
Bremelanotide, sold under the brand name Vyleesi, is a medication used to treat low sexual desire in women. Specifically it is used for low sexual desire which occurs before menopause and is not due to medical problems, psychiatric problems, or problems within the relationship. It is given by an injection just under the skin of the thigh or abdomen.

The dopamine receptor D4 is a dopamine D2-like G protein-coupled receptor encoded by the DRD4 gene on chromosome 11 at 11p15.5.
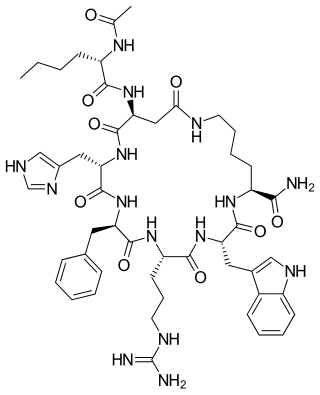
Melanotan II is a synthetic analogue of the peptide hormone α-melanocyte-stimulating hormone (α-MSH) that stimulates melanogenesis and increases sexual arousal.
Melanocortin receptors are members of the rhodopsin family of 7-transmembrane G protein-coupled receptors.
The galanin receptor is a G protein-coupled receptor, or metabotropic receptor which binds galanin.

The δ-opioid receptor, also known as delta opioid receptor or simply delta receptor, abbreviated DOR or DOP, is an inhibitory 7-transmembrane G-protein coupled receptor coupled to the G protein Gi/G0 and has enkephalins as its endogenous ligands. The regions of the brain where the δ-opioid receptor is largely expressed vary from species model to species model. In humans, the δ-opioid receptor is most heavily expressed in the basal ganglia and neocortical regions of the brain.
The tachykinin receptor 1 (TACR1) also known as neurokinin 1 receptor (NK1R) or substance P receptor (SPR) is a G protein coupled receptor found in the central nervous system and peripheral nervous system. The endogenous ligand for this receptor is Substance P, although it has some affinity for other tachykinins. The protein is the product of the TACR1 gene.

SNC-80 is an opioid analgesic compound that selectively activates μ–δ opioid receptor heteromers and is used primarily in scientific research. Discovered in 1994, SNC-80 was a pioneering non-peptide compound regarded as a highly selective agonist for the δ-opioid receptor.

Melanocortin 4 receptor (MC4R) is a melanocortin receptor that in humans is encoded by the MC4R gene. It encodes the MC4R protein, a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) that binds α-melanocyte stimulating hormone (α-MSH). In mouse models, MC4 receptors have been found to be involved in feeding behaviour, the regulation of metabolism, sexual behaviour, and male erectile function.

The adenosine A2B receptor, also known as ADORA2B, is a G-protein coupled adenosine receptor, and also denotes the human adenosine A2b receptor gene which encodes it.

The 5HT6 receptor is a subtype of 5HT receptor that binds the endogenous neurotransmitter serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine, 5HT). It is a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) that is coupled to Gs and mediates excitatory neurotransmission. HTR6 denotes the human gene encoding for the receptor.

Melanocortin 3 receptor (MC3R) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MC3R gene.

Melanocortin 5 receptor (MC5R) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MC5R gene. It is located on the chromosome 18 in the human genome. When the MC5R was disrupted in transgenic mice, it induced disruption of their exocrine glands and resulted in decreased production of sebum.

The 5-HT7 receptor is a member of the GPCR superfamily of cell surface receptors and is activated by the neurotransmitter serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine, 5-HT). The 5-HT7 receptor is coupled to Gs (stimulates the production of the intracellular signaling molecule cAMP) and is expressed in a variety of human tissues, particularly in the brain, the gastrointestinal tract, and in various blood vessels. This receptor has been a drug development target for the treatment of several clinical disorders. The 5-HT7 receptor is encoded by the HTR7 gene, which in humans is transcribed into 3 different splice variants.
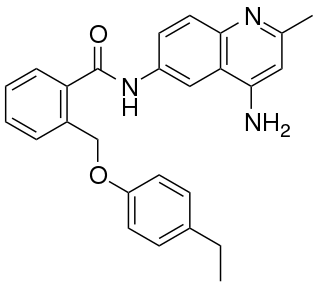
JTC-801 is an opioid analgesic drug used in scientific research.

N6-Cyclopentyladenosine (CPA) is a drug which acts as a selective adenosine A1 receptor agonist. It has mainly cardiovascular effects with only subtle alterations of behavior. CPA is widely used in scientific research into the adenosine receptors and has been used to derive a large family of derivatives.
α-Melanocyte-stimulating hormone (α-MSH) is an endogenous peptide hormone and neuropeptide of the melanocortin family, with a tridecapeptide structure and the amino acid sequence Ac-Ser-Tyr-Ser-Met-Glu-His-Phe-Arg-Trp-Gly-Lys-Pro-Val-NH2. It is the most important of the melanocyte-stimulating hormones (MSHs) (also known as melanotropins) in stimulating melanogenesis, a process that in mammals (including humans) is responsible for pigmentation primarily of the hair and skin. It also plays a role in feeding behavior, energy homeostasis, sexual activity, and protection against ischemia and reperfusion injury.
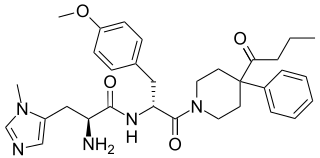
BMS-470539 is a small-molecule experimental drug which acts as a potent and highly selective full agonist of the MC1 receptor. It was discovered in 2003 as part of an effort to understand the role of the MC1 receptor in immunomodulation, and has since been used in scientific research to determine its role in inflammatory processes. The compound was designed with the intention of mimicking the central His-Phe-Arg-Trp pharmacophore of the melanocortins, and this proved to be successful based on its favorable pharmacodynamic profile.

PF-00446687 is a drug developed by Pfizer for the treatment of erectile dysfunction, which is a non-peptide agonist selective for the melanocortin receptor subtype MC4. It was found to be active in preliminary human trials, with the 200mg dose being of similar effectiveness to 100mg sildenafil, though lower doses were ineffective.

HS665 is a drug which acts as a potent and selective κ-opioid receptor agonist, and has analgesic effects in animal studies. HS665 is not an agonist for the mu receptor, leading to less potential for abuse.

















