
Swansea is a coastal city and the second-largest city of Wales. It forms a principal area, officially known as the City and County of Swansea.

Glamorgan, or sometimes Glamorganshire, is one of the thirteen historic counties of Wales and a former administrative county of Wales. Originally an early medieval petty kingdom of varying boundaries known as Glywysing, then taken over by the Normans as a lordship, the area that became known as Glamorgan was both a rural, pastoral area, and a conflict point between the Norman lords and the Welsh princes. It was defined by a large concentration of castles.

Gower or the Gower Peninsula in southwest Wales, projects towards the Bristol Channel. It is the most westerly part of the historic county of Glamorgan. In 1956, the majority of Gower became the first area in the United Kingdom to be designated an Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty.

Wales is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by England to the east, the Irish Sea to the north and west, Celtic Sea to the south west and the Bristol Channel to the south. It had a population in 2011 of 3,063,456 and has a total area of 20,779 km2 (8,023 sq mi). Wales has over 1,680 miles (2,700 km) of coastline and is largely mountainous with its higher peaks in the north and central areas, including Snowdon, its highest summit. The country lies within the north temperate zone and has a changeable, maritime climate. The capital and largest city is Cardiff.

Wales is a constituent country of the United Kingdom that has a distinctive culture, including its own language, customs, politics, festivals and music. Wales is primarily represented by the symbol of the red Welsh Dragon, but other national emblems include the leek and the daffodil.

The University of Wales is a confederal university based in Cardiff, Wales. Founded by Royal Charter in 1893 as a federal university with three constituent colleges – Aberystwyth, Bangor and Cardiff – the university was the first university established in Wales, one of the four countries in the United Kingdom. The university was, prior to the break up of the federation, the second largest university in the UK.

Swansea University is a public research university located in Swansea, Wales, United Kingdom. It was chartered as University College of Swansea in 1920, as the fourth college of the University of Wales. In 1996, it changed its name to the University of Wales Swansea following structural changes within the University of Wales. The title of Swansea University was formally adopted on 1 September 2007 when the University of Wales became a non-membership confederal institution and the former members became universities in their own right.

Neath Port Talbot is a county borough in the south-west of Wales. Its principal towns are Neath, Port Talbot, Briton Ferry and Pontardawe. The county borough borders Bridgend County Borough and Rhondda Cynon Taf to the east, Powys and Carmarthenshire to the north; and Swansea to the west.

Llanelli is a market town and the largest community in Carmarthenshire and the preserved county of Dyfed, Wales. It is located on the Loughor estuary 10.5 miles (16.9 km) north-west of Swansea and 12 miles (19 km) south-east of the county town, Carmarthen. The town had a population of 25,168 in 2011, estimated in 2019 at 26,225. The local authority was Llanelli Borough Council when the county of Dyfed existed, but it has been under Carmarthenshire County Council since 1996.

The National Library of Wales, Aberystwyth, is the national legal deposit library of Wales and is one of the Welsh Government sponsored bodies. It is the biggest library in Wales, holding over 6.5 million books and periodicals, and the largest collections of archives, portraits, maps and photographic images in Wales. The Library is also home to the national collection of Welsh manuscripts, the National Screen and Sound Archive of Wales, and the most comprehensive collection of paintings and topographical prints in Wales. As the primary research library and archive in Wales and one of the largest research libraries in the United Kingdom, the National Library is a member of Research Libraries UK (RLUK) and the Consortium of European Research Libraries (CERL).
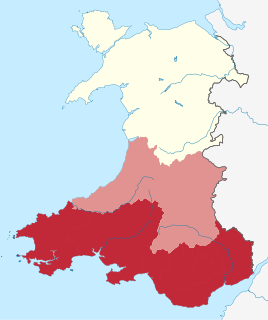
South Wales is a loosely defined region of Wales bordered by England to the east and mid Wales to the north. It has a population of around 2.2 million, almost three-quarters of the whole of Wales, including 400,000 in Cardiff, 250,000 in Swansea and 150,000 in Newport. Generally considered to include the historic counties of Glamorgan and Monmouthshire, south Wales extends westwards to include Carmarthenshire and Pembrokeshire. In the western extent, from Swansea westwards, local people would probably recognise that they lived in both south Wales and west Wales. The Brecon Beacons National Park covers about a third of south Wales, containing Pen y Fan, the highest British mountain south of Cadair Idris in Snowdonia.
The history of Swansea in South Wales covers a period of continuous occupation stretching back a thousand years, while there is archaeological evidence of prehistoric human occupation of the surrounding area for thousands of years before that.

The National Eisteddfod of Wales is the most important of several eisteddfodau that are held annually, mostly in Wales. Its eight days of competitions and performances are considered the largest music and poetry festival in Europe. Competitors typically number 6,000 or more, and overall attendance generally exceeds 150,000 visitors. The 2018 Eisteddfod was held in Cardiff Bay with a fence-free 'Maes'. In 2020 the event was held virtually under the name AmGen; events were held over a one-week period.

Christianity is the largest religion in Wales. Wales has a strong tradition of nonconformism, particularly Methodism. Until 1920 the established church was the Church of England, but from 1920 the disestablished Church in Wales, still Anglican, was self-governing.

Lewis Weston Dillwyn, FRS was a British porcelain manufacturer, naturalist and Whig Member of Parliament (MP).

The Royal Institution of South Wales is a Welsh learned society founded by George Grant Francis in Swansea in 1835.

Welsh art refers to the traditions in the visual arts associated with Wales and its people. Most art found in, or connected with, Wales is essentially a regional variant of the forms and styles of the rest of the British Isles, a very different situation from that of Welsh literature. The term Art in Wales is often used in the absence of a clear sense of what "Welsh art" is, and to include the very large body of work, especially in landscape art, produced by non-Welsh artists in Wales since the later 18th century.
Cambria: A Welsh Geographical Review was a journal published in Wales between 1974 and 1989. Though edited by members of the Geography Departments of Swansea University and Aberystwyth University, the publication was run as an independent business, and production values were basic. Cambria was an annual English-language academic journal containing articles and book reviews on geographical and related topics. It has been digitized by the Welsh Journals Online project at the National Library of Wales.
James Motley was a Yorkshireman closely associated with South Wales and Borneo.

Audrey Williams, née Davies, (1902–1978) was a Welsh archaeologist. She was the first woman president of the Royal Institution of South Wales (RISW) and a Fellow of the Society of Antiquaries. She worked on several notable excavations during the mid-20th century in Wales, London and south-east England, including the Gower Peninsula, Verulamium and the Temple of Mithras in London.














