
The Mojave Air and Space Port at Rutan Field is in Mojave, California, United States, at an elevation of 2,801 feet (854 m). It is the first facility to be licensed in the United States for horizontal launches of reusable spacecraft, being certified as a spaceport by the Federal Aviation Administration on June 17, 2004. The facility covers 2,998 acres and has three runways.

A warbird is any vintage military aircraft now operated by civilian organizations and individuals, or in some instances, by historic arms of military forces, such as the Battle of Britain Memorial Flight, the RAAF Museum Historic Flight, or the South African Air Force Museum Historic Flight.

The Reno Air Races, officially known as the National Championship Air Races, are a multi-day event tailored to the aviation community that took place each September at the Reno Stead Airport a few miles north of Reno, Nevada, with the last races held in 2023. The Reno Air Racing Association plans to resume racing at a new venue in 2025. Air racing is billed as "the world's fastest motor sport" and Reno was one of the few remaining venues. The event includes races in six classes and demonstrations by airshow pilots.

The Beechcraft Bonanza is an American general aviation aircraft introduced in 1947 by Beech Aircraft Corporation of Wichita, Kansas. The six-seater, single-engined aircraft is still produced by Beechcraft and has been in continuous production longer than any other aircraft in history. More than 17,000 Bonanzas of all variants have been built, produced in both distinctive V-tail and conventional tail configurations; early conventional-tail versions were marketed as the Debonair.

Beginning in the late 1950s the United States aircraft company Bay Aviation produced nine twin-engine conversions of the Beechcraft Bonanza called the Super "V" Bonanza. After production was shifted to Canada in 1962, five more aircraft were built for a total production run of fourteen. The basis of the conversion was the early Model 35 Bonanza with the original small V-tail surfaces. The Super-V competed with Beechcraft's own Travel Air twin-engine Bonanza derivative.
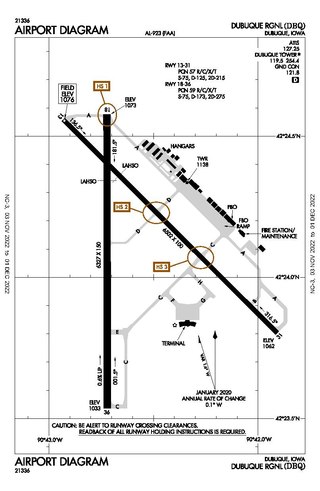
Dubuque Regional Airport is a regional airport located eight miles south of Dubuque, in Dubuque County, Iowa. On U.S. Highway 61, the airport is owned by the city of Dubuque and is operated as a department of the city government. The city council appoints people for four-year terms to the Airport Commission board, which oversees the airport. For day-to-day operations, the Commission hires an airport manager. DBQ is used for general aviation and sees one airline. A charter service is run by Sun Country Airlines. The airport offers maintenance and refueling services, including service for jets.

The Cirrus VK-30 is a single-engine pusher-propeller homebuilt aircraft originally sold as a kit by Cirrus Design, and was the company's first model, introduced in 1987.

Rare Bear is a highly modified Grumman F8F Bearcat that saw major success at the Reno Air Races over multiple decades.

Gladwin Zettel Memorial Airport is a public use airport located one nautical mile (2 km) southeast of the central business district of Gladwin, a city in Gladwin County, Michigan, United States. The airport is owned by the city and county. It is included in the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) National Plan of Integrated Airport Systems for 2017–2021, in which it is categorized as a local general aviation facility.

The ICON A5 is an American amphibious light-sport aircraft (LSA) designed and produced by ICON Aircraft. A concept aircraft was first flown in 2008, and creation of the production tooling began in December 2012. The first production aircraft made its first flight on July 7, 2014, and made its public debut at EAA AirVenture Oshkosh on July 27, 2014. A year later at AirVenture, it was temporarily donated to the youth group Young Eagles, with the first official A5 customer deliveries occurring in 2016. As of 2019, 100 A5s had been delivered, although company legal and financial issues have slowed production since 2016.

The Epic LT is an American kit-built single-engined turboprop aircraft intended for use by private pilots. The Epic Dynasty was the proposed certified version of the LT that was intended be sold as a completed aircraft, prior to Epic Aircraft's bankruptcy in August 2009 and later acquisition by new owners in April 2010. Under ownership of the reorganized company, the certified version is called the Epic E1000. After FAA certification in 2019, deliveries began in 2020.

The Bugatti Model 100 was a purpose-built air racer designed to compete in the 1939 Deutsch de la Meurthe Cup Race. The aircraft was not completed by the September 1939 deadline and was put in storage prior to the German invasion of France.

Steve Hinton is an American aviator who held a world speed record from 1979 to 1989 and won six Unlimited-class air races, including two national championships. He won four consecutive Unlimited races in one year.

The Red Baron was a North American P-51D Mustang NX7715C, original serial number 44-84961. It raced from 1966 to 1973 under the names Miss R.J. and Roto-Finish Special, winning Unlimited Gold in 1972. In February 1974, it was purchased by Ed Browning of Red Baron Flying Service in Idaho Falls, Idaho and renamed the Red Baron.

The Galloping Ghost was a P-51D Mustang air racer that held various airspeed records and whose fatal crash in 2011 led to several NTSB recommendations to make air shows safer.

On September 16, 2011, The Galloping Ghost, a highly modified North American P-51D Mustang racing aircraft, crashed into spectators while competing at the Reno Air Races in Reno, Nevada, killing the pilot, Jimmy Leeward, and ten people on the ground. Sixty-nine more people on the ground were injured. It was the third-deadliest airshow disaster in U.S. history, following accidents in 1972 and 1951.

The Bell 525 Relentless is an American super-medium-lift helicopter, under development by Bell Textron. The Bell 525 was unveiled at the 2012 Heli-Expo in Dallas, Texas in February 2012. The helicopter first flew on 1 July 2015. It is designed to transport up to 19 passengers. The aircraft is the first fly-by-wire civilian aircraft and suffered a crash of its prototype, and is still slowly working towards certification. As of 2024, Bell is still working towards completing flight certification it has secured its first order.
Wesley "Lee" Behel Jr was an American aviator and air racing champion. He was the creator and, at the time of his death, the president of the "Sport Class", a group of racing airplanes designed for planes under 1000 cubic inches in engine size that participate in the Reno Air Races every September, as well as a retired Lt. Colonel in the Nevada Air National Guard.

Precious Metal is a custom-built racing aircraft based on the North American P-51 Mustang.

Transair Flight 810 was a Boeing 737-200 converted freighter aircraft, owned and operated by Rhoades Aviation under the Transair trade name, on a short cargo flight en route from Honolulu International Airport to Kahului Airport on the neighboring Hawaiian island of Maui. Immediately after an early morning takeoff on July 2, 2021, one of its two Pratt & Whitney JT8D turbofan engines faltered, and the first officer, who was flying the aircraft, reduced power to both engines. The two pilots—the only occupants of the aircraft—began executing the Engine Failure or Shutdown checklist, but became preoccupied with talking to air traffic control (ATC) and performing other flying tasks, never reaching the section of the checklist where the failing engine was to be positively identified and shut down. The captain assumed control but misidentified the failing engine, increased power to that engine, and did not increase power to the other, properly functioning engine. Convinced that neither engine was working properly and unable to maintain altitude with one engine faltering and the other idling, the pilots ditched off the coast of Oahu about 11 minutes into the flight.


















