
In the epic Mahabharata, Ambalika is the daughter of Kashya, the King of Kashi, and wife of Vichitravirya, the King of Hastinapur.

The Harivamsa is an important work of Sanskrit literature, containing 16,374 shlokas, mostly in the anustubh metre. The text is also known as the Harivamsa Purana. This text is believed to be a khila to the Mahabharata and is traditionally ascribed to Vyasa. The most celebrated commentary of the Mahabharata by Neelakantha Chaturdhara, the Bharata Bhava Deepa also covers the Harivamsha. According to a traditional version of the Mahabharata, the Harivamsha is divided into two parvas (books) and 12,000 verses. The manuscripts found in the 19th century in different parts of India included three portions known as parvas: the Adi Parva, the Vishnu Parva and the Bhavishya Parva. These are included with the eighteen parvas of the Mahabharata. The Critical Edition has three parvas and 5,965 verses.
List of the avatars of great epic Mahābhārata and the original devatas or deities whose avatars they were.
The Adi Parva or The Book of the Beginning is the first of eighteen books of the Mahabharata. "Adi" is a Sanskrit word that means "first".

Sabha Parva, also called the "Book of the Assembly Hall", is the second of eighteen books of Mahabharata. Sabha Parva traditionally has 10 sub-books and 81 chapters. The critical edition of Sabha Parva has 9 sub-books and 72 chapters.

Vana Parva or Aranya Parva, also known as the “Book of the Forest”, is the third of eighteen parvas of the Indian epic Mahabharata. Aranya Parva traditionally has 21 sub-books and 324 chapters. The critical edition of Aranya Parva has 16 sub-books and 299 chapters. It is one of the longest books in the Epic.

Virata Parva, also known as the “Book of Virata”, is the fourth of eighteen books of the Indian Epic Mahabharata. Virata Parva traditonally has 4 sub-books and 72 chapters. The critical edition of Virata Parva has 4 sub-books and 67 chapters.

The Udyoga Parva, or the Book of Effort, is the fifth of eighteen books of the Indian Epic Mahabharata. Udyoga Parva traditionally has 10 sub-books and 199 chapters. The critical edition of Sabha Parva has 12 sub-books and 197 chapters.

The Shalya Parva, or the Book of Shalya, is the ninth of eighteen books of the Indian epic Mahabharata. Shalya Parva traditionally has 4 sub-books and 65 chapters. The critical edition of Shalya Parva has 4 sub-books and 64 chapters.

The Drona Parva, or the Book of Drona, is the seventh of eighteen books of the Indian epic Mahabharata. Drona Parva traditionally has 8 sub-books and 204 chapters. The critical edition of Drona Parva has 8 sub-books and 173 chapters.

The Karna Parva, or the Book of Karna, is the eighth of eighteen books of the Indian Epic Mahabharata. Karna Parva traditionally has 96 chapters. The critical edition of Karna Parva has 69 chapters
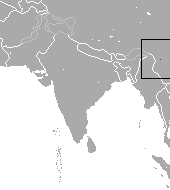
The pygmy brown-toothed shrew is a species of shrew in the Soricomorpha order. It is distributed in China. C. parva was initially thought to be the same as Chodsigoa lamula, but it was found to be a separate species.

The Sauptika Parva, or the "Book of the Sleepers," is the tenth of eighteen books of the Indian Epic Mahabharata. Sauptika Parva traditionally has 2 sub-books and 18 chapters, as does the critical edition.

The Shanti Parva is the twelfth of eighteen books of the Indian Epic Mahabharata. It traditionally has 3 sub-books and 365 chapters. The critical edition has 3 sub-books and 353 chapters. It is the longest book among the eighteen books of the epic.

Anushasana Parva or the "Book of Instructions", is the thirteenth of eighteen books of the Indian Epic Mahabharata. It traditionally has 2 sub-books and 168 chapters. The critical edition has 2 sub-books and 154 chapters. Sometimes this parva is referred to as the "Book of Precepts".

Ashvamedhika Parva, or the "Book of Horse Sacrifice," is the fourteenth of eighteen books of the Indian Epic Mahabharata. It traditionally has 2 sub-books and 96 chapters. The critical edition has one sub-book and 92 chapters.

Ashramvasik Parva, or the "Book of Hermitage", is the fifteenth of eighteen books of the Indian epic Mahabharata. It traditionally has 3 sub-books and 39 chapters. The critical edition has 3 sub-books and 47 chapters.

Svargarohana Parva(Sanskrit: स्वर्गारोहण पर्व) or the Book of the Ascent to Heaven, is the last of eighteen books of the Indian Epic Mahabharata. It traditionally has 6 chapters. The critical edition has 5 chapters. It is one of the shortest books in the Mahabharata.

The Stri Parva, or the "Book of the Women," is the eleventh of eighteen books of the Indian Epic Mahabharata. It traditionally has 4 sub-books and 27 chapters, as does the critical edition.

Sybra is a genus of beetles in the family Cerambycidae, containing the following species:




















