
The USS Queen of the West was a sidewheel steamer ram ship and the flagship of the United States Ram Fleet and the Mississippi Marine Brigade. It was built at Cincinnati, Ohio in 1854. It served as a commercial steamer until purchased by Colonel Charles Ellet Jr. in 1862 and converted for use as a ram ship. The ship operated in conjunction with the Mississippi River Squadron during the Union brown-water navy battle against the Confederate River Defense Fleet for control of the Mississippi River and its tributaries during the American Civil War.

Laurent Millaudon was a wooden side-wheel river steamboat launched at Cincinnati, Ohio, in 1856 operating in the New Orleans, Louisiana, area, and captained by W. S. Whann. At the beginning of the American Civil War she was taken into service by the Confederate Navy as CSS General Sterling Price. On 6 June 1862, she was sunk at the Battle of Memphis. She was raised and repaired by the Union army, and on 16 June 1862 was moved into Union service as USS General Price and served until the end of the war.

The United States Ram Fleet was a Union Army unit of steam powered ram ships during the American Civil War. The unit was independent of the Union Army and Navy and reported directly to the Secretary of War, Edwin M. Stanton. The ram fleet operated in coordination with the Mississippi River Squadron during the Union brown-water navy battle against the Confederate River Defense Fleet for control of the Mississippi River and its tributaries.
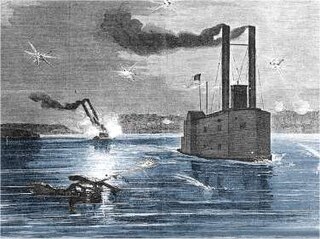
USS Lancaster was a sidewheel civilian steamer tow boat built in 1855 at Cincinnati. It was originally named Lancaster Number 3 then Kosciusko. In March through May 1862, she was purchased and converted to a ram by Colonel Charles Ellet Jr. to serve during the American Civil War as part of the United States Ram Fleet and the Mississippi Marine Brigade.
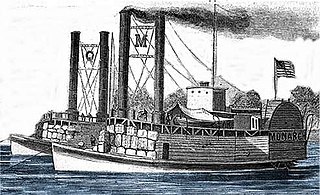
USS Monarch was a United States Army sidewheel ram that saw service in the American Civil War as part of the United States Ram Fleet and the Mississippi Marine Brigade. She operated on the Mississippi River and Yazoo River during 1862 and 1863.

The Battle of Forts Jackson and St. Philip was the decisive battle for possession of New Orleans in the American Civil War. The two Confederate forts on the Mississippi River south of the city were attacked by a Union Navy fleet. As long as the forts could keep the Federal forces from moving on the city, it was safe, but if they were negated, there were no fall-back positions to impede the Union advance.

The City-class ironclad USS Cincinnati was a stern-wheel casemate gunboat in the United States Navy during the American Civil War. She was named for Cincinnati, Ohio, and was the first ship to bear that name in the United States Navy.

USS General Bragg (1851) was a heavy (1,043-ton) steamer captured by Union Navy forces during the American Civil War. She was outfitted as a U.S. Navy gunboat and was assigned to enforce the Union blockade of the waterways of the Confederate States of America.

USS Mound City was a City-class ironclad gunboat built for service on the Mississippi River and its tributaries in the American Civil War. Originally commissioned as part of the Union Army's Western Gunboat Flotilla, she remained in that service until October 1862. Then the flotilla was transferred to the Navy and she became part of the Mississippi River Squadron, where she remained until the end of the war.

The CSS General Earl Van Dorn, a side-wheel river steamer, was fitted out in early 1862 at New Orleans, Louisiana as a River Defense Fleet "cottonclad" ram. It was named for Confederate general Earl Van Dorn, born and raised in Mississippi.

CSS Colonel Lovell was a cotton-clad ram ship of the Confederate States Navy during the American Civil War

The first USS Mingo, a stern-wheel steamer built at California, Pennsylvania, in 1859 and used to tow coal barges, was purchased at Pittsburgh by Colonel Charles Ellet Jr. in April 1862 for usage in the U.S. Ram Fleet during the American Civil War.

Seth Ledyard Phelps was an American naval officer, and in later life, a politician and diplomat. Phelps received his first commission in United States Navy as a midshipman aboard the famous USS Independence. He served patrolling the coast of West Africa guarding against slavers. During the Mexican–American War he served on gunboats, giving support to Winfield Scott's army, and later served in the Mediterranean and Caribbean squadrons.

Little Rebel was a cotton-clad ram that had been converted from a Mississippi River steamer to serve as the flagship of the Confederate River Defense Fleet in the American Civil War. Sent from New Orleans to defend against the Federal descent of the Mississippi, she was among the force that engaged vessels of the Union Army's Western Gunboat Flotilla at the Battle of Plum Point Bend on May 10, 1862. On June 6, she again was involved in an action with the Federal gunboats, this time at the Battle of Memphis. In the battle, a shot from a Federal gun pierced her boiler, disabling her, and she was then pushed aground by the Federal ram USS Monarch and captured.

USS New Era (1862) was a steamer acquired by the Union Navy during the American Civil War. She was used by the Union Navy as a gunboat in support of the Union Navy blockade of Confederate waterways. New Era was also a name initially carried by a timbercladUSS Essex.

USS Sumter was a 525-ton sidewheel paddle steamer captured by the Union Navy during the Union blockade of the American Civil War.

The River Defense Fleet was a set of fourteen vessels in Confederate service, intended to assist in the defense of New Orleans in the early days of the American Civil War. All were merchant ships or towboats that were seized by order of the War Department in Richmond and converted into warships by arming each with one or two guns, protecting their engines by an interior bulkhead, and strengthening their bows so they could be used as rams. Although they were nominally a part of the Confederate States Army, all of their officers and most of their crews were civilians. A portion of the fleet was retained in the south part of the Mississippi River and a portion was sent north to defend against Union movement from the north.

The Pook Turtles, or City-class gunboats to use their semi-official name, were war vessels intended for service on the Mississippi River during the American Civil War. They were also sometimes referred to as "Eads gunboats." The labels are applied to seven vessels of uniform design built from the keel up in Carondelet, Missouri shipyards owned by James Buchanan Eads. Eads was a wealthy St. Louis industrialist who risked his fortune in support of the Union.

CSS General Beauregard was a cottonclad sidewheel ram of the Confederate Navy during the American Civil War.
CSS General M. Jeff Thompson was a cotton-clad sidewheel ram of the Confederate Navy during the American Civil War.


















