetts. Built in 1815–1816 between Long Wharf and India Wharf, it originally extended from India Street nearly a quarter-mile into Boston Harbor. Today, the much-shortened wharf serves as the home of the New England Aquarium.

The Flour and Grain Exchange Building is a 19th-century office building in Boston. Located at 177 Milk Street in the Custom House District, at the edge of the Financial District near the waterfront, it is distinguished by the large black slate conical roof at its western end. It is referred to as the Grain Exchange Building and sometimes as the Boston Chamber of Commerce Building.
























