
A DNA virus is a virus that has a genome made of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) that is replicated by a DNA polymerase. They can be divided between those that have two strands of DNA in their genome, called double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) viruses, and those that have one strand of DNA in their genome, called single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) viruses. dsDNA viruses primarily belong to two realms: Duplodnaviria and Varidnaviria, and ssDNA viruses are almost exclusively assigned to the realm Monodnaviria, which also includes some dsDNA viruses. Additionally, many DNA viruses are unassigned to higher taxa. Reverse transcribing viruses, which have a DNA genome that is replicated through an RNA intermediate by a reverse transcriptase, are classified into the kingdom Pararnavirae in the realm Riboviria.

A retrovirus is a type of virus that inserts a DNA copy of its RNA genome into the DNA of a host cell that it invades, thus changing the genome of that cell. After invading a host cell's cytoplasm, the virus uses its own reverse transcriptase enzyme to produce DNA from its RNA genome, the reverse of the usual pattern, thus retro (backwards). The new DNA is then incorporated into the host cell genome by an integrase enzyme, at which point the retroviral DNA is referred to as a provirus. The host cell then treats the viral DNA as part of its own genome, transcribing and translating the viral genes along with the cell's own genes, producing the proteins required to assemble new copies of the virus. Many retroviruses cause serious diseases in humans, other mammals, and birds.
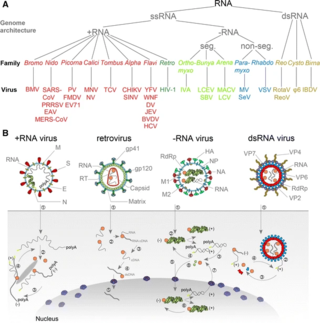
An RNA virus is a virus—other than a retrovirus—that has ribonucleic acid (RNA) as its genetic material. The nucleic acid is usually single-stranded RNA (ssRNA) but it may be double-stranded (dsRNA). Notable human diseases caused by RNA viruses include the common cold, influenza, SARS, MERS, COVID-19, Dengue Virus, hepatitis C, hepatitis E, West Nile fever, Ebola virus disease, rabies, polio, mumps, and measles.

A reverse transcriptase (RT) is an enzyme used to generate complementary DNA (cDNA) from an RNA template, a process termed reverse transcription. Reverse transcriptases are used by viruses such as HIV and hepatitis B to replicate their genomes, by retrotransposon mobile genetic elements to proliferate within the host genome, and by eukaryotic cells to extend the telomeres at the ends of their linear chromosomes. Contrary to a widely held belief, the process does not violate the flows of genetic information as described by the classical central dogma, as transfers of information from RNA to DNA are explicitly held possible.

Transcription is the process of copying a segment of DNA into RNA. The segments of DNA transcribed into RNA molecules that can encode proteins produce messenger RNA (mRNA). Other segments of DNA are transcribed into RNA molecules called non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs).

Picornaviruses are a group of related nonenveloped RNA viruses which infect vertebrates including fish, mammals, and birds. They are viruses that represent a large family of small, positive-sense, single-stranded RNA viruses with a 30 nm icosahedral capsid. The viruses in this family can cause a range of diseases including the common cold, poliomyelitis, meningitis, hepatitis, and paralysis.

Rubella virus (RuV) is the pathogenic agent of the disease rubella, transmitted only between humans via the respiratory route, and is the main cause of congenital rubella syndrome when infection occurs during the first weeks of pregnancy.

Nodaviridae is a family of nonenveloped positive-strand RNA viruses. Vertebrates and invertebrates serve as natural hosts. Diseases associated with this family include: viral encephalopathy and retinopathy in fish. There are nine species in the family, assigned to two genera.

Tombusviridae is a family of single-stranded positive sense RNA plant viruses. There are three subfamilies, 17 genera, and 95 species in this family. The name is derived from Tomato bushy stunt virus (TBSV).
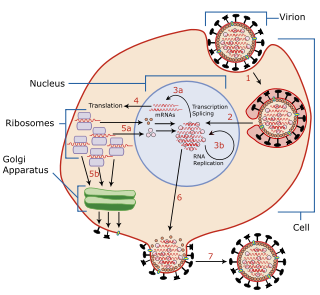
Viral replication is the formation of biological viruses during the infection process in the target host cells. Viruses must first get into the cell before viral replication can occur. Through the generation of abundant copies of its genome and packaging these copies, the virus continues infecting new hosts. Replication between viruses is greatly varied and depends on the type of genes involved in them. Most DNA viruses assemble in the nucleus while most RNA viruses develop solely in cytoplasm.

Nidovirales is an order of enveloped, positive-strand RNA viruses which infect vertebrates and invertebrates. Host organisms include mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, fish, arthropods, molluscs, and helminths. The order includes the families Coronaviridae, Arteriviridae, Roniviridae, and Mesoniviridae.
Baltimore classification is a system used to classify viruses based on their manner of messenger RNA (mRNA) synthesis. By organizing viruses based on their manner of mRNA production, it is possible to study viruses that behave similarly as a distinct group. Seven Baltimore groups are described that take into consideration whether the viral genome is made of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) or ribonucleic acid (RNA), whether the genome is single- or double-stranded, and whether the sense of a single-stranded RNA genome is positive or negative.
In molecular biology and genetics, the sense of a nucleic acid molecule, particularly of a strand of DNA or RNA, refers to the nature of the roles of the strand and its complement in specifying a sequence of amino acids. Depending on the context, sense may have slightly different meanings. For example, the negative-sense strand of DNA is equivalent to the template strand, whereas the positive-sense strand is the non-template strand whose nucleotide sequence is equivalent to the sequence of the mRNA transcript.
Cowpea chlorotic mottle virus, known by the abbreviation CCMV, is a virus that specifically infects the cowpea plant, or black-eyed pea. The leaves of infected plants develop yellow spots, hence the name "chlorotic". Similar to its "brother" virus, Cowpea mosaic virus (CPMV), CCMV is produced in high yield in plants. In the natural host, viral particles can be produced at 1–2 mg per gram of infected leaf tissue. Belonging to the bromovirus genus, cowpea chlorotic mottle virus (CCMV) is a small spherical plant virus. Other members of this genus include the brome mosaic virus (BMV) and the broad bean mottle virus (BBMV).

Alfalfa mosaic virus (AMV), also known as Lucerne mosaic virus or Potato calico virus, is a worldwide distributed phytopathogen that can lead to necrosis and yellow mosaics on a large variety of plant species, including commercially important crops. It is the only Alfamovirus of the family Bromoviridae. In 1931 Weimer J.L. was the first to report AMV in alfalfa. Transmission of the virus occurs mainly by some aphids, by seeds or by pollen to the seed.

Potexvirus is a genus of pathogenic viruses in the order Tymovirales, in the family Alphaflexiviridae. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are 48 species in this genus, three of which are assigned to a subgenus. Diseases associated with this genus include: mosaic and ringspot symptoms. The genus name comes from POTato virus X).

Positive-strand RNA viruses are a group of related viruses that have positive-sense, single-stranded genomes made of ribonucleic acid. The positive-sense genome can act as messenger RNA (mRNA) and can be directly translated into viral proteins by the host cell's ribosomes. Positive-strand RNA viruses encode an RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) which is used during replication of the genome to synthesize a negative-sense antigenome that is then used as a template to create a new positive-sense viral genome.
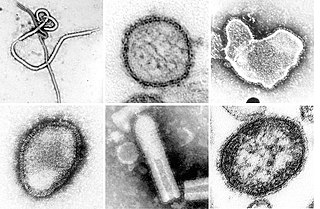
Negative-strand RNA viruses are a group of related viruses that have negative-sense, single-stranded genomes made of ribonucleic acid (RNA). They have genomes that act as complementary strands from which messenger RNA (mRNA) is synthesized by the viral enzyme RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp). During replication of the viral genome, RdRp synthesizes a positive-sense antigenome that it uses as a template to create genomic negative-sense RNA. Negative-strand RNA viruses also share a number of other characteristics: most contain a viral envelope that surrounds the capsid, which encases the viral genome, −ssRNA virus genomes are usually linear, and it is common for their genome to be segmented.

Monodnaviria is a realm of viruses that includes all single-stranded DNA viruses that encode an endonuclease of the HUH superfamily that initiates rolling circle replication of the circular viral genome. Viruses descended from such viruses are also included in the realm, including certain linear single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) viruses and circular double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) viruses. These atypical members typically replicate through means other than rolling circle replication.

Orthornavirae is a kingdom of viruses that have genomes made of ribonucleic acid (RNA), including genes which encode an RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp). The RdRp is used to transcribe the viral RNA genome into messenger RNA (mRNA) and to replicate the genome. Viruses in this kingdom share a number of characteristics which promote rapid evolution, including high rates of genetic mutation, recombination, and reassortment.

















