
The Mall is a ceremonial route and roadway in the City of Westminster, central London, that travels 1 kilometre (0.62 mi) between Buckingham Palace at its western end and Trafalgar Square via Admiralty Arch to the east. Along the north side of The Mall is green space and St. James's Palace with other official buildings, and to the south is St James's Park. Near the east end at Trafalgar Square and Whitehall it is met by Horse Guards Road and Spring Gardens, near the west end at the Victoria Memorial it is met by the Constitution Hill roadway and the Spur Road to the street of Buckingham Gate. It is closed to traffic on Saturdays, Sundays, public holidays and on ceremonial occasions.

Greenwich Park is a former hunting park in Greenwich and one of the largest single green spaces in south-east London. One of the Royal Parks of London, and the first to be enclosed, it covers 74 hectares, and is part of the Greenwich World Heritage Site. Surrounding the hilltop Royal Observatory and straddling the Greenwich Prime Meridian, it commands elevated views over the River Thames, the Isle of Dogs and the City of London.

Blackfriars Railway Bridge is a railway bridge crossing the River Thames in London, between Blackfriars Bridge and the Millennium Bridge.

Cheapside is a street in the City of London, the historic and modern financial centre of London, England, which forms part of the A40 London to Fishguard road. It links St Martin's Le Grand with Poultry. Near its eastern end at Bank junction, where it becomes Poultry, is Mansion House, the Bank of England, and Bank station. To the west is St Paul's Cathedral, St Paul's tube station and square.

Cannon Street is a road in the City of London, the historic nucleus of London and its modern financial centre. It runs roughly parallel with the River Thames, about 250 metres (820 ft) north of it, in the north of the City.

Gracechurch Street is a main road in the City of London, the historic and financial centre of London, England, which is designated the A1213.

Eastcheap is a street in central London that is a western continuation of Great Tower Street towards Monument junction. Its name derives from cheap, the Old English word for market, with the prefix 'East' distinguishing it from Westcheap, another former market street that today is called Cheapside.

Fenchurch Street is a street in London, England, linking Aldgate at its eastern end with Lombard Street and Gracechurch Street in the west. It is a well-known thoroughfare in the City of London financial district and is the site of many corporate offices and headquarters. The name "Fenchurch" means "church in the fenny or marshy ground" and presumably refers to St Gabriel Fenchurch, which stood at the junction of Fenchurch Street and Cullum Street until it was destroyed by the Great Fire.

Cornhill is a ward and street in the City of London, the historic nucleus and financial centre of modern London, England. The street runs between Bank Junction and Leadenhall Street.

Northumberland Avenue is a street in the City of Westminster, Central London, running from Trafalgar Square in the west to the Thames Embankment in the east. The road was built on the site of Northumberland House, the London home of the Percy family, the Dukes of Northumberland between 1874 and 1876, and on part of the parallel Northumberland Street.

Birdcage Walk is a street in the City of Westminster in London. It runs east–west as a continuation of Great George Street, from the crossroads with Horse Guards Road and Storey's Gate, with the Treasury building and the Institution of Mechanical Engineers on the northeast corner, to a junction with Buckingham Gate, at the southeast corner of Buckingham Palace. St. James's Park lies to the north, whilst to the south are the backs of buildings on Old Queen Street, Queen Anne's Gate and Petty France, and, at the western end, the Wellington Barracks of the Brigade of Guards.
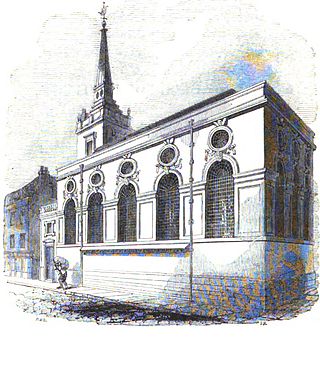
St. Michael Queenhithe was a church in the City of London located in what is now Upper Thames Street. First recorded in the 12th century, the church was destroyed during the Great Fire of London in 1666. Rebuilt by the office of Sir Christopher Wren, it was demolished in 1876.

Puddle Dock is a street in Blackfriars in the City of London. It was once the site of one of London's docks, and was later the site of the Mermaid Theatre. The dock was filled in during redevelopment in the 1960s and 1970s.

Great Tower Street, originally known just as Tower Street, is a street in the City of London, the historic nucleus and modern financial centre of London, England. It forms an eastern continuation of Eastcheap starting at Idol Lane, and leads towards Byward Street and Tower Hill. On Byward Street, opposite Great Tower Street, is the historic church All Hallows-by-the-Tower.

Queen Victoria Street, named after the British monarch who reigned from 1837 to 1901, is a street in London which runs east by north from its junction with New Bridge Street and Victoria Embankment in the Castle Baynard ward of the City of London, along a section that divides the wards of Queenhithe and Bread Street, then lastly through the middle of Cordwainer ward, until it reaches Mansion House Street at Bank junction. Beyond Bank junction, the street continues north-east as Threadneedle Street which joins Bishopsgate. Other streets linked to Queen Victoria Street include Puddle Dock, Cannon Street, Walbrook and Poultry.

Suffolk Place was a mansion house located on the west side of Borough High Street in Southwark, Surrey, on the south bank of the River Thames opposite the City of London. It was the London town house of the Dukes of Suffolk, and was located near Winchester Palace, London seat of the Bishop of Winchester. The position was highly prominent as Borough High Street was the principal thoroughfare leading from London Bridge and the City of London, to Canterbury and Dover, a route used by monarchs and others, including the pilgrims in Chaucer's Canterbury Tales. It was built in the fifteenth century and rebuilt in fine Renaissance style in 1522 by Charles Brandon, 1st Duke of Suffolk (c.1484-1545) a favourite of King Henry VIII. On 4 February 1536 it was taken over by King Henry VIII who exchanged it with Brandon for Norwich Place on the Strand, on the north side of the Thames, nearer to the Palace of Westminster.

Byward Street is a road in the City of London, the historic and financial centre of London. It forms part of the A3211 route and, if travelling eastward, is a short continuation of Lower Thames Street from a junction with Great Tower Street, to Tower Hill. It is located within the City ward of Tower.

The 2012 Olympic Marathon Course is that of both the men's and women's marathon races at the 2012 Olympic and Paralympic Games in London.

Queen Street is a street in the City of London which runs between Upper Thames Street at its southern end to Cheapside in the north. The thoroughfares of Queen Street and King Street were newly laid out, cutting across more ancient routes in the City, following the Great Fire of London in 1666; they were the only notable new streets following the fire's destruction of much of the City.

Coldharbour, also spelled Cold Harbour, Cold Harborough, Cold Herbergh, Cold Herberge, and Cold Inn, were two London neighbouring estates in the since dissolved parishes of All-Hallows-the-Less and All-Hallows-the-Great, in today's Dowgate Ward of the City of London. From the 13th century to the mid-17th century Coldharbour occupied the area between Upper Thames Street and the Thames to the east of Cannon Street station. It was destroyed in the Great Fire of 1666. One of the estates was used by the Dukes of Exeter and briefly as a college of heralds.





















