
Chania, also sometimes romanized as Hania, is a city in Greece and the capital of the Chania regional unit. It lies along the north west coast of the island Crete, about 70 km (43 mi) west of Rethymno and 145 km (90 mi) west of Heraklion.

Euboea, also known by its modern spelling Evia, is the second-largest Greek island in area and population, after Crete, and the sixth largest island in the Mediterranean Sea. It is separated from Boeotia in mainland Greece by the narrow Euripus Strait. In general outline it is a long and narrow island; it is about 180 km (110 mi) long, and varies in breadth from 50 km (31 mi) to 6 km (3.7 mi). Its geographic orientation is from northwest to southeast, and it is traversed throughout its length by a mountain range, which forms part of the chain that bounds Thessaly on the east, and is continued south of Euboia in the lofty islands of Andros, Tinos and Mykonos.

Elis also known as Ellis or Ilia is a historic region in the western part of the Peloponnese peninsula of Greece. It is administered as a regional unit of the modern region of Western Greece. Its capital is Pyrgos. Until 2011 it was Elis Prefecture, covering the same territory.

Lamia is a city in central Greece. The city dates back to antiquity, and is today the capital of the regional unit of Phthiotis and of the Central Greece region. According to the 2021 census, the Municipality of Lamia has a population of 66,657 while Lamia itself has 47,529 inhabitants. The city is located on the slopes of Mount Othrys, near the river Spercheios. It serves as the agricultural center of a fertile rural and livestock area.

Pyrgos is a city in the northwestern Peloponnese, Greece, capital of the regional unit of Elis and the seat of the Municipality of Pyrgos. The city is located in the middle of a plain, 4 kilometres from the Ionian Sea. The river Alfeios flows into sea about 7 km (4 mi) south of Pyrgos. The population of the town Pyrgos is 26,052, and of the municipality 45,365 (2021). Pyrgos is 16 km (10 mi) west of Olympia, 16 km (10 mi) southeast of Amaliada, 70 km (43 mi) southwest of Patras and 85 km (53 mi) west of Tripoli.

Tinos is a Greek island situated in the Aegean Sea. It is part of the Cyclades archipelago. The closest islands are Andros, Delos, and Mykonos. It has a land area of 194.464 square kilometres (75.083 sq mi) and a 2021 census population of 8,934 inhabitants.

Konitsa is a town of Ioannina in Epirus, Greece. It is located north of the capital Ioannina and near the Albanian border. Konitsa lies northeast of a group of villages known as the Zagorochoria. The town was built amphitheatrically-shaped on a mountain slope of the Pindos mountain range from where it overlooks the valley where the river Aoos meets the river Voidomatis.

Komotini is a city in the region of East Macedonia and Thrace, northeastern Greece and its capital. It is also the capital of the Rhodope. It was the administrative centre of the Rhodope-Evros super-prefecture until its abolition in 2010, by the Kallikratis Plan. The city is home to the Democritus University of Thrace, founded in 1973. Komotini is home to a sizeable Turkish speaking Muslim minority. They were excluded from the 1923 population exchange. According to the 2021 census, the municipality of Komotini had population of 65,243 citizens.

Ioannina Island is an island in the Lake of Ioannina, Epirus, Greece, a municipal unit of the municipality of Ioannina. Its land area is 0.675 km2, with biggest length 800 meters and biggest width 500 meters. Until the 2011 reform of local government, it was a community within the Ioannina regional unit. It is one of only two inhabited lake islands in Greece, the other being Agios Achilleios. It is reached by boat from the city of Ioannina or by ferry from the nearby shore.

Angelokastro is a Byzantine castle on the island of Corfu, Greece. It is located at the top of the highest peak of the island's shoreline in the northwest coast near Palaiokastritsa and built on particularly precipitous and rocky terrain. It stands 1,000 ft (305 m) on a steep cliff above the sea and surveys the City of Corfu and the mountains of mainland Greece to the southeast and a wide area of Corfu toward the northeast and northwest.
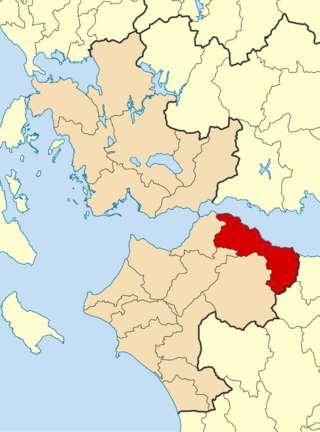
Aigialeia is a municipality and a former province (επαρχία) in the eastern part of the Achaea regional unit, Greece. The seat of the municipality is the town Aigio. The municipality has an area of 723.063 km2. The main towns are Aigio, Akrata and Diakopto. The municipality Aigialeia stretches from the south coast of the Gulf of Corinth to the mountainous interior of the Peloponnese peninsula. The main rivers of the municipality are the Selinountas and the Vouraikos.

Veria, officially transliterated Veroia, historically also spelled Beroea or Berea, is a city in Central Macedonia, in the geographic region of Macedonia, northern Greece, capital of the regional unit of Imathia. It is located 511 kilometres north-northwest of the capital Athens and 73 km (45 mi) west-southwest of Thessaloniki.

Nartë is a community in Vlorë County. At the 2015 local government reform it became part of the municipality Vlorë. It is situated northwest of the city of Vlorë. It is predominantly inhabited by ethnic Greeks who speak a unique northern Greek dialect, as well as Albanian.
Poliçan is a village in Gjirokastër County, southern Albania. At the 2015 local government reform it became part of the municipality Dropull. It is within the wider Pogoni region that stretches in both Greece and Albania. Poliçan was the municipal center of the former Pogon commune in Albania. It is nicknamed "the Bride of the Pogoni region" and is inhabited by ethnic Greeks.

Dirfi is a mountain in the central part of the island of Euboea, in central Greece. At 1,743 m elevation, it is the highest mountain of Euboea. The Dirfi gave its name to the municipal unit Dirfys. Its summit is 4 km west of Stropones, 5 km north of Steni Dirfyos and 28 km northeast of the city of Chalcis. There are forests on the lower slopes while most of the mountain is covered with grassland and in winter with permafrost and snow.

The Çelebi Sultan Mehmed Mosque, also known as the Bayezid Mosque and the Great Mosque, is an early 15th-century Ottoman mosque in Didymoteicho, East Macedonia and Thrace, in the far northeast of Greece.

The Panagia Episkopi is the former middle-Byzantine cathedral of the Greek Cycladic island of Santorini (Thira). It is also called Panagia tis Episkopis or Church of Episkopi Thiras. According to an old, now almost completely destroyed inscription, the building of the church was commissioned by the Byzantine Emperor Alexios I Komnenos at the end of the 11th century, and took the place of a previous three-aisled early Byzantine basilica. The church was dedicated to the Panagia ("All-holy"), a Greek Orthodox appellation for the Virgin Mary. The second part of the name (Episkopi) means "episcopal". The Panagia Episkopi was the seat of the Orthodox diocese of Santorini until 1207 and again from 1537 to 1827.

The Old Metropolis is an early 11th-century Byzantine basilica, dedicated to Saint Paul, that during the Ottoman period of the city became an Ottoman mosque as the Hünkar Mosque, in the northern Greek city of Veria.

The Church of Hagia Sophia or Holy Wisdom is a 10th-century Byzantine church in the town of Drama, Greece.

The Nativity of the Theotokos Church is located in Limni, Euboea. It was built in the period 1837-1841 and is a representative monument of modern Greek ecclesiastical architecture.





















