Related Research Articles
In radio communication, a transceiver is an electronic device which is a combination of a radio transmitter and a receiver, hence the name. It can both transmit and receive radio waves using an antenna, for communication purposes. These two related functions are often combined in a single device to reduce manufacturing costs. The term is also used for other devices which can both transmit and receive through a communications channel, such as optical transceivers which transmit and receive light in optical fiber systems, and bus transceivers which transmit and receive digital data in computer data buses.

In electronics and telecommunications, a radio transmitter or just transmitter is an electronic device which produces radio waves with an antenna with the purpose of signal transmission up to a radio receiver. The transmitter itself generates a radio frequency alternating current, which is applied to the antenna. When excited by this alternating current, the antenna radiates radio waves.

Ultra high frequency (UHF) is the ITU designation for radio frequencies in the range between 300 megahertz (MHz) and 3 gigahertz (GHz), also known as the decimetre band as the wavelengths range from one meter to one tenth of a meter. Radio waves with frequencies above the UHF band fall into the super-high frequency (SHF) or microwave frequency range. Lower frequency signals fall into the VHF or lower bands. UHF radio waves propagate mainly by line of sight; they are blocked by hills and large buildings although the transmission through building walls is strong enough for indoor reception. They are used for television broadcasting, cell phones, satellite communication including GPS, personal radio services including Wi-Fi and Bluetooth, walkie-talkies, cordless phones, satellite phones, and numerous other applications.
In-band on-channel (IBOC) is a hybrid method of transmitting digital radio and analog radio broadcast signals simultaneously on the same frequency. The name refers to the new digital signals being broadcast in the same AM or FM band (in-band), and associated with an existing radio channel (on-channel). By utilizing additional digital subcarriers or sidebands, digital information is multiplexed on existing signals, thus avoiding re-allocation of the broadcast bands.
A subcarrier is a sideband of a radio frequency carrier wave, which is modulated to send additional information. Examples include the provision of colour in a black and white television system or the provision of stereo in a monophonic radio broadcast. There is no physical difference between a carrier and a subcarrier; the "sub" implies that it has been derived from a carrier, which has been amplitude modulated by a steady signal and has a constant frequency relation to it.

Digital radio is the use of digital technology to transmit or receive across the radio spectrum. Digital transmission by radio waves includes digital broadcasting, and especially digital audio radio services.
Code of Federal Regulations, Title 47, Part 15 is an oft-quoted part of Federal Communications Commission (FCC) rules and regulations regarding unlicensed transmissions. It is a part of Title 47 of the Code of Federal Regulations (CFR), and regulates everything from spurious emissions to unlicensed low-power broadcasting. Nearly every electronics device sold inside the United States radiates unintentional emissions, and must be reviewed to comply with Part 15 before it can be advertised or sold in the US market.
An automatic transmission system (ATS) is an automated system designed to keep a broadcast radio or television station's transmitter and antenna system running without direct human oversight or attention for long periods. Such systems are occasionally referred to as automated transmission systems to avoid confusion with the automatic transmission of an automobile.

HD Radio (HDR) is a trademark for an in-band on-channel (IBOC) digital radio broadcast technology. HD radio generally simulcasts an existing analog radio station in digital format with less noise and with additional text information. HD Radio is used primarily by AM and FM radio stations in the United States, U.S. Virgin Islands, Canada, Mexico and the Philippines, with a few implementations outside North America.

FM broadcasting is a method of radio broadcasting that uses frequency modulation (FM) of the radio broadcast carrier wave. Invented in 1933 by American engineer Edwin Armstrong, wide-band FM is used worldwide to transmit high-fidelity sound over broadcast radio. FM broadcasting offers higher fidelity—more accurate reproduction of the original program sound—than other broadcasting techniques, such as AM broadcasting. It is also less susceptible to common forms of interference, having less static and popping sounds than are often heard on AM. Therefore, FM is used for most broadcasts of music and general audio. FM radio stations use the very high frequency range of radio frequencies.
Subsidiary Communications Authorization (SCA) in the United States, and Subsidiary Communications Multiplex Operation (SCMO) in Canada, is a subcarrier on a radio station, allowing the station to broadcast additional services as part of its signal.
A television transmitter is a transmitter that is used for terrestrial (over-the-air) television broadcasting. It is an electronic device that radiates radio waves that carry a video signal representing moving images, along with a synchronized audio channel, which is received by television receivers belonging to a public audience, which display the image on a screen. A television transmitter, together with the broadcast studio which originates the content, is called a television station. Television transmitters must be licensed by governments, and are restricted to a certain frequency channel and power level. They transmit on frequency channels in the VHF and UHF bands. Since radio waves of these frequencies travel by line of sight, they are limited by the horizon to reception distances of 40–60 miles depending on the height of transmitter station.
A broadcast transmitter is an electronic device which radiates radio waves modulated with information content intended to be received by the general public. Examples are a radio broadcasting transmitter which transmits audio (sound) to broadcast radio receivers (radios) owned by the public, or a television transmitter, which transmits moving images (video) to television receivers (televisions). The term often includes the antenna which radiates the radio waves, and the building and facilities associated with the transmitter. A broadcasting station consists of a broadcast transmitter along with the production studio which originates the broadcasts. Broadcast transmitters must be licensed by governments, and are restricted to specific frequencies and power levels. Each transmitter is assigned a unique identifier consisting of a string of letters and numbers called a callsign, which must be used in all broadcasts.
Modulated continuous wave (MCW) is Morse code telegraphy transmitted using an audio tone to modulate a carrier wave.
A television station is a set of equipment managed by a business, organisation or other entity such as an amateur television (ATV) operator, that transmits video content and audio content via radio waves directly from a transmitter on the earth's surface to any number of tuned receivers simultaneously.
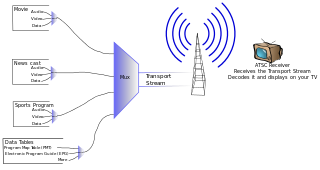
An ATSCtuner, often called an ATSC receiver or HDTV tuner, is a type of television tuner that allows reception of digital television (DTV) television channels that use ATSC standards, as transmitted by television stations in North America, parts of Central America, and South Korea. Such tuners are usually integrated into a television set, VCR, digital video recorder (DVR), or set-top box which provides audio/video output connectors of various types.

KRBC-TV is a television station in Abilene, Texas, United States, affiliated with NBC. It is owned by Mission Broadcasting, which maintains joint sales and shared services agreements (JSA/SSA) with Nexstar Media Group, owner of dual CBS/Telemundo affiliate KTAB-TV, for the provision of certain services. The two stations share studios on South 14th Street in western Abilene; KRBC-TV's transmitter is located on Texas State Highway 36 in neighboring Callahan County.

Microwave transmission is the transmission of information by electromagnetic waves with wavelengths in the microwave frequency range of 300 MHz to 300 GHz of the electromagnetic spectrum. Microwave signals are normally limited to the line of sight, so long-distance transmission using these signals requires a series of repeaters forming a microwave relay network. It is possible to use microwave signals in over-the-horizon communications using tropospheric scatter, but such systems are expensive and generally used only in specialist roles.

Radio is the technology of communicating using radio waves. Radio waves are electromagnetic waves of frequency between 3 hertz (Hz) and 300 gigahertz (GHz). They are generated by an electronic device called a transmitter connected to an antenna which radiates oscillating electrical energy, often characterized as a wave. They can be received by other antennas connected to a radio receiver, this is the fundamental principle of radio communication. In addition to communication, radio is used for radar, radio navigation, remote control, remote sensing, and other applications.
The Automatic Transmitter Identification System (ATIS) is a communications protocol used for the station identification of television channels carried on satellite television.
References
- ↑ Skip., Pizzi (2014). A Broadcast Engineering Tutorial for Non-Engineers. Jones, Graham (Electrical engineer) (4th ed.). Hoboken: Taylor and Francis. ISBN 9781317906834. OCLC 879025861.
- CFR Title 47: Telecommunication Part 74—Experimental Radio, Auxiliary, Special Broadcast and Other Program Distributional Services
- CFR Title 47: Telecommunication Chapter I—Federal Communications Commission Subchapter C—Part 73—Broadcast Radio Services