
A coma is a deep state of prolonged unconsciousness in which a person cannot be awakened, fails to respond normally to painful stimuli, light, or sound, lacks a normal wake-sleep cycle and does not initiate voluntary actions. The person may experience respiratory and circulatory problems due to the body's inability to maintain normal bodily functions. People in a coma often require extensive medical care to maintain their health and prevent complications such as pneumonia or blood clots. Coma patients exhibit a complete absence of wakefulness and are unable to consciously feel, speak or move. Comas can be derived by natural causes, or can be medically induced.

Locked-in syndrome (LIS), also known as pseudocoma, is a condition in which a patient is aware but cannot move or communicate verbally due to complete paralysis of nearly all voluntary muscles in the body except for vertical eye movements and blinking. The individual is conscious and sufficiently intact cognitively to be able to communicate with eye movements. Electroencephalography results are normal in locked-in syndrome. Total locked-in syndrome, or completely locked-in state (CLIS), is a version of locked-in syndrome wherein the eyes are paralyzed as well. Fred Plum and Jerome B. Posner coined the term for this disorder in 1966.
A vegetative state (VS) or post-coma unresponsiveness (PCU), is a disorder of consciousness in which patients with severe brain damage are in a state of partial arousal rather than true awareness. After four weeks in a vegetative state, the patient is classified as being in a persistent vegetative state (PVS). This diagnosis is classified as a permanent vegetative state some months after a non-traumatic brain injury or one year after a traumatic injury. The term unresponsive wakefulness syndrome may be alternatively used, as "vegetative state" has some negative connotations among the public.
In philosophy and neuroscience, neuroethics is the study of both the ethics of neuroscience and the neuroscience of ethics. The ethics of neuroscience concerns the ethical, legal and social impact of neuroscience, including the ways in which neurotechnology can be used to predict or alter human behavior and "the implications of our mechanistic understanding of brain function for society... integrating neuroscientific knowledge with ethical and social thought".

Ruben Kuzniecky is a neurologist scientist who is Vice-chair academic affairs and professor of neurology at Northwell Health specializing in the field of epilepsy, epilepsy surgery and neuro-imaging.

A minimally conscious state or MCS is a disorder of consciousness distinct from persistent vegetative state and locked-in syndrome. Unlike persistent vegetative state, patients with MCS have partial preservation of conscious awareness. MCS is a relatively new category of disorders of consciousness. The natural history and longer term outcome of MCS have not yet been thoroughly studied. The prevalence of MCS was estimated to be 9 times of PVS cases, or between 112,000 and 280,000 in the US by year 2000.

Neuroimaging is the use of quantitative (computational) techniques to study the structure and function of the central nervous system, developed as an objective way of scientifically studying the healthy human brain in a non-invasive manner. Increasingly it is also being used for quantitative research studies of brain disease and psychiatric illness. Neuroimaging is highly multidisciplinary involving neuroscience, computer science, psychology and statistics, and is not a medical specialty. Neuroimaging is sometimes confused with neuroradiology.
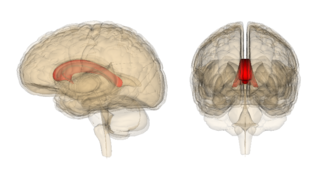
Marchiafava–Bignami disease is a progressive neurological disease of alcohol use disorder, characterized by corpus callosum demyelination and necrosis and subsequent atrophy. The disease was first described in 1903 by the Italian pathologists Amico Bignami and Ettore Marchiafava in an Italian Chianti drinker. In this autopsy, Marchiafava and Bignami noticed that the middle two-thirds of the corpus callosum were necrotic. It is very difficult to diagnose and there is no specific treatment. Until 2008 only around 300 cases had been reported. If caught early enough, most patients survive.
EEG-fMRI is a multimodal neuroimaging technique whereby EEG and fMRI data are recorded synchronously for the study of electrical brain activity in correlation with haemodynamic changes in brain during the electrical activity, be it normal function or associated with disorders.

National Brain Research Centre is a research institute in Manesar, Gurgaon, India. It is an autonomous institute under the Department of Biotechnology, Ministry of Science and Technology, Government of India. The institute is dedicated to research in neuroscience and brain functions in health and diseases using multidisciplinary approaches. This is the first autonomous institute by DBT to be awarded by the Ministry of Education, Government of India, formerly known as the Ministry of Human Resource Development, in May 2002. NBRC was dedicated to the nation by the Honorable President of India Dr. A.P.J. Abdul Kalam in December 2003. The founder chairman of NBRC Society is Prof. Prakash Narain Tandon, whereas the founder director Prof. Vijayalakshmi Ravindranath was followed by Prof. Subrata Sinha and Prof. Neeraj Jain. The current director of NBRC is Prof. Krishanu Ray.

Magnetic resonance neurography (MRN) is the direct imaging of nerves in the body by optimizing selectivity for unique MRI water properties of nerves. It is a modification of magnetic resonance imaging. This technique yields a detailed image of a nerve from the resonance signal that arises from in the nerve itself rather than from surrounding tissues or from fat in the nerve lining. Because of the intraneural source of the image signal, the image provides a medically useful set of information about the internal state of the nerve such as the presence of irritation, nerve swelling (edema), compression, pinch or injury. Standard magnetic resonance images can show the outline of some nerves in portions of their courses but do not show the intrinsic signal from nerve water. Magnetic resonance neurography is used to evaluate major nerve compressions such as those affecting the sciatic nerve (e.g. piriformis syndrome), the brachial plexus nerves (e.g. thoracic outlet syndrome), the pudendal nerve, or virtually any named nerve in the body. A related technique for imaging neural tracts in the brain and spinal cord is called magnetic resonance tractography or diffusion tensor imaging.

A neurological disorder is any disorder of the nervous system. Structural, biochemical or electrical abnormalities in the brain, spinal cord or other nerves can result in a range of symptoms. Examples of symptoms include paralysis, muscle weakness, poor coordination, loss of sensation, seizures, confusion, pain, tauopathies, and altered levels of consciousness. There are many recognized neurological disorders, some relatively common, but many rare. They may be assessed by neurological examination, and studied and treated within the specialties of neurology and clinical neuropsychology.
Rom Houben is a Belgian man believed to be comatose and in a vegetative state for 23 years after a near-fatal automobile accident, who was diagnosed with locked-in syndrome in 2006.
Fred Plum was an American neurologist who developed the terms "persistent vegetative state" and "locked-in syndrome" as part of his continuing research on consciousness and comas and care of the comatose.

Adrian Mark Owen is a British neuroscientist and best-selling author. He is best known for his 2006 discovery, published in the journal Science, showing that some patients thought to be in a persistent vegetative state are in fact fully aware and able to communicate with the outside world using functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI). In the 2019 New Year Honours List, Owen was made an Officer of the Most Excellent Order of the British Empire (OBE) for services to scientific research.
Disorders of consciousness are medical conditions that inhibit consciousness. Some define disorders of consciousness as any change from complete self-awareness to inhibited or absent self-awareness and arousal. This category generally includes minimally conscious state and persistent vegetative state, but sometimes also includes the less severe locked-in syndrome and more severe but rare chronic coma. Differential diagnosis of these disorders is an active area of biomedical research. Finally, brain death results in an irreversible disruption of consciousness. While other conditions may cause a moderate deterioration or transient interruption of consciousness, they are not included in this category.

Consciousness after death is a common theme in society and culture, and the belief in some form of life after death is a feature of many religions. However, scientific research has established that the physiological functioning of the brain, the cessation of which defines brain death, is closely connected to mental states.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to brain mapping:
John Douglas Pickard is a British professor emeritus of neurosurgery in the Department of Clinical Neurosciences of University of Cambridge. He is the honorary director of the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) Healthcare Technology Cooperative (HTC) for brain injury. His research focuses on advancing the care of patients with acute brain injury, hydrocephalus and prolonged disorders of consciousness through functional brain imaging, studies of pathophysiology and new treatments; as well as focusing on health, economic and ethical aspects.

Hal Blumenfeld is a Professor of Neurology, Neuroscience, and Neurosurgery at Yale University. He is an expert on brain mechanisms of consciousness and on altered consciousness in epilepsy. As director of the Yale Clinical Neuroscience Imaging Center (CNIC) he leads multi-disciplinary research and is also well known for his teaching contributions in neuroanatomy and clinical neuroscience.












