

The Suwannee County, Florida paleontological sites are assemblages of Early Miocene invertebrates and vertebrates occurring in Suwannee County, Florida.


The Suwannee County, Florida paleontological sites are assemblages of Early Miocene invertebrates and vertebrates occurring in Suwannee County, Florida.
Era : Neogene
Period : Early Miocene
Faunal stage : Arikareean (30.8—20.6 Ma.), calculates to a period of approximately 1.2 million years.
S1BA site aka Live Oak site. AEO: ~21.8—21.7 Mya., approximately 0.1 million years [1]
Coordinates: 30°18′N83°00′W / 30.3°N 83.0°W

The Mustelidae are a diverse family of carnivoran mammals, including weasels, badgers, otters, polecats, martens, grisons, and wolverines. Otherwise known as mustelids, they form the largest family in the suborder Caniformia of the order Carnivora with about 66 to 70 species in nine subfamilies.

Menoceras is a genus of extinct, small rhinocerotids endemic to most of southern North America and ranged as far south as Panama during the early Miocene epoch. It lived from around 30.7—19.7 Ma, existing for approximately 11 million years.

Phlaocyon is an extinct genus of the Borophaginae subfamily of canids native to North America. It lives from the Early Oligocene to the Early Miocene epoch 33.3–16.3 Mya, existing for approximately 17.3 million years. It is closely related to Cynarctoides.

Hesperocyon is an extinct genus of canids that was endemic to North America, ranging from southern Canada to Colorado. It appeared during the Uintan age, –Bridgerian age (NALMA) of the Mid-Eocene– 42.5 Ma to 31.0 Ma. (AEO). Hesperocyon existed for approximately 11.5 million years.

Daphoenus is an extinct genus of amphicyonids. Daphoenus inhabited North America from the Late Eocene to the Middle Miocene, 37.2—16.0 Mya, existing for approximately 21 million years.

Tomarctus is a canid genus of the extinct subfamily Borophaginae which inhabited most of North America during the late Early Miocene to the Early Barstovian age of the Middle Miocene. Tomarctus existed for approximately 6.83 million years.
The cat gap is a period in the fossil record of approximately 25 million to 18.5 million years ago in which there are few fossils of cats or cat-like species found in North America. The cause of the "cat gap" is disputed, but it may have been caused by changes in the climate, changes in the habitat and environmental ecosystem, the increasingly hypercarnivorous trend of the cats, volcanic activity, evolutionary changes in dental morphology of the Canidae species present in North America, or a periodicity of extinctions called van der Hammen cycles.

Megalictis is an extinct genus of large predatory mustelids that existed in North America during the "cat gap" from the Late Arikareean (Ar4) in the Miocene epoch. It is thought to have resembled a huge, jaguar-sized ferret, weighing up to 60–100 kilograms (130–220 lb).

The Thomas Farm site is an Early Miocene, Hemingfordian assemblage of vertebrate fossils located in Gilchrist County, northern Florida.

The Torreya Formation is a Miocene geologic formation with an outcrop in North Florida. It is within the Hawthorn Group.

The Leon County paleontological sites are assemblages of Early Miocene invertebrates and vertebrates of Leon County, Florida, United States.

The Gadsden County paleontological sites are assemblages of Early Miocene invertebrates and vertebrates occurring in Gadsden County, Florida, United States.

The Jefferson County, Florida paleontological sites are assemblages of Mid-Miocene to Late Pleistocene vertebrates from Jefferson County, Florida, United States.

The Choctaw Sea was a Cenozoic eutropical subsea, which along with the Okeechobean Sea, occupied the eastern Gulf of Mexico basin system bounding Florida.
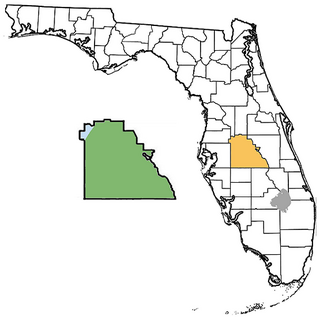
The Polk County paleontological sites are assemblages of Early Miocene to Late Pleistocene vertebrates occurring in Polk County, Florida, United States.

Sthenictis is an extinct genus in the weasel family (mustelids) endemic to North America and Asia during the Miocene epoch living from ~15.97—5.33 Ma (AEO) existing for approximately 11 million years.
Trigonictis macrodon is an extinct species of mammal related to the living grison (genus Galictis). It lived in North America during the Pliocene to Pleistocene epochs, from ~4.1–1.6 Ma. (AEO), existing for approximately 2.5 million years. Fossil specimens have been found across the United States, from Washington and Oregon in the northwest to California and Florida in the south.

Enhydritherium terraenovae is an extinct marine otter endemic to North America that lived during the Miocene through Pliocene epochs from ~9.1–4.9 Ma. (AEO), existing for approximately 4.2 million years.
The Parachucla Formation is a geologic formation in the southeastern United States. It preserves fossils from the Aquitanian stage of the early Miocene period. The formation is included in the Hawthorn Group. An exposure at the northern end of the formation has produced fossils estimated to be 19.4 to 20.5 Million years ago (Ma). Another exposure at the southern end of the formation has produced fossils estimated to be 23.9 to 24.7 Ma.
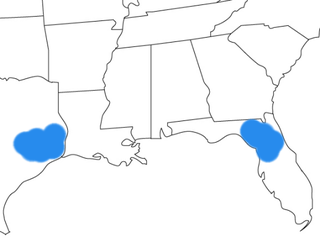
Floridachoerus olseni is an extinct peccary that lived during the Hemingfordian age of the Early Miocene, and was endemic to North America. F. olseni was in existence for approximately 4.46 million years. Remains of this extinct mammal were located at the fossil rich Thomas Farm site in Gilchrist County, Florida and Toledo Bend site, Newton County, Texas. Floridachoerus olseni was named after Stanley. J. Olsen of the Florida Geological Survey in 1962. Olsen previously worked at the site for Harvard University.