External links
| | This Papua New Guinea-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
| | This article related to an ethnic group in Oceania is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
Tairora is a tribal group of people living in the Eastern Highlands of Papua New Guinea in or near the Aiyura Valley. They are the traditional enemy of the Gadsup.

The Semitic languages are a branch of the Afroasiatic language family. They are spoken by more than 330 million people across much of West Asia, the Horn of Africa, and latterly North Africa, Malta, West Africa, Chad, and in large immigrant and expatriate communities in North America, Europe, and Australasia. The terminology was first used in the 1780s by members of the Göttingen school of history, who derived the name from Shem, one of the three sons of Noah in the Book of Genesis.
Whistled languages like some Bird linguistics are languages that use whistling to emulate speech and facilitate communication. A whistled language is a system of whistled communication which allows fluent whistlers to transmit and comprehend a potentially unlimited number of messages over long distances. Whistled languages are different in this respect from the restricted codes sometimes used by herders or animal trainers to transmit simple messages or instructions. Generally, whistled languages emulate the tones or vowel formants of a natural spoken language, as well as aspects of its intonation and prosody, so that trained listeners who speak that language can understand the encoded message.

Pacific Islanders, Pasifika, Pasefika, Pacificans or rarely Pacificers are the peoples of the Pacific Islands. As an ethnic/racial term, it is used to describe the original peoples—inhabitants and diasporas—of any of the three major subregions of Oceania.

Venda or Tshivenda, Setswetla is a Bantu language and an official language of South Africa. It is mainly spoken by the Venda people or Batswetla in the northern part of South Africa's Limpopo province, as well as by some Lemba people in South Africa. Setswetla or Tshivenda language is related to Northern Sotho which is spoken in Southern Africa. Setswetla/Venda is a Sotho language that was corrupted by Karanga which came with the Singo people when they invaded the present day Venda from present day Zimbabwe under Dimbanyika. During the apartheid era of South Africa, the bantustan of Venda was set up to cover the Venda speakers of South Africa.

The indigenous peoples of Western New Guinea in Indonesia and Papua New Guinea, commonly called Papuans, are Melanesians. There is genetic evidence for two major historical lineages in New Guinea and neighboring islands: a first wave from the Malay Archipelago perhaps 50,000 years ago when New Guinea and Australia were a single landmass called Sahul and, much later, a wave of Austronesian people from the north who introduced Austronesian languages and pigs about 3,500 years ago. They also left a small but significant genetic trace in many coastal Papuan peoples.

Ukarumpa is an intentional international community that is the main centre for SIL-PNG, located in the Eastern Highlands Province of Papua New Guinea. It lies approximately 11 kilometres (7 mi) by road from Kainantu in the Aiyura Valley. The population consists of a variety of paid staff and volunteer staff who live nearby. The centre was established in 1957. The current population is approximately 600. It is at an elevation of approximately 1600 m above sea level.

Aiyura is the name of a valley located in the Eastern Highlands of Papua New Guinea. It is the home of the Aiyura Agricultural Research Station, which was operated originally as the "Highlands Agricultural Experiment Station, Aiyura" begun in 1936 by Mr. Bill Brechin, an Australian Agriculturist. In 1937 work was begun clearing the land for the airstrip which is now the home in Papua New Guinea of JAARS, Airstrip IATA code AYU known as Aiyura Airport. Aiyura played a role in World War II when the Aiyura Airstrip was bombed by the Japanese on June 15, 1943, with six bombers and six fighter aircraft.
Gadsup is a tribal group of people living in Eastern Highlands Province of Papua New Guinea in or near the Aiyura Valley. They are traditional enemies of the Tairora people. They speak the Gadsup language.
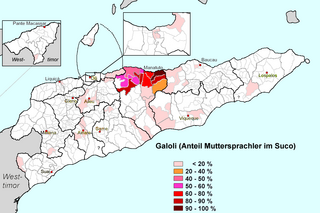
The Galoli, or Galolen, are a people of East Timor with a population of about 50,000, primarily along the northern coast of the district of Manatuto. To the west lies the Mambai people. There is an old colony on the southern coast of Wetar island, the Talo, who speak the Talur dialect.

Kiga is a Great Lakes Bantu language of the Kiga people (Bakiga). Kiga is a similar and partially mutually intelligible with the Nkore language. It was first written in the second half of the 19th century. Kiga is largely spoken in the ancient Kigezi region which includes about 5 districts, namely Rubanda, Rukiga, Kabale, Kanungu and some parts of Rukungiri. As of 2021, Kiga is spoken natively by about 1.3 million people in Uganda.
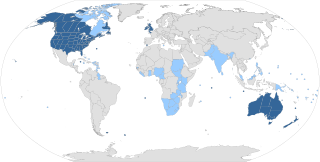
English is a West Germanic language in the Indo-European language family, with its earliest forms spoken by the inhabitants of early medieval England. It is named after the Angles, one of the ancient Germanic peoples that migrated to the island of Great Britain. Existing on a dialect continuum with Scots and then most closely related to the Low Saxon and Frisian languages, Modern English is genealogically Germanic. However, its vocabulary also shows major influences from French and Latin, plus some grammar and a small amount of core vocabulary influenced by Old Norse. Speakers of English are called Anglophones.

The Kainantu–Goroka languages are a family of Papuan languages established by Arthur Capell in 1948 under the name East Highlands. They formed the core of Stephen Wurm's 1960 East New Guinea Highlands family, and are one of the larger branches of Trans–New Guinea in the 2005 classification of Malcolm Ross.
Bakumpai is an Austronesian language belonging to the West Barito languages. It is spoken by about 100,000 Bakumpai people living in the central Kalimantan, Indonesia.
Aka, also known as Yaka or Beka, is a Bantu language spoken in the Central African Republic and Republic of Congo, along the Ubangi River dividing the two countries.
Tairoa (Tairora) is a Kainantu language spoken in Papua New Guinea.
Binumarien, or Afaqinna ufa as it is known to its speakers, is a Kainantu language of Papua New Guinea. The name used in the literature was used under Australian administration and is still used by Binumarien people when they speak Tok Pisin. It comes from the now-abandoned village of Pinumareena. Pinumareena is also one of the four Binumarien clans.
Alas-Kluet, Alas, or Batak Alas, is an Austronesian language of Sumatra. The three dialects, Alas, Kluet, and Singkil (Kade-Kade), may not constitute a single language; Alas may be closer to Karo, and the others closer to Dairi. By linguistic affiliation, Alas–Kluet belongs to the Batak subgroup. Ethnically, however, its speakers generally do not identify as Batak, mostly because of their religion.
Tairora may refer to:
Proto-Trans–New Guinea is the reconstructed proto-language ancestral to the Trans–New Guinea languages. Reconstructions have been proposed by Malcolm Ross and Andrew Pawley.

Gadsup/Tairora Rural LLG is a local-level government (LLG) of Eastern Highlands Province, Papua New Guinea. The Gadsup language and Tairora language are spoken in the LLG.