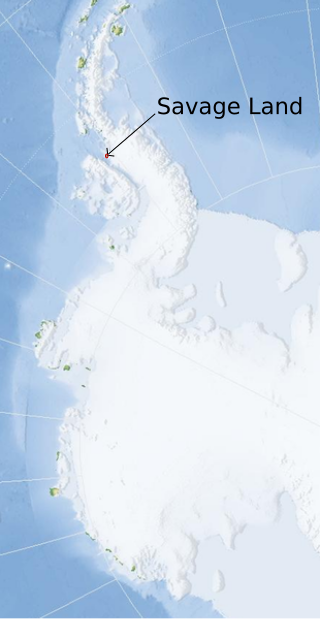
The Savage Land is a hidden prehistoric land appearing in American comic books published by Marvel Comics. It is a tropical preserve hidden in Antarctica. It has appeared in many story arcs in Uncanny X-Men as well as other related books.

The Cherokee are one of the indigenous peoples of the Southeastern Woodlands of the United States. Prior to the 18th century, they were concentrated in their homelands, in towns along river valleys of what is now southwestern North Carolina, southeastern Tennessee, edges of western South Carolina, northern Georgia, and northeastern Alabama.

The Potawatomi, also spelled Pottawatomi and Pottawatomie, are a Native American people of the Great Plains, upper Mississippi River, and western Great Lakes region. They traditionally speak the Potawatomi language, a member of the Algonquin family. The Potawatomi call themselves Neshnabé, a cognate of the word Anishinaabe. The Potawatomi are part of a long-term alliance, called the Council of Three Fires, with the Ojibway and Odawa (Ottawa). In the Council of Three Fires, the Potawatomi are considered the "youngest brother" and are referred to in this context as Bodéwadmi, a name that means "keepers of the fire" and refers to the council fire of three peoples.

Madoc ab Owain Gwynedd was, according to folklore, a Welsh prince who sailed to America in 1170, over three hundred years before Christopher Columbus's voyage in 1492.
Donald Laycock (1936–1988) was an Australian linguist and anthropologist. He is best remembered for his work on the languages of Papua New Guinea.

The Kuki people are an ethnic group native to the Mizo Hills, a mountainous region in the southeastern part of Mizoram and Manipur in India. The Kuki constitute one of several hill tribes within India, Bangladesh, and Myanmar. In Northeast India, they are present in all states except Arunachal Pradesh.
Mangani is the name of a fictional species of great apes in the Tarzan novels of Edgar Rice Burroughs, and of the invented language used by these apes. In the invented language, Mangani is the apes' word for their own kind, although the term is also applied to humans. The Mangani are represented as the apes who foster and raise Tarzan.

The Cherokee Nation, also known as the Cherokee Nation of Oklahoma, is the largest of three Cherokee federally recognized tribes in the United States. It was established in the 20th century and includes people descended from members of the Old Cherokee Nation who relocated, due to increasing pressure, from the Southeast to Indian Territory and Cherokee who were forced to relocate on the Trail of Tears. The tribe also includes descendants of Cherokee Freedmen, Absentee Shawnee, and Natchez Nation. As of 2023, over 450,000 people were enrolled in the Cherokee Nation.

Operation Auca was an attempt by five Evangelical Christian missionaries from the United States to bring Christianity to the Waodani or Huaorani people of the rain forest of Ecuador. The Huaorani, also known pejoratively as Aucas, were an isolated tribe known for their violence, against both their own people and outsiders who entered their territory. With the intention of being the first Christians to evangelize the previously uncontacted Huaorani, the missionaries began making regular flights over Huaorani settlements in September 1955, dropping gifts, which were reciprocated. After several months of exchanging gifts, on January 3, 1956, the missionaries established a camp at "Palm Beach", a sandbar along the Curaray River, a few kilometers from Huaorani settlements. Their efforts came to an end on January 8, 1956, when all five—Jim Elliot, Nate Saint, Ed McCully, Peter Fleming, and Roger Youderian—were attacked and speared by a group of Huaorani warriors. The news of their deaths was broadcast around the world, and Life magazine covered the event with a photo essay.

Kuringgai is an ethnonym referring to an Indigenous Australian peoples occupying the territory between the southern borders of the Gamilaraay and the area around Sydney, and an historical people with its own distinctive language, located in part of that territory.

Tantor is a generic name for elephants in Mangani, the fictional language of the great apes in the Tarzan novels of Edgar Rice Burroughs. In Burroughs's works a number of elephants appear under the name of Tantor, most notably one particular bull elephant the ape man befriends in his youth in the first Tarzan novel, Tarzan of the Apes and in the 1999 Animated Walt Disney film he is a red African Forest Elephant and friends with the ape Terk.
Dayuma was a member of the Huaorani tribe and a citizen of Ecuador. She is a central figure in the Operation Auca saga, in that she was the first Huao to convert to Christianity, as well as the missionaries' key to unlocking the Huaorani language, a language that had not been previously studied. Later Dayuma also became an influential figure in her tribe.
The Aweti people are a group of Native Americans living in the Xingu Indigenous Park, close to the headwaters of the Xingu River in Brazil. The Aweti inhabit two villages in the region. One is called Tazu’jyretam, and the other is unnamed. Tazu’jyretam is the main village of the Aweti people, and has been inhabited since at least the 19th century. Tazu’jyretam also has a small port. Both of these villages are located in an area between the Curisevo and Tuatuarí rivers, which feed into the Xingu further upstream. Their population was 196 in 2011, up from 140 in 2006.
The Waziri are a fictional African tribe created by Edgar Rice Burroughs in his Tarzan novels. Burroughs characterizes the Waziri as the greatest warriors in Africa, though small in numbers. They are feared by Arabic ivory and slave traders as well as cannibal tribes, and known from western to eastern Africa. The Waziri also appear in other media based on the novels.

The Tasaday are a Philippine indigenous people of the Lake Sebu area in Mindanao. They are considered to belong to the Lumad group, along with the other indigenous groups on the island. They attracted widespread media attention in 1971, when a journalist of the Manila Associated Press bureau chief reported their discovery, amid apparent "Stone Age" technology and in complete isolation from the rest of Philippine society. Multiple agencies were also contacted, such as National Geographic. They again attracted attention in the 1980s when some accused the Tasaday of living in the jungle and speaking in their dialect as being part of an elaborate hoax, and doubts were raised as to their isolation and nature as a separate ethnic group. The Tasaday language is distinct from that of neighboring tribes, and linguists believe it probably split from the adjacent Manobo languages 200 years ago.
The Hewa are an indigenous people that live in the Koroba Lake Kopiago Electorate of Hela Province of Papua New Guinea near the junction of the Strickland River. They were one of the last peoples in Papua New Guinea to come into contact with the outside world. They number about 2,000 persons, and their rugged rainforest terrain comprises about 200 square miles (518 km2), some of which was unexplored until 2008. Their language belongs to the Sepik family.

The Sepik is the longest river on the island of New Guinea, and the second largest in Oceania by discharge volume after the Fly River. The majority of the river flows through the Papua New Guinea (PNG) provinces of Sandaun and East Sepik, with a small section flowing through the Indonesian province of Papua.
Kwoma is a Sepik language of Papua New Guinea also known as Washkuk. The word 'Kwoma' means "hill people". Washkuk is a government name for the people of Kwoma. Linguists have the given the name 'Kwoma' as the primary name of the language, but 'Nukuma' is the specific name for the Northern dialect. Nukuma means people who live along the upper reaches of the Sanchi River. The speakers of Kwoma are located in the Ambunti district of the Sepik River region. There are two dialects known as Kwoma (Washkuk) and Nukuma. The Kwoma dialect or "hill people" is located in the Washkuk Hills which is a range of mountains on the north side of the Sepik. The Nukuma dialect or "headwater people" live to the north and west of the Washkuk range along the Sepik River. Kwoma is considered an endangered language with an estimated 2,925 native speakers worldwide.
Ngala, or Sogap, is one of the Ndu languages of Sepik River region of northern Papua New Guinea. It is spoken in the single village of Swagap in Ambunti Rural LLG of East Sepik Province.
The Lokono or Arawak are an Arawak people native to northern coastal areas of South America. Today, approximately 10,000 Lokono live primarily along the coasts and rivers of Venezuela, Guyana, Suriname, Barbados and French Guiana. They speak the Arawak language, the eponymous language of the Arawakan language family, as well as various Creole languages, and English.