In mathematics, the tensor product of two vector spaces V and W is a vector space to which is associated a bilinear map that maps a pair to an element of denoted
In mathematics, a Clifford algebra is an algebra generated by a vector space with a quadratic form, and is a unital associative algebra. As K-algebras, they generalize the real numbers, complex numbers, quaternions and several other hypercomplex number systems. The theory of Clifford algebras is intimately connected with the theory of quadratic forms and orthogonal transformations. Clifford algebras have important applications in a variety of fields including geometry, theoretical physics and digital image processing. They are named after the English mathematician William Kingdon Clifford (1845–1879).
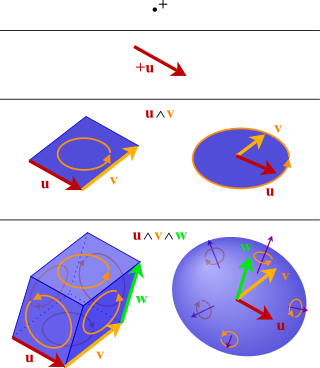
In mathematics, the exterior product or wedge product of vectors is an algebraic construction used in geometry to study areas, volumes, and their higher-dimensional analogs. The exterior product of two vectors u and v, denoted by u ∧ v, is called a bivector and lives in a space called the exterior square, a vector space that is distinct from the original space of vectors. The magnitude of u ∧ v can be interpreted as the area of the parallelogram with sides u and v, which in three dimensions can also be computed using the cross product of the two vectors. Like the cross product, the exterior product is anticommutative, meaning that u ∧ v = −(v ∧ u) for all vectors u and v, but, unlike the cross product, the exterior product is associative. One way to visualize a bivector is as a family of parallelograms all lying in the same plane, having the same area and orientation, which is a choice of rotational direction within the plane (clockwise or counterclockwise from some view).
The Fock space is an algebraic construction used in quantum mechanics to construct the quantum states space of a variable or unknown number of identical particles from a single particle Hilbert space H. It is named after V. A. Fock who first introduced it in his 1932 paper "Konfigurationsraum und zweite Quantelung".
In mathematics, a Lie superalgebra is a generalisation of a Lie algebra to include a Z2‑grading. Lie superalgebras are important in theoretical physics where they are used to describe the mathematics of supersymmetry. In most of these theories, the even elements of the superalgebra correspond to bosons and odd elements to fermions.
In mathematics, the Hodge star operator or Hodge star is a linear map defined on the exterior algebra of a finite-dimensional oriented vector space endowed with a nondegenerate symmetric bilinear form. Applying the operator to an element of the algebra produces the Hodge dual of the element. This map was introduced by W. V. D. Hodge.
In mathematics, particularly homological algebra, an exact functor is a functor that preserves short exact sequences. Exact functors are convenient for algebraic calculations because they can be directly applied to presentations of objects. Much of the work in homological algebra is designed to cope with functors that fail to be exact, but in ways that can still be controlled.
In mathematics, the symmetric algebraS(V) (also denoted Sym(V)) on a vector space V over a field K is a commutative algebra over K that contains V, and is, in some sense, minimal for this property. Here, "minimal" means that S(V) satisfies the following universal property: for every linear map f from V to a commutative algebra A, there is a unique algebra homomorphism g : S(V) → A such that f = g ∘ i, where i is the inclusion map of V in S(V).
In linear algebra and functional analysis, the partial trace is a generalization of the trace. Whereas the trace is a scalar valued function on operators, the partial trace is an operator-valued function. The partial trace has applications in quantum information and decoherence which is relevant for quantum measurement and thereby to the decoherent approaches to interpretations of quantum mechanics, including consistent histories and the relative state interpretation.
In mathematics, nuclear operators between Banach spaces are a linear operators between Banach spaces in infinite dimensions that share some of the properties of their counter-part in finite dimension. In Hilbert spaces such operators are usually called trace class operators and one can define such things as the trace. In Banach spaces this is no longer possible for general nuclear operators, it is however possible for -nuclear operator via the Grothendieck trace theorem.
In mathematics, nuclear spaces are topological vector spaces that can be viewed as a generalization of finite dimensional Euclidean spaces and share many of their desirable properties. Nuclear spaces are however quite different from Hilbert spaces, another generalization of finite dimensional Euclidean spaces. They were introduced by Alexander Grothendieck.
In mathematics, Milnor K-theory is an algebraic invariant defined by John Milnor as an attempt to study higher algebraic K-theory in the special case of fields. It was hoped this would help illuminate the structure for algebraic K-theory and give some insight about its relationships with other parts of mathematics, such as Galois cohomology and the Grothendieck–Witt ring of quadratic forms. Before Milnor K-theory was defined, there existed ad-hoc definitions for and . Fortunately, it can be shown Milnor K-theory is a part of algebraic K-theory, which in general is the easiest part to compute.
In mathematics, the tensor product of modules is a construction that allows arguments about bilinear maps to be carried out in terms of linear maps. The module construction is analogous to the construction of the tensor product of vector spaces, but can be carried out for a pair of modules over a commutative ring resulting in a third module, and also for a pair of a right-module and a left-module over any ring, with result an abelian group. Tensor products are important in areas of abstract algebra, homological algebra, algebraic topology, algebraic geometry, operator algebras and noncommutative geometry. The universal property of the tensor product of vector spaces extends to more general situations in abstract algebra. The tensor product of an algebra and a module can be used for extension of scalars. For a commutative ring, the tensor product of modules can be iterated to form the tensor algebra of a module, allowing one to define multiplication in the module in a universal way.
In mathematics, a metric connection is a connection in a vector bundle E equipped with a bundle metric; that is, a metric for which the inner product of any two vectors will remain the same when those vectors are parallel transported along any curve. This is equivalent to:
In mathematics, a Pfister form is a particular kind of quadratic form, introduced by Albrecht Pfister in 1965. In what follows, quadratic forms are considered over a field F of characteristic not 2. For a natural number n, an n-fold Pfister form over F is a quadratic form of dimension 2n that can be written as a tensor product of quadratic forms
In mathematics, specifically in symplectic topology and algebraic geometry, a quantum cohomology ring is an extension of the ordinary cohomology ring of a closed symplectic manifold. It comes in two versions, called small and big; in general, the latter is more complicated and contains more information than the former. In each, the choice of coefficient ring significantly affects its structure, as well.
In number theory, the Néron–Tate height is a quadratic form on the Mordell–Weil group of rational points of an abelian variety defined over a global field. It is named after André Néron and John Tate.
In mathematics, the spin representations are particular projective representations of the orthogonal or special orthogonal groups in arbitrary dimension and signature. More precisely, they are two equivalent representations of the spin groups, which are double covers of the special orthogonal groups. They are usually studied over the real or complex numbers, but they can be defined over other fields.
In mathematics, Hochschild homology (and cohomology) is a homology theory for associative algebras over rings. There is also a theory for Hochschild homology of certain functors. Hochschild cohomology was introduced by Gerhard Hochschild (1945) for algebras over a field, and extended to algebras over more general rings by Henri Cartan and Samuel Eilenberg (1956).
In mathematics, a noncommutative ring is a ring whose multiplication is not commutative; that is, there exist a and b in the ring such that ab and ba are different. Equivalently, a noncommutative ring is a ring that is not a commutative ring.











