Related Research Articles
In cell biology, an organelle is a specialized subunit, usually within a cell, that has a specific function. The name organelle comes from the idea that these structures are parts of cells, as organs are to the body, hence organelle, the suffix -elle being a diminutive. Organelles are either separately enclosed within their own lipid bilayers or are spatially distinct functional units without a surrounding lipid bilayer. Although most organelles are functional units within cells, some function units that extend outside of cells are often termed organelles, such as cilia, the flagellum and archaellum, and the trichocyst.
A signal peptide is a short peptide present at the N-terminus of most newly synthesized proteins that are destined toward the secretory pathway. These proteins include those that reside either inside certain organelles, secreted from the cell, or inserted into most cellular membranes. Although most type I membrane-bound proteins have signal peptides, most type II and multi-spanning membrane-bound proteins are targeted to the secretory pathway by their first transmembrane domain, which biochemically resembles a signal sequence except that it is not cleaved. They are a kind of target peptide.
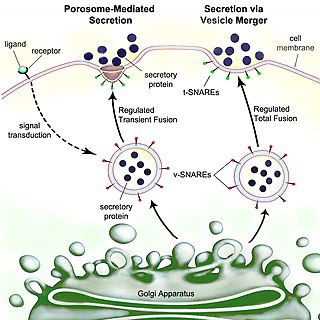
Secretion is the movement of material from one point to another, such as a secreted chemical substance from a cell or gland. In contrast, excretion is the removal of certain substances or waste products from a cell or organism. The classical mechanism of cell secretion is via secretory portals at the plasma membrane called porosomes. Porosomes are permanent cup-shaped lipoprotein structures embedded in the cell membrane, where secretory vesicles transiently dock and fuse to release intra-vesicular contents from the cell.
The periplasm is a concentrated gel-like matrix in the space between the inner cytoplasmic membrane and the bacterial outer membrane called the periplasmic space in Gram-negative bacteria. Using cryo-electron microscopy it has been found that a much smaller periplasmic space is also present in Gram-positive bacteria, between cell wall and the plasma membrane. The periplasm may constitute up to 40% of the total cell volume of gram-negative bacteria, but is a much smaller percentage in gram-positive bacteria.
The cell envelope comprises the inner cell membrane and the cell wall of a bacterium. In Gram-negative bacteria an outer membrane is also included. This envelope is not present in the Mollicutes where the cell wall is absent.
Protein subcellular localization prediction involves the prediction of where a protein resides in a cell, its subcellular localization.

The bacterial outer membrane is found in gram-negative bacteria. Gram-negative bacteria form two lipid bilayers in their cell envelopes - an inner membrane (IM) that encapsulates the cytoplasm, and an outer membrane (OM) that encapsulates the periplasm.
A bacterium, despite its simplicity, contains a well-developed cell structure which is responsible for some of its unique biological structures and pathogenicity. Many structural features are unique to bacteria and are not found among archaea or eukaryotes. Because of the simplicity of bacteria relative to larger organisms and the ease with which they can be manipulated experimentally, the cell structure of bacteria has been well studied, revealing many biochemical principles that have been subsequently applied to other organisms.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to cell biology:

Chromosome 11 open reading frame 54 (C11orf54) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the C11orf54 gene. The "Homo sapiens" gene, C11orf54 is also known as PTD012 and PTOD12. C11orf54 exhibits hydrolase activity on p-nitrophenyl acetate and acts on ester bonds, though the overall function is still not fully understood by the scientific community. The protein is highly conserved with the most distant homolog found is in bacteria.

PSORTdb is a database of protein subcellular localization (SCL) for bacteria and archaea. It is a member of the PSORT family of bioinformatics tools. The database consists of two datasets, ePSORTdb and cPSORTdb, which contain information determined through experimental validation and computational prediction, respectively. The ePSORTdb dataset is the largest curated collection of experimentally verified SCL data.
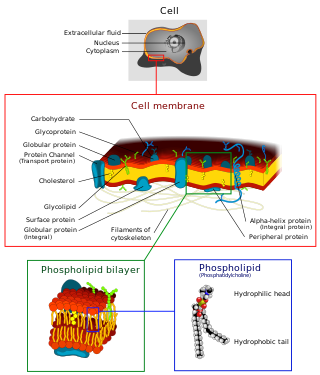
The cell membrane is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of a cell from the outside environment. The cell membrane consists of a lipid bilayer, made up of two layers of phospholipids with cholesterols interspersed between them, maintaining appropriate membrane fluidity at various temperatures. The membrane also contains membrane proteins, including integral proteins that span the membrane and serve as membrane transporters, and peripheral proteins that loosely attach to the outer (peripheral) side of the cell membrane, acting as enzymes to facilitate interaction with the cell's environment. Glycolipids embedded in the outer lipid layer serve a similar purpose. The cell membrane controls the movement of substances in and out of a cell, being selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules. In addition, cell membranes are involved in a variety of cellular processes such as cell adhesion, ion conductivity, and cell signalling and serve as the attachment surface for several extracellular structures, including the cell wall and the carbohydrate layer called the glycocalyx, as well as the intracellular network of protein fibers called the cytoskeleton. In the field of synthetic biology, cell membranes can be artificially reassembled.
Secretomics is a type of proteomics which involves the analysis of the secretome—all the secreted proteins of a cell, tissue or organism. Secreted proteins are involved in a variety of physiological processes, including cell signaling and matrix remodeling, but are also integral to invasion and metastasis of malignant cells. Secretomics has thus been especially important in the discovery of biomarkers for cancer and understanding molecular basis of pathogenesis. The analysis of the insoluble fraction of the secretome has been termed matrisomics.
The secretome is the set of proteins expressed by an organism and secreted into the extracellular space. In humans, this subset of the proteome encompasses 13-20% of all proteins, including cytokines, growth factors, extracellular matrix proteins and regulators, and shed receptors. The secretome of a specific tissue can be measured by mass spectrometry and its analysis constitutes a type of proteomics known as secretomics.
Membrane vesicle trafficking in eukaryotic animal cells involves movement of biochemical signal molecules from synthesis-and-packaging locations in the Golgi body to specific release locations on the inside of the plasma membrane of the secretory cell. It takes place in the form of Golgi membrane-bound micro-sized vesicles, termed membrane vesicles (MVs).

CXorf66 also known as Chromosome X Open Reading Frame 66, is a 361aa protein in humans that is encoded by the CXorf66 gene. The protein encoded is predicted to be a type 1 transmembrane protein; however, its exact function is currently unknown.
Proteome Analyst (PA) is a freely available web server and online toolkit for predicting protein subcellular localization, or where a protein resides in a cell. In the field of proteomics, accurately predicting a protein's subcellular localization, or where a specific protein is located inside a cell, is an important step in the large scale study of proteins. This computational prediction problem is known as Protein subcellular localization prediction. Over the last decade, more than a dozen web servers and computer programs have been developed to attempt to solve this problem. Proteome Analyst is an example of one of the better performing subcellular prediction tools. Proteome Analyst makes predictions for both prokaryotic eukaryotic proteins using a text mining approach. Proteome Analyst was originally developed by the Proteome Analyst Research Group at the University of Alberta, and was initially released in March 2004. It was recently updated in January 2014.
The bacterial murein precursor exporter (MPE) family is a member of the cation diffusion facilitator (CDF) superfamily of membrane transporters. Members of the MPE family are found in a large variety of Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria and facilitate the translocation of lipid-linked murein precursors. A representative list of proteins belonging to the MPE family can be found in the Transporter Classification Database.
References
- ↑ Schuler D. (2004). Molecular analysis of a subcellular compartment: the magnetosome membrane in Magnetospirillum gryphiswaldense. Arch Microbiol. 181:1-7
- ↑ Fyshe, Alona; Yifeng Liu; Duane Szafron; Russell Greiner; Paul Lu (2008). "Improving Subcellular Localization Prediction using Text Classification and the Gene Ontology". Bioinformatics. 24 (21): 2512–7. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btn463 . PMID 18728042.