Related Research Articles

Elasmosaurus is a genus of plesiosaur that lived in North America during the Campanian stage of the Late Cretaceous period, about 80.5 million years ago. The first specimen was discovered in 1867 near Fort Wallace, Kansas, US, and was sent to the American paleontologist Edward Drinker Cope, who named it E. platyurus in 1868. The generic name means "thin-plate reptile", and the specific name means "flat-tailed". Cope originally reconstructed the skeleton of Elasmosaurus with the skull at the end of the tail, an error which was made light of by the paleontologist Othniel Charles Marsh, and became part of their "Bone Wars" rivalry. Only one incomplete Elasmosaurus skeleton is definitely known, consisting of a fragmentary skull, the spine, and the pectoral and pelvic girdles, and a single species is recognized today; other species are now considered invalid or have been moved to other genera.

The Plesiosauria or plesiosaurs are an order or clade of extinct Mesozoic marine reptiles, belonging to the Sauropterygia.
Liopleurodon is an extinct genus of carnivorous pliosaurid pliosaurs that lived from the Callovian stage of the Middle Jurassic to the Kimmeridgian stage of the Late Jurassic period. The type species is L. ferox, which is probably the only valid species. Some studies also include the second species L. pachydeirus, but this latter is considered as a probable junior synonym of L. ferox due to its lack of viable diagnosis. As the holotype specimen of L. ferox consists of a single tooth preserving questionable distinctive features, recent studies therefore recommend the necessary identification of a neotype in order to preserve the validity of the genus. Numerous fossil specimens attributed to Liopleurodon, even including numerous skeletons, have been discovered in Europe, Russia, and Mexico. Other additional species were even proposed, but these are currently seen as coming from other pliosaurid genera.

Ornithocheirus is a pterosaur genus known from fragmentary fossil remains uncovered from sediments in the United Kingdom and possibly Morocco.

Cryptoclidus is a genus of plesiosaur reptile from the Middle Jurassic period of England, France, and Cuba.
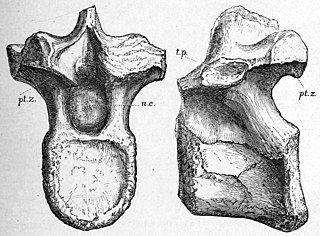
Syngonosaurus is an extinct genus of ornithopod dinosaur from the Early Cretaceous. It was an iguanodontian discovered in the Cambridge Greensand of England and was first described in 1879. The type species, S. macrocercus, was described by British paleontologist Harry Seeley in 1879 and it was later synonymised with Acanthopholis, but the genus was reinstated in a 2020 study, when Syngonosaurus and Eucercosaurus were reinterpreted as basal iguanodontians.

Macrurosaurus is the name given to a genus of dinosaur from the Early Cretaceous. It was a titanosauriform which lived in what is now England. The type species, M. semnus, was named in 1876. A second species, M. platypus, may also exist.

Elasmosauridae is an extinct family of plesiosaurs, often called elasmosaurs. They had the longest necks of the plesiosaurs and existed from the Hauterivian to the Maastrichtian stages of the Cretaceous, and represented one of the two groups of plesiosaurs present at the end of the Cretaceous alongside Polycotylidae.
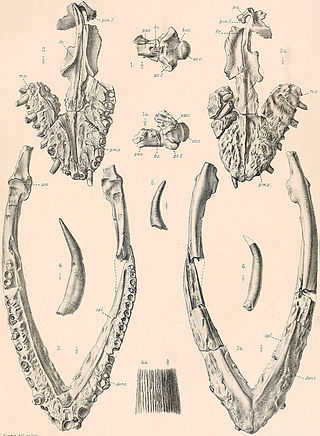
Muraenosaurus is an extinct genus of cryptoclidid plesiosaur reptile from the Oxford Clay of Southern England. The genus was given its name due to the eel-like appearance of the long neck and small head. Muraenosaurus grew up to 5.2 metres (17 ft) in length and lived roughly between 160 Ma and 164 Ma in the Callovian of the middle Jurassic. Charles E. Leeds collected the first Muraenosaurus which was then described by H. G. Seeley. The specimen may have suffered some damage due to the casual style of Charles Leeds’ collection. The first muraenosaur was recovered with pieces missing from the skull and many of the caudal vertebrae absent. Because the animal was described from Charles Leeds’ collection it was given the name Muraenosaurus Leedsi. M. leedsi is the most complete specimen belonging to the genus Muraenosaurus and also the only species that is undoubtedly a member of the genus. Two other species have been tentatively referred to as members of the genus Muraenosaurus: M. reedii and Muraenosaurus beloclis Seeley 1892, which in 1910 became the separate genus Picrocleidus.
Peloneustes is a genus of pliosaurid plesiosaur from the Middle Jurassic of England. Its remains are known from the Peterborough Member of the Oxford Clay Formation, which is Callovian in age. It was originally described as a species of Plesiosaurus by palaeontologist Harry Govier Seeley in 1869, before being given its own genus by naturalist Richard Lydekker in 1889. While many species have been assigned to Peloneustes, P. philarchus is currently the only one still considered valid, with the others moved to different genera, considered nomina dubia, or synonymised with P. philarchus. Some of the material formerly assigned to P. evansi have since been reassigned to "Pliosaurus" andrewsi. Peloneustes is known from many specimens, including some very complete material.

Rhomaleosaurus is an extinct genus of Early Jurassic rhomaleosaurid pliosauroid known from Northamptonshire and from Yorkshire of the United Kingdom. It was first named by Harry Seeley in 1874 and the type species is Rhomaleosaurus cramptoni. It was one of the earliest large marine reptile predators which hunted in the seas of Mesozoic era, measuring about 7 metres (23 ft) long. Like other pliosaurs, Rhomaleosaurus fed on ichthyosaurs, ammonites and other plesiosaurs.

Pliosauridae is a family of plesiosaurian marine reptiles from the Latest Triassic to the early Late Cretaceous of Australia, Europe, North America and South America. The family is more inclusive than the archetypal short-necked large headed species that are placed in the subclade Thalassophonea, with basal forms resembling other plesiosaurs with long necks. They became extinct during the early Late Cretaceous and were subsequently replaced by the mosasaurs. It was formally named by Harry G. Seeley in 1874.
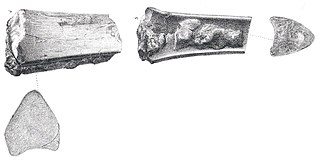
Ornithostoma is a genus of pterodactyloid pterosaur that lived during the Early Cretaceous period of Europe, around 110 million years ago. Ornithostoma was once thought to have been a senior synonym of the pteranodontid Pteranodon due to its toothless anatomy and prior naming.

Picrocleidus is an extinct genus of plesiosaur from the Middle Jurassic Oxford Clay Formation of the United Kingdom.

Colymbosaurus is a genus of cryptoclidid plesiosaur from the Late Jurassic (Callovian-Tithonian) of the UK and Svalbard, Norway. There are two currently recognized species, C. megadeirus and C. svalbardensis.

Eretmosaurus is an extinct genus of plesiosaur from the Early and Middle Jurassic of England and Russia. Two species are known: E. rugosus and E. dubius.

This timeline of plesiosaur research is a chronologically ordered list of important fossil discoveries, controversies of interpretation, taxonomic revisions, and cultural portrayals of plesiosaurs, an order of marine reptiles that flourished during the Mesozoic Era. The first scientifically documented plesiosaur fossils were discovered during the early 19th century by Mary Anning. Plesiosaurs were actually discovered and described before dinosaurs. They were also among the first animals to be featured in artistic reconstructions of the ancient world, and therefore among the earliest prehistoric creatures to attract the attention of the lay public. Plesiosaurs were originally thought to be a kind of primitive transitional form between marine life and terrestrial reptiles. However, now plesiosaurs are recognized as highly derived marine reptiles descended from terrestrial ancestors.

Lonchodraco is a genus of lonchodraconid pterodactyloid pterosaur from the Late Cretaceous of southern England. The genus includes species that were previously assigned to other genera.

Camposipterus is a genus of pterodactyloid pterosaur from the Early Cretaceous of England. Fossil remains of Camposipterus dated back to the Early Cretaceous, about 112 million years ago.

Aerodraco is a genus of anhanguerid pterosaur from the Albian–Cenomanian-age Cambridge Greensand of England. It contains only one species, Aerodraco sedgwickii. It was originally assigned to the genus Pterodactylus.
References
- ↑ Seeley, H.G. (1869). Index to the fossil remains of Aves, Ornithosauria and Reptilia, from the Secondary system of strata arranged in the Woodwardian Museum of the University of Cambridge. Cambridge, 143 pp.
- H. G. Seeley. 1892. The Nature of the Shoulder Girdle and Clavicular Arch in Sauropterygia. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London 51:119-151