
The Eleventh Air Force (11 AF) is a Numbered Air Force of the United States Air Force Pacific Air Forces (PACAF). It is headquartered at Joint Base Elmendorf–Richardson, Alaska.

Air Transport Command (ATC) was a United States Air Force unit that was created during World War II as the strategic airlift component of the United States Army Air Forces.

Edward G. Pitka Sr. Airport is a state owned, public use airport located in Galena, a city in the Yukon-Koyukuk Census Area of the U.S. state of Alaska.
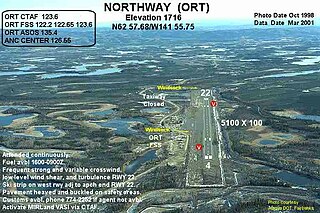
Northway Airport is a state owned, public use airport serving Northway, a community located in the Southeast Fairbanks Census Area of the U.S. state of Alaska. It is included in the National Plan of Integrated Airport Systems for 2011–2015, which categorized it as a general aviation facility.

Marks Air Force Base is a former United States Air Force facility located two nautical miles (4 km) west of the central business district of Nome, a city in the Nome Census Area of the U.S. state of Alaska. Following its closure, it was redeveloped into Nome Airport.
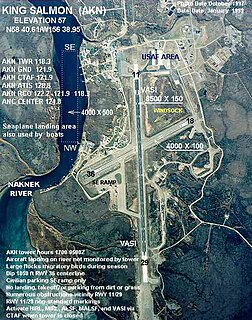
Naknek Air Force Base is a former United States Air Force base located just southeast of King Salmon, in the Bristol Bay Borough of the U.S. state of Alaska. Following its closure, it has since been redeveloped into King Salmon Airport.

ALSIB was the Soviet Union portion of the Alaska-Siberian air road receiving Lend-Lease aircraft from the Northwest Staging Route. Aircraft manufactured in the United States were flown over this route for World War II combat service on the Eastern Front.

Allen Army Airfield is a public and military use airport serving Fort Greely and located three miles (5 km) south of the central business district of Delta Junction, a city in the Southeast Fairbanks Census Area of the U.S. state of Alaska. It is owned by the United States Army, which has an agreement with the City of Delta Junction for joint use of the airfield by both military and civilian aircraft.

Minneapolis–Saint Paul Joint Air Reserve Station is a United States Air Force base, located at Minneapolis–Saint Paul International Airport. It is located 7.1 miles (11.4 km) south-southeast of Minneapolis, Minnesota. It was formerly the location of Naval Air Station Twin Cities.

Thornbrough Air Force Base is a former facility of the United States Air Force in Cold Bay, Alaska. Following its closure, it was redeveloped into Cold Bay Airport.

Bowers Field is a county-owned, public-use airport in Kittitas County, Washington, United States. It is located two nautical miles (4 km) north of the central business district of Ellensburg, Washington. This airport is included in the National Plan of Integrated Airport Systems for 2011–2015, which categorized it as a general aviation facility.

Gambell Army Airfield is a former United States Army airfield located in Gambell, a city in the Nome Census Area of the U.S. state of Alaska.

Northway Army Airfield is a former United States Army airfield located in Northway, a community located in the Southeast Fairbanks Census Area of the U.S. state of Alaska. During World War II for northbound Lend-Lease aircraft on the Northwest Staging Route, the flight strip at Northway was the first stop in the Territory of Alaska.. It is now the state owned Northway Airport.
The West Coast Wing (WCW) is an inactive United States Air Force unit. Its last assignment was with the Pacific Division, Air Transport Command, headquartered at Fairfield-Suisun Air Force Base, California. It was inactivated on 30 September 1946.

Joint Base Elmendorf–Richardson is a United States military facility in Anchorage, the largest city in Alaska. It is an amalgamation of the United States Air Force's Elmendorf Air Force Base and the United States Army's Fort Richardson, which were merged in 2010.
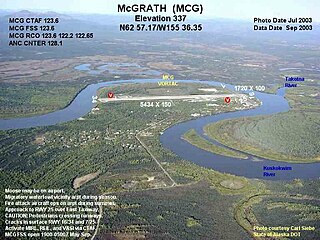
McGrath Army Airbase is former United States Army airbase located in McGrath, a city in the Yukon-Koyukuk Census Area of the U.S. state of Alaska.

Moses Point Army Airfield is a former United States Army airfield located in Elim, a city in the Nome Census Area of the U.S. state of Alaska.

Bethel Air Base is a former United States Army airfield located three nautical miles (6 km) southwest of the central business district of Bethel, a city in the Bethel Census Area of the U.S. state of Alaska.






















