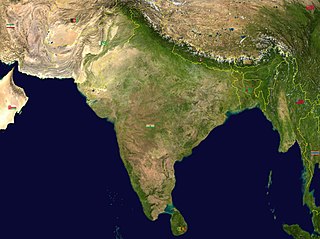
India is situated north of the equator between 8°4' north to 37°6' north latitude and 68°7' east to 97°25' east longitude. It is the seventh-largest country in the world, with a total area of 3,287,263 square kilometres (1,269,219 sq mi). India measures 3,214 km (1,997 mi) from north to south and 2,933 km (1,822 mi) from east to west. It has a land frontier of 15,200 km (9,445 mi) and a coastline of 7,516.6 km (4,671 mi).

Nepal measures about 880 kilometers (547 mi) along its Himalayan axis by 150 to 250 kilometers across. It has an area of 147,516 km2 (56,956 sq mi).

The Himalayas, or Himalaya, is a mountain range in Asia, separating the plains of the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau. The range has some of the Earth's highest peaks, including the highest, Mount Everest; more than 100 peaks exceeding elevations of 7,200 m (23,600 ft) above sea level lie in the Himalayas.

The Indo-Gangetic Plain, also known as the North Indian River Plain, is a 700-thousand km2 (172-million-acre) fertile plain encompassing northern regions of the Indian subcontinent, including most of modern-day northern and eastern India, most of eastern-Pakistan, virtually all of Bangladesh and southern plains of Nepal. Also known as the Indus–Ganga Plain, the region is named after the Indus and the Ganges rivers and encompasses a number of large urban areas. The plain is bounded on the north by the Himalayas, which feed its numerous rivers and are the source of the fertile alluvium deposited across the region by the two river systems. The southern edge of the plain is marked by the Deccan Plateau. On the west rises the Iranian Plateau. Many developed cities like Delhi, Dhaka, Kolkata, Lahore, Islamabad and Karachi are located in the Indo-Gangetic Plain.

The Sivalik Hills, also known as the Shivalik Hills and Churia Hills, are a mountain range of the outer Himalayas that stretches over about 2,400 km (1,500 mi) from the Indus River eastwards close to the Brahmaputra River, spanning the northern parts of the Indian subcontinent. It is 10–50 km (6.2–31.1 mi) wide with an average elevation of 1,500–2,000 m (4,900–6,600 ft). Between the Teesta and Raidāk Rivers in Assam is a gap of about 90 km (56 mi). The literal translation of "Sivalik" is 'tresses of Shiva'. Sivalik region is home to the Soanian archaeological culture. The hills are well known for their Neogene and Pleistocene aged vertebrate fossils.
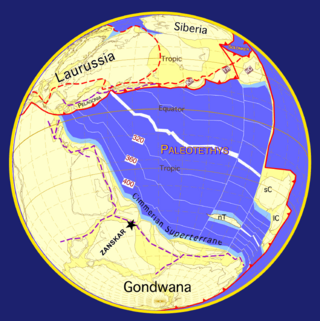
The geology of the Himalayas is a record of the most dramatic and visible creations of the immense mountain range formed by plate tectonic forces and sculpted by weathering and erosion. The Himalayas, which stretch over 2400 km between the Namcha Barwa syntaxis at the eastern end of the mountain range and the Nanga Parbat syntaxis at the western end, are the result of an ongoing orogeny — the collision of the continental crust of two tectonic plates, namely, the Indian Plate thrusting into the Eurasian Plate. The Himalaya-Tibet region supplies fresh water for more than one-fifth of the world population, and accounts for a quarter of the global sedimentary budget. Topographically, the belt has many superlatives: the highest rate of uplift, the highest relief, among the highest erosion rates at 2–12 mm/yr, the source of some of the greatest rivers and the highest concentration of glaciers outside of the polar regions. This last feature earned the Himalaya its name, originating from the Sanskrit for "the abode of the snow".

The geology of India is diverse. Different regions of India contain rocks belonging to different geologic periods, dating as far back as the Eoarchean Era. Some of the rocks are very deformed and altered. Other deposits include recently deposited alluvium that has yet to undergo diagenesis. Mineral deposits of great variety are found in the Indian subcontinent in huge quantities. Even India's fossil record is impressive in which stromatolites, invertebrates, vertebrates and plant fossils are included. India's geographical land area can be classified into the Deccan Traps, Gondwana and Vindhyan.

The geology of Nepal is dominated by the Himalaya, the highest, youngest and a very highly active mountain range. Himalaya is a type locality for the study of on-going continent-continent collision tectonics. The Himalayan arc extends about 2,400 km (1,500 mi) from Nanga Parbat by the Indus River in northern Pakistan eastward to Namche Barwa by the gorge of the Tsangpo-Brahmaputra in eastern Tibet. About 800 km (500 mi) of this extent is in Nepal; the remainder includes Bhutan and parts of Pakistan, India, and China.
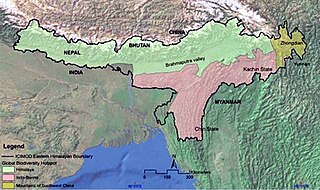
The Eastern Himalayas extend from eastern Nepal across Northeast India, Bhutan, the Tibet Autonomous Region to Yunnan in China and northern Myanmar. The climate of this region is influenced by the monsoon of South Asia from June to September. It is a biodiversity hotspot, with notable biocultural diversity.
The Soanian culture is a prehistoric technological culture from the Siwalik Hills in the Indian subcontinent. It is named after the Soan Valley in Pakistan. Soanian sites are found along the Siwalik region in present-day India, Nepal and Pakistan. The Soanian culture has been approximated to have taken place during the Middle Pleistocene period or the mid-Holocene epoch (Northgrippian). Debates still goes on today regarding the exact period occupied by the culture due to artefacts often being found in non-datable surface context. This culture was first discovered and named by the anthropology and archaeology team led by Helmut De Terra and Thomas Thomson Paterson. Soanian artifacts were manufactured on quartzite pebbles, cobbles, and occasionally on boulders, all derived from various fluvial sources on the Siwalik landscape. Soanian assemblages generally comprise varieties of choppers, discoids, scrapers, cores, and numerous flake type tools, all occurring in varying typo-technological frequencies at different sites.
Siwalik is a highland region between the Mahabharat and Chure mountain ranges in Nepal.
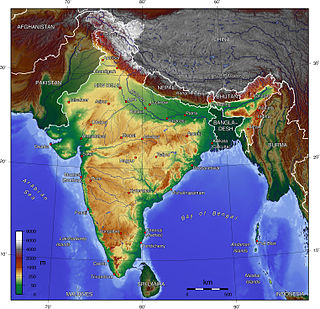
The Indian Himalayan Region is the section of the Himalayas within the Republic of India, spanning thirteen Indian states and union territories, namely Ladakh, Jammu and Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Sikkim, West Bengal, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Tripura, Assam, and Arunachal Pradesh. The region is responsible for providing water to a large part of the Indian subcontinent and contains various flora and fauna.
The ecology of the Himalayas varies with climate, rainfall, altitude, and soils. The climate ranges from tropical at the base of the mountains to permanent ice and snow at the highest elevations. The amount of yearly rainfall increases from west to east along the southern front of the range. This diversity of climate, altitude, rainfall and soil conditions supports a variety of distinct plant and animal species, such as the Nepal gray langur
Rashid Ahmed Khan Tahirkheli was the vice-chancellor of Gandhara University. Prior to his appointment he was Director of the Geology Department and ex Vice-Chancellor at Peshawar University. He was also Professor Emeritus in the National Centre of Excellence in Geology, University of Peshawar. His scholarly reputation rests on his contributions to the Geology of the Himalayas, Karakoram and Hindukush. He received prizes including Sitara-i-Imtiaz in 1982.

The Main Central Thrust is a major geological fault where the Indian Plate has pushed under the Eurasian Plate along the Himalaya. The fault slopes down to the north and is exposed on the surface in a NW-SE direction (strike). It is a thrust fault that continues along 2900 km of the Himalaya mountain belt.

The Himalayan foreland basin is an active collisional foreland basin system in South Asia. Uplift and loading of the Eurasian Plate on to the Indian Plate resulted in the flexure (bending) of the Indian Plate, and the creation of a depression adjacent to the Himalayan mountain belt. This depression was filled with sediment eroded from the Himalaya, that lithified and produced a sedimentary basin ~3 to >7 km deep. The foreland basin spans approximately 2,000 kilometres (1,200 mi) in length and 450 kilometres (280 mi) in width. From west to east the foreland basin stretches across five countries: Pakistan, India, Nepal, Bangladesh, and Bhutan.

Pre-collisional Himalaya is the arrangement of the Himalayan rock units before mountain-building processes resulted in the collision of Asia and India. The collision began in the Cenozoic and it is a type locality of a continental-continental collision. The reconstruction of the initial configuration of the rock units and the relationship between them is highly controversial, and major concerns relate to the arrangements of the different rock units in three dimensions. Several models have been advanced to explain the possible arrangements and petrogenesis of the rock units.
One of the major depositional strata in the Himalaya is the Lesser Himalayan Strata from the Paleozoic to Mesozoic eras. It had a quite different marine succession during the Paleozoic, as most parts of it are sparsely fossiliferous or even devoid of any well-defined fossils. Moreover, it consists of many varied lithofacies, making correlation work more difficult. This article describes the major formations of the Paleozoic – Mesozoic Lesser Himalayan Strata, including the Tal Formation, Gondwana Strata, Singtali Formation and Subathu Formation.
The geology of Bhutan is less well studied than many countries in Asia, together with the broader Eastern Himalayas region. Older Paleozoic and Precambrian rocks often appear mixed together with younger sediments due to the Himalayan orogeny.
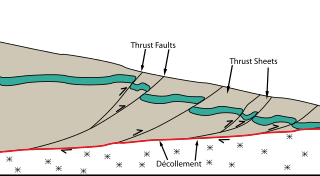
The Main Himalayan Thrust (MHT) is a décollement under the Himalaya Range. This thrust fault follows a NW-SE strike, reminiscent of an arc, and gently dips about 10 degrees towards the north, beneath the region. It is the largest active continental megathrust fault in the world.












