Related Research Articles
The internal capsule is a white matter structure situated in the inferomedial part of each cerebral hemisphere of the brain. It carries information past the basal ganglia, separating the caudate nucleus and the thalamus from the putamen and the globus pallidus. The internal capsule contains both ascending and descending axons, going to and coming from the cerebral cortex. It also separates the caudate nucleus and the putamen in the dorsal striatum, a brain region involved in motor and reward pathways.

The trapezoid body or ventral acoustic stria is a structure in the pontine tegmentum formed by the crossing-over (decussation) of a portion of the efferent second-order fibers of the ventral cochlear nucleus. After decussating, some of these fibres proceed to ascend in the contralateral lateral lemniscus to reach and terminate in the dorsal nucleus of lateral lemniscus, and inferior colliculus.

The pontine nuclei are all neurons of the ventral pons collectively. Corticopontine fibres project from the primary motor cortex to the ipsilateral pontine nucleus; pontocerebellar fibers then relay the information to the contralateral cerebellum via the middle cerebellar peduncle.

In the human body, the lateral thoracic artery is a blood vessel that supplies oxygenated blood to approximately one-third of the lateral structures of the thorax and breast.

The anterior choroidal artery is a bilaterally paired artery of the brain. It is typically a branch of the internal carotid artery which supplies the choroid plexus of lateral ventricle and third ventricle as well as numerous structures of the brain.

The inferior phrenic artery is a bilaterally paired artery of the abdominal cavity which represents the main source of arterial supply to the diaphragm. Each artery usually arises either from the coeliac trunk or the abdominal aorta, however, their origin is highly variable and the different sites of origin are different for the left artery and right artery. The superior suprarenal artery is a branch of the inferior phrenic artery.

The right colic artery is an artery of the abdomen, a branch of the superior mesenteric artery supplying the ascending colon. It divides into two terminal branches - an ascending branch and a descending branch - which form anastomoses with the middle colic artery, and ileocolic artery (respectively).

The deep auricular artery is a branch of the maxillary artery. The deep auricular artery pierces the external acoustic meatus. It provides arterial supply to the skin of the external acoustic meatus, and contributes arterial supply to the tympanic membrane, and the temporomandibular joint.

The artery to the ductus deferens is an artery in males that provides blood to the ductus deferens.

The inferior cervical ganglion is one of the three cervical sympathetic ganglia. It is situated between the base of the transverse process of the last cervical vertebra and the neck of the first rib, on the medial side of the costocervical artery.

The deep circumflex iliac vein is formed by the union of the venae comitantes of the deep iliac circumflex artery. It drains venous blood from the walls of the iliac fossa. It empties into the external iliac vein about 2 cm superior to the inguinal ligament, just distal to where the inferior epigastric vein does so. The DCIV runs across the external iliac artery. It forms anastomoses with the iliolumbar vein, and lower two lumbar veins.

The posteromedial central arteries or paramedian arteries (also are branches of the posterior cerebral artery, and posterior communicating artery. They entering the substance of the brain through the posterior perforated substance. They supply a large portion of the diencephalon as well as some subcortical telencephalic structures.

The ventral posteromedial nucleus (VPM) is a nucleus of the thalamus and serves an analogous somatosensory relay role for the ascending trigeminothalamic tracts as its lateral neighbour the ventral posterolateral nucleus serves for dorsal column–medial lemniscus pathway 2nd-order neurons.

The anterolateral central arteries or lenticulostriate arteries are a group of small arteries mostly arising from the middle cerebral artery that enter the brain through the anterior perforated substance to provide arterial supply to parts of the basal ganglia. They are end arteries.

The supraduodenal artery are 1-2 small arteries which usually arise from the gastroduodenal artery, and sometimes from the posterior superior pancreaticoduodenal arteries, or common hepatic artery. They provide arterial supply to the anterosuperior portion of the proximal duodenum.
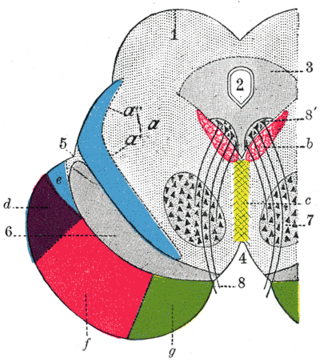
Corticopontine fibers are projections from the cerebral cortex to the pontine nuclei of the ventral pons. They represent the first link in a cortico-cerebello-cortical pathway mediating neocerebellar control of the motor cortex. The pathway is especially important for voluntary movements.

The lateral posterior nucleus is a nucleus of the thalamus. It represents the rostral continuation of the pulvinar. It is thought to be involved in complex sensory integration.
Perihypoglossal nuclei are three prominent groups of neurons in the caudal medulla oblongata near the hypoglossal nucleus: the nucleus prepositus hypoglossi, intercalated nucleus, and sublingual nucleus. They are involved in controlling eye movements: they send their principal projections to the three cranial nerve nuclei controlling extrinsic eye muscles via the medial longitudinal fasciculus.
The thalamoperforating arteries are posteromedial central arteries which supply parts of the thalamus.

Posterolateral central arteries are arteries that arise from the posterior cerebral artery distal to its first - pre-communicating (P1) -segment.
References
- 1 2 3 4 "Thalamogeniculate artery - Dictionnaire médical de l'Académie de Médecine". www.academie-medecine.fr. Retrieved 2024-07-02.
- 1 2 3 4 Standring, Susan (2020). Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice (42th ed.). New York: Elsevier. p. 419. ISBN 978-0-7020-7707-4. OCLC 1201341621.
- ↑ Waschke, Jens; Böckers, Tobias M.; Paulsen, Friedrich; Arnold, Wolfgang; Bechmann, Ingo, eds. (2018). Sobotta Anatomy Textbook: English Edition with Latin Nomenclature (1st ed.). München: Elsevier. p. 660. ISBN 978-0-7020-6760-0.