
Elasmucha grisea, common name parent bug, is a species of shield bugs or stink bugs belonging to the family Acanthosomatidae. The term parent bugs includes also the other species of the genus Elasmucha and some species of the family Acanthosomatidae.

Magnaporthe grisea, also known as rice blast fungus, rice rotten neck, rice seedling blight, blast of rice, oval leaf spot of graminea, pitting disease, ryegrass blast, and Johnson spot, is a plant-pathogenic fungus that causes a serious disease affecting rice. It is now known that M. grisea consists of a cryptic species complex containing at least two biological species that have clear genetic differences and do not interbreed. Complex members isolated from Digitaria have been more narrowly defined as M. grisea. The remaining members of the complex isolated from rice and a variety of other hosts have been renamed Magnaporthe oryzae. Confusion on which of these two names to use for the rice blast pathogen remains, as both are now used by different authors.
HomoloGene, a tool of the United States National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI), is a system for automated detection of homologs among the annotated genes of several completely sequenced eukaryotic genomes.

Acanthosomatidae is a family of Hemiptera, commonly named "shield bugs," for which Kumar in his 1979 world revision recognized 47 genera; now this number is 55 genera, with about 200 species, and is one of the least diversified families within Pentatomoidea.

Madurella grisea is a fungal species of the genus Madurella. Along with Exophiala jeanselmei, Madurella grisea is one of the most common pathogenic agents associated with eumycetoma.
Prunus grisea is a species of plant in the family Rosaceae. It is found in Malaysia, the Philippines, Singapore, and Taiwan.

Peters's tube-nosed bat is a species of vesper bat in the family Vespertilionidae, found in the Indian Subcontinent, mainly in the Western Himalayas. They have tube-shaped nostrils which assist them with their feeding. They are brown with white-yellow and underparts and have specks of orange around their neck. While they are roosting, their fur, which seems to appear as a dead plant, camouflages them from predators. They are 3.3-6.0 cm in length and have round heads, large eyes and soft fur. This bat is found in India. They are endangered due to clearing of the rain forests in which they live in and are not protected by the World Conservation Union. They feed on rain forest fruit and blossoms.
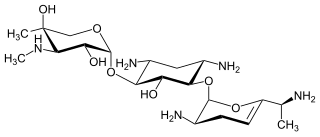
Verdamicin is an aminoglycoside antibiotic produced by Micromonospora grisea.

Acronicta grisea is a moth of the family Noctuidae. It is found from the Atlantic to the Pacific coast in southern Canada and the northern United States.

Quercus grisea, commonly known as the gray oak, shin oak or scrub oak, is a North American species deciduous or evergreen shrub or medium-sized tree in the white oak group. It is native to the mountains of the southwestern United States and northern Mexico. It hybridizes with four other oak species where the ranges of each overlap, the Arizona white oak, the Gambel oak, the Mohr oak and the sandpaper oak.
Papurana grisea is a species of true frog. It is known with certainty only from its type locality in the Went Mountains, in the Indonesian province of Papua, New Guinea. Similar frogs are widespread in New Guinea, usually above 1,200 m (3,900 ft) above sea level, as well as on the Seram Island, but their identity is uncertain; they possibly represent another, undescribed species. Common names Went Mountains frog and Montaen swamp frog have been coined for it.
Etiella grisea is a species of snout moth in the genus Etiella. It was described by George Hampson in 1903. It is found in Sri Lanka, the Chagos Archipelago, Tahiti, the Cook Islands, Samoa, Fiji, the New Hebrides, the Solomon Islands, Australia, the Tanimbar Islands, New Guinea and Guam.

Sybra is a genus of beetles in the family Cerambycidae, containing the following species:

Nicholas José Talbot FRS FRSB is Group Leader and Executive Director at The Sainsbury Laboratory in Norwich.

Sybra umbratica is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Pascoe in 1865.

Sybra ordinata is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Bates in 1873.
Sybra pascoei is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Lameere in 1893.

Boletopsis grisea is a species of fungus in the family Bankeraceae. The fruit bodies are gray, fleshy polypores that grow on the ground in a mycorrhizal association with Scots pine. It is found in Asia, North America, and Europe.
Sophronica grisea is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Per Olof Christopher Aurivillius in 1908.
Nupserha grisea is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Per Olof Christopher Aurivillius in 1914.














