Related Research Articles

Shagnasty Island is a small, rocky ice-free island lying 0.3 miles (0.5 km) west of Lenton Point in the north part of Clowes Bay, close off the south coast of Signy Island in the South Orkney Islands. Roughly charted in 1933 by Discovery Investigations personnel, and surveyed in 1947 by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS). The name, applied by FIDS, arose from the unpleasant state of the island due to its occupation by a large colony of blue-eyed shags.

Worswick Hill is a rounded summit, 36 km, at the west end of Brisbane Heights on Coronation Island, in the South Orkney Islands. The peak appears on some early charts of the South Orkney Islands but is not accurately located. It was roughly surveyed by DI personnel in 1933 and resurveyed by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS) in 1948–49. Named by the United Kingdom Antarctic Place-Names Committee (UK-APC) for Robert F. Worswick of the FIDS, meteorologist at Signy Island in 1950 and 1951, who reached this hill during a sledge journey in 1950.

Christoffersen Island is a small island immediately west of the southern end of Powell Island in the South Orkney Islands of Antarctica. The name appears on a chart by Norwegian whaling captain Petter Sorlle, who made a running survey of these islands in 1912–13.
Conroy Point is a headland midway along the northwest side of Moe Island in the South Orkney Islands. It was named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee after James W.H. Conroy, ornithologist on Signy Island, 1967–68.
Fyr Channel is a channel 0.2 nautical miles (0.4 km) wide between the southwest end of Signy Island and Moe Island, in the South Orkney Islands. The name "Fyr Strait" appears on a manuscript chart drawn by Captain Petter Sorlle in 1912, and corrected by Hans Borge in 1913, but the generic term channel is approved because of the small size of this feature. The Corral Whaling Co. of Bergen, a subsidiary of Messrs. Christensen and Co., Corral, Chile, operated the steam whaler Fyr in the South Orkney Islands in 1912–13.
Ellefsen Harbour is a harbour lying at the south end of Powell Island between Christoffersen Island and Michelsen Island, in the South Orkney Islands. It was discovered in the course of a joint cruise by Captain George Powell, a British sealer, and Captain Nathaniel Palmer, an American sealer, in December 1821. Shortly afterward, it was briefly occupied by Sam Pointer. The name first appeared on Powell's chart published in 1822.
Falkland Harbour is a harbour along the southwest side of Powell Island in the South Orkney Islands. It was charted by Norwegian whaling captain Petter Sorlle in 1912–13, and named for the floating whale factory Falkland which was badly damaged while entering the harbour in the 1912–13 season.
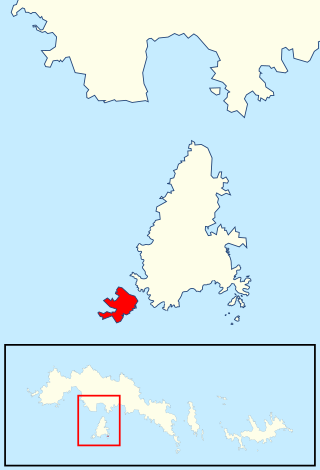
Moe Island is an island 2 km (1.2 mi) long in the South Orkney Islands off Antarctica, separated from the south-west end of Signy Island by Fyr Channel. It was charted by Captain Petter Sørlle in 1912–13, and named after M. Thoralf Moe of Sandefjord, Norway, a contemporary whaling captain who worked in this area. The northernmost point of the island is Spaull Point, named by United Kingdom Antarctic Place-Names Committee (UK-APC) after Vaughan W. Spaull, British Antarctic Survey (BAS) biologist on Signy Island, 1969.

Fredriksen Island is an island 5 km (3.1 mi) long and 1 km (0.62 mi) wide, lying 1 km south-east of Powell Island in the South Orkney Islands of Antarctica. It was discovered by Captains Nathaniel Palmer and George Powell in the course of their joint cruise in December 1821. It was named by Norwegian whaling captain Petter Sorlle, who made a running survey of the island in the 1912–13 summer.
Garnet Hill is a rocky hill, 230 metres (750 ft) high, rising above the east side of McLeod Glacier in the south part of Signy Island, in the South Orkney Islands. It forms the south end of a line of rock and ice cliffs which separate McLeod Glacier from Orwell Glacier. It was so named by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey, following their survey of 1947, because of the abundance of garnets found there.

Gerd Island is an island 1 nautical mile (2 km) west-southwest of Stene Point at the east side of the entrance to Norway Bight, off the south coast of Coronation Island in the South Orkney Islands. It was charted and named by Norwegian whaling captain Petter Sorlle, who made a running survey of the South Orkney Islands in 1912–13.
The Gneiss Hills are two prominent hills, 270 and 260 metres high, at the west side of McLeod Glacier in the south part of Signy Island, in the South Orkney Islands, Antarctica. They were so named by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey, following their survey of 1947, because of a band of pink gneiss outcrops near the summits.
Graptolite Island is an island 0.8 km (0.50 mi) long in the north-east part of Fitchie Bay, lying off the south-east portion of Laurie Island in the South Orkney Islands of Antarctica. James Weddell's chart published in 1825 shows two islands in essentially this position. Existence of a single island was determined in 1903 by the Scottish National Antarctic Expedition under William Speirs Bruce, who so named it because what were thought to be graptolite fossils were found there. Later analysis showed that the fossils on Graptolite Island were merely the remains of ancient plants.
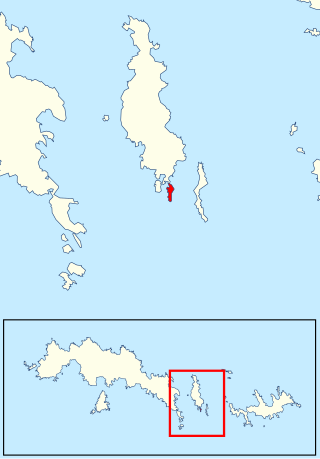
Michelsen Island is a small island in the South Orkney Islands off Antarctica. It is joined to the southern end of Powell Island by a narrow isthmus of occasionally submerged boulders. The island was first observed and roughly mapped in 1821 by Captains George Powell and Nathaniel Palmer. It was named on a map by Captain Petter Sørlle, a Norwegian whaler who made a running survey of the South Orkney Islands in 1912–13.
McLeod Glacier is a glacier 1 nautical mile (2 km) long, flowing in a southeasterly direction into Clowes Bay on the south side of Signy Island, in the South Orkney Islands off Antarctica. It was named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee in 1954 for Michael McLeod, following a survey by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey in 1947. On 12 December 1821, the cutter Beaufoy under McLeod sailed to a position at least 60 nautical miles (110 km) west of the South Orkney Islands, where a chart annotation indicates that land was sighted, possibly Coronation Island.

Matthews Island is the largest of the Robertson Islands in the South Orkney Islands off Antarctica. It lies immediately south-east of Coronation Island, from which it is separated by a narrow channel known as the Divide. Matthews Island was mapped as part of Coronation Island until January 1957 when a Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS) party established its insularity. It was named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee in 1959 for Drummond H. Matthews, a FIDS geologist at Signy Island in 1956.

Mansfield Point is a point marking the east side of the entrance to Norway Bight on the south coast of Coronation Island, in the South Orkney Islands, Antarctica. It was surveyed by Discovery Investigations personnel in 1933 and by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS) in 1948–49. The feature was named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee for Arthur W. Mansfield of the FIDS, a meteorologist at Grytviken, South Georgia, in 1951, and leader, meteorologist and biologist at Signy Island in 1952.
Tilbrook Hill is a hill rising to 70 m between Hillier Moss and Caloplaca Cove in southeast Signy Island, South Orkney Islands. Named by the United Kingdom Antarctic Place-Names Committee (UK-APC) in 1990 after Peter J. Tilbrook, British Antarctic Survey (BAS) terrestrial biologist, 1961-75, who initiated two long-term research sites close to this feature.
Tioga Hill is a rounded summit, 290 m, standing at the west side the head of McLeod Glacier on Signy Island, in the South Orkney Islands. The hill is the highest point on the island. Surveyed in 1947 by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS). Named by the United Kingdom Antarctic Place-Names Committee (UK-APC) in 1954 for the Tioga, owned by Messrs. Christensen and Co., which was one of the first floating factories to flense whales at sea. It was wrecked at nearby Port Jebsen during a gale on February 4, 1913.
Landing Cove is a cove north of Conroy Point on the northwest side of Moe Island in the South Orkney Islands, Antarctica. It was so named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee because the cove provides the only possible landing place for small boats on the island.
References
- ↑ "Antarctica Detail - The Divide". geonames.usgs.gov. Retrieved 15 December 2020.
![]() This article incorporates public domain material from "The Divide (South Orkney Islands)". Geographic Names Information System . United States Geological Survey.
This article incorporates public domain material from "The Divide (South Orkney Islands)". Geographic Names Information System . United States Geological Survey.