
Organometallic chemistry is the study of organometallic compounds, chemical compounds containing at least one chemical bond between a carbon atom of an organic molecule and a metal, including alkali, alkaline earth, and transition metals, and sometimes broadened to include metalloids like boron, silicon, and selenium, as well. Aside from bonds to organyl fragments or molecules, bonds to 'inorganic' carbon, like carbon monoxide, cyanide, or carbide, are generally considered to be organometallic as well. Some related compounds such as transition metal hydrides and metal phosphine complexes are often included in discussions of organometallic compounds, though strictly speaking, they are not necessarily organometallic. The related but distinct term "metalorganic compound" refers to metal-containing compounds lacking direct metal-carbon bonds but which contain organic ligands. Metal β-diketonates, alkoxides, dialkylamides, and metal phosphine complexes are representative members of this class. The field of organometallic chemistry combines aspects of traditional inorganic and organic chemistry.

Nickel(II) chloride (or just nickel chloride) is the chemical compound NiCl2. The anhydrous salt is yellow, but the more familiar hydrate NiCl2·6H2O is green. Nickel(II) chloride, in various forms, is the most important source of nickel for chemical synthesis. The nickel chlorides are deliquescent, absorbing moisture from the air to form a solution. Nickel salts have been shown to be carcinogenic to the lungs and nasal passages in cases of long-term inhalation exposure.
In organic chemistry, hydrocyanation is a process for conversion of alkenes to nitriles. The reaction involves the addition of hydrogen cyanide and requires a catalyst. This conversion is conducted on an industrial scale for the production of precursors to nylon.

Nickelocene is the organonickel compound with the formula Ni(η5-C5H5)2. Also known as bis(cyclopentadienyl)nickel or NiCp2, this bright green paramagnetic solid is of enduring academic interest, although it does not yet have any known practical applications.
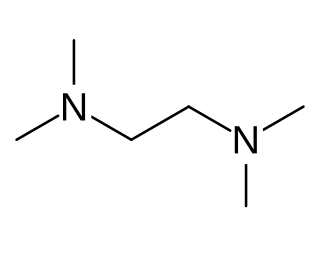
Tetramethylethylenediamine (TMEDA or TEMED) is a chemical compound with the formula (CH3)2NCH2CH2N(CH3)2. This species is derived from ethylenediamine by replacement of the four amine hydrogens with four methyl groups. It is a colorless liquid, although old samples often appear yellow. Its odor is similar to that of rotting fish.
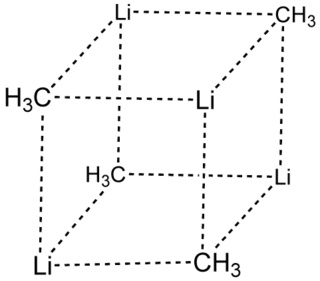
Methyllithium is the simplest organolithium reagent with the empirical formula CH3Li. This s-block organometallic compound adopts an oligomeric structure both in solution and in the solid state. This highly reactive compound, invariably used in solution with an ether as the solvent, is a reagent in organic synthesis as well as organometallic chemistry. Operations involving methyllithium require anhydrous conditions, because the compound is highly reactive toward water. Oxygen and carbon dioxide are also incompatible with MeLi. Methyllithium is usually not prepared, but purchased as a solution in various ethers.
Bioorganometallic chemistry is the study of biologically active molecules that contain carbon directly bonded to metals or metalloids. The importance of main-group and transition-metal centers has long been recognized as important to the function of enzymes and other biomolecules. However, only a small subset of naturally-occurring metal complexes and synthetically prepared pharmaceuticals are organometallic; that is, they feature a direct covalent bond between the metal(loid) and a carbon atom. The first, and for a long time, the only examples of naturally occurring bioorganometallic compounds were the cobalamin cofactors (vitamin B12) in its various forms. In the 21st century, discovery of new systems containing carbon-metal bonds in biology, bioorganometallic chemistry is rapidly emerging as a distinct subdiscipline of bioinorganic chemistry that straddles organometallic chemistry and biochemistry. Naturally occurring bioorganometallics include enzymes and sensor proteins. Also within this realm are synthetically prepared organometallic compounds that serve as new drugs and imaging agents (technetium-99m sestamibi) as well as the principles relevant to the toxicology of organometallic compounds (e.g., methylmercury). Consequently, bioorganometallic chemistry is increasingly relevant to medicine and pharmacology.

Organonickel chemistry is a branch of organometallic chemistry that deals with organic compounds featuring nickel-carbon bonds. They are used as a catalyst, as a building block in organic chemistry and in chemical vapor deposition. Organonickel compounds are also short-lived intermediates in organic reactions. The first organonickel compound was nickel tetracarbonyl Ni(CO)4, reported in 1890 and quickly applied in the Mond process for nickel purification. Organonickel complexes are prominent in numerous industrial processes including carbonylations, hydrocyanation, and the Shell higher olefin process.
In chemistry, carbonylation refers to reactions that introduce carbon monoxide (CO) into organic and inorganic substrates. Carbon monoxide is abundantly available and conveniently reactive, so it is widely used as a reactant in industrial chemistry. The term carbonylation also refers to oxidation of protein side chains.

In organometallic chemistry, a metallacycle is a derivative of a carbocyclic compound wherein a metal has replaced at least one carbon center; this is to some extent similar to heterocycles. Metallacycles appear frequently as reactive intermediates in catalysis, e.g. olefin metathesis and alkyne trimerization. In organic synthesis, directed ortho metalation is widely used for the functionalization of arene rings via C-H activation. One main effect that metallic atom substitution on a cyclic carbon compound is distorting the geometry due to the large size of typical metals.

Bis(cyclooctadiene)nickel(0) is the organonickel compound with the formula Ni(C8H12)2, also written Ni(cod)2. It is a diamagnetic coordination complex featuring tetrahedral nickel(0) bound to the alkene groups in two 1,5-cyclooctadiene ligands. This highly air-sensitive yellow solid is a common source of Ni(0) in chemical synthesis.
Organosodium chemistry is the chemistry of organometallic compounds containing a carbon to sodium chemical bond. The application of organosodium compounds in chemistry is limited in part due to competition from organolithium compounds, which are commercially available and exhibit more convenient reactivity.
Organoplatinum chemistry is the chemistry of organometallic compounds containing a carbon to platinum chemical bond, and the study of platinum as a catalyst in organic reactions. Organoplatinum compounds exist in oxidation state 0 to IV, with oxidation state II most abundant. The general order in bond strength is Pt-C (sp) > Pt-O > Pt-N > Pt-C (sp3). Organoplatinum and organopalladium chemistry are similar, but organoplatinum compounds are more stable and therefore less useful as catalysts.

Nickel(II) bis(acetylacetonate) is a coordination complex with the formula [Ni(acac)2]3, where acac is the anion C5H7O2− derived from deprotonation of acetylacetone. It is a dark green paramagnetic solid that is soluble in organic solvents such as toluene. It reacts with water to give the blue-green diaquo complex Ni(acac)2(H2O)2.

Transition metal benzyne complexes are organometallic complexes that contain benzyne ligands (C6H4). Unlike benzyne itself, these complexes are less reactive although they undergo a number of insertion reactions.

Transition metal alkyl complexes are coordination complexes that contain a bond between a transition metal and an alkyl ligand. Such complexes are not only pervasive but are of practical and theoretical interest.
In organic chemistry, hydrovinylation is the formal insertion of an alkene into the C-H bond of ethylene. The more general reaction, hydroalkenylation, is the formal insertion of an alkene into the C-H bond of any terminal alkene. The reaction is catalyzed by metal complexes. A representative reaction is the conversion of styrene and ethylene to 3-phenybutene:
Organonickel(IV) complex are organonickel compounds that feature nickel in the +4 oxidation state. These high-valent nickel compounds are intermediates or models thereof for various catalytic reactions.

(Trimethylsilyl)methyllithium is classified both as an organolithium compound and an organosilicon compound. It has the empirical formula LiCH2Si(CH3)3, often abbreviated LiCH2tms. It crystallizes as the hexagonal prismatic hexamer [LiCH2tms]6, akin to some polymorphs of methyllithium. Many adducts have been characterized including the diethyl ether complexed cubane [Li4(μ3-CH2tms)4(Et2O)2] and [Li2(μ-CH2tms)2(tmeda)2].

Bis(allyl)nickel is an organonickel compound with the formula Ni(η3-C3H5)2. The molecule consists of two allyl ligands bound to nickel(II). It has inversion symmetry. It is a volatile yellow liquid.













