Related Research Articles
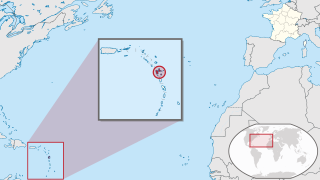
Guadeloupe is an overseas department and region of France in the Caribbean. It consists of six inhabited islands—Basse-Terre, Grande-Terre, Marie-Galante, La Désirade, and two Îles des Saintes—as well as many uninhabited islands and outcroppings. It is south of Antigua and Barbuda and Montserrat and north of Dominica. The capital city is Basse-Terre, on the southern west coast of Basse-Terre Island; the most populous city is Les Abymes and the main centre of business is neighbouring Pointe-à-Pitre, both on Grande-Terre Island. It had a population of 395,726 in 2024.
Soca music, or the "soul of calypso", is a genre of music that originated in Trinidad and Tobago in the 1970s. It is considered an offshoot of calypso, with influences from West African and East Indian rhythms. It was created by Ras Shorty I in an effort to revive traditional calypso, the popularity of which had been declining amongst younger generations in Trinidad due to the rise in popularity of reggae from Jamaica and soul and funk from the United States. From the 1980s onward, soca has developed into a range of new styles.
The music of Trinidad and Tobago is best known for its calypso music, soca music, chutney music, and steelpan. Calypso's internationally noted performances in the 1950s from native artists such as Lord Melody, Lord Kitchener and Mighty Sparrow. The art form was most popularised at that time by Harry Belafonte. Along with folk songs and African- and Indian-based classical forms, cross-cultural interactions have produced other indigenous forms of music including soca, rapso, parang, chutney, and other derivative and fusion styles. There are also local communities which practice and experiment with international classical and pop music, often fusing them with local steelpan instruments.
The music of Guadeloupe encompasses a large popular music industry, which gained in international renown after the success of zouk music in the later 20th century. Zouk's popularity was particularly intense in France, where the genre became an important symbol of identity for Guadeloupe and Martinique. Zouk's origins are in the folk music of Guadeloupe and Martinique, especially Guadeloupan gwo ka and Martinican chouval bwa, and the pan-Caribbean calypso tradition.
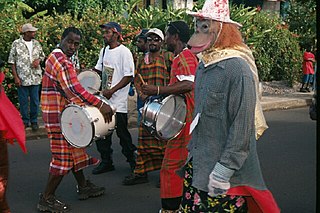
The music of Dominica includes a variety of genres including all the popular genres of the world. Popular music is widespread, with a number of native Dominican performers gaining national fame in imported genres such as calypso, reggae, soca, kompa, zouk and rock and roll. Dominica's own popular music industry has created a form called bouyon, which combines elements from several styles and has achieved a wide fanbase in Dominica. Groups include WCK, Native musicians in various forms, such as reggae, kadans (Ophelia Marie, and calypso, have also become stars at home and abroad.

Eurogliders are a band formed in 1980 in Perth, Western Australia, which included Grace Knight on vocals, Bernie Lynch on guitar and vocals, and Amanda Vincent on keyboards. In 1984, Eurogliders released an Australian top ten album, This Island, which spawned their No. 2 hit single, "Heaven ". "Heaven" also peaked at No. 21 on the United States Billboard Mainstream Rock charts and appeared on the Hot 100. Another Australian top ten album, Absolutely, followed in 1985, which provided two further local top ten singles, "We Will Together" and "Can't Wait to See You". They disbanded in 1989, with Knight having a successful career as a jazz singer. Australian rock music historian Ian McFarlane described Eurogliders as "the accessible face of post-punk new wave music. The band's sophisticated brand of pop was traditional in its structure, but displayed the decidedly 'modern veneer' ". The band reformed in 2005 releasing two new albums followed in 2014 by their seventh album.
Kassav', also alternatively spelled Kassav, is a French Caribbean band that originated from Guadeloupe in 1979. The band's musical style is rooted in the Guadeloupean gwoka rhythm, as well as the Martinican tibwa and Mendé rhythms. Regarded as one of the most influential bands in 20th-century French West Indies music, Kassav is often credited with pioneering the zouk musical genre. Their musical evolution is a synthesis of cadence-lypso and compas traditions.

Compas, also known as konpa or kompa, is a modern méringue dance music genre of Haiti. The genre was popularized by Nemours Jean-Baptiste following the creation of Ensemble Aux Callebasses in 1955, which became Ensemble Nemours Jean-Baptiste in 1957. The frequent tours of the many Haitian bands have cemented the style in all the Caribbean. Therefore, compas is the main music of several countries such as Dominica and the French Antilles. Whether it is called zouk, where French Antilles artists of Martinique and Guadeloupe have taken it, or konpa in places where Haitian artists have toured, this méringue style is influential in part of the Caribbean, Portugal, Cape Verde, France, part of Canada, and South and North America.

The culture of Dominica is formed by the inhabitants of the Commonwealth of Dominica. Dominica is home to a wide range of people. Although it was historically occupied by several native tribes, it was the Taíno and Island Caribs (Kalinago) tribes that remained by the time European settlers reached the island. "Massacre" is a name of a river dedicated to the murders of the native villagers by both French and British settlers, because the river "ran red with blood for days." Each claimed the island and imported slaves from Africa. The remaining Caribs now live on a 3,700-acre (15 km2) Carib Territory on the east coast of the island. They elect their own chief.
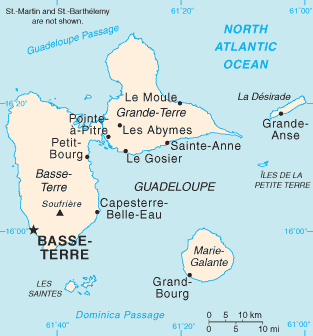
Marie-Galante is one of the dependencies of Guadeloupe, an overseas department of France. Marie-Galante has a land area of 158.1 km2. It had 11,528 inhabitants at the start of 2013, but by the start of 2018 the total was officially estimated to be 10,655, with a population density of 62.5/km2 (162/sq mi).
Cadence-lypso is a fusion of cadence rampa from Haiti, Jazz, Blues and calypso from Trinidad and Tobago that has also spread to other English speaking countries of the Caribbean. Originated in the 1970s by the Dominican band Exile One, it spread and became popular in the dance clubs around the Creole world and Africa as well as the French Antilles.

RAM is a mizik rasin band based in the city of Port-au-Prince, Haiti. The band derives its name from the initials of its founder, songwriter, and lead male vocalist, Richard A. Morse. The band's music has been described by Morse as "Vodou rock 'n' roots", and has been one of the prominent bands in the mizik rasin musical movement in Haiti. RAM began performing together in 1990, and recorded their first album in 1996. The band's music incorporates traditional Vodou lyrics and instruments, such as rara horns and petro drums, into modern rock and roll. The band's songs include lyrics in Haitian Creole, French, and English.

The Îles des Saintes, also known as Les Saintes, is a group of small islands in the archipelago of Guadeloupe, an overseas department of France. It is part of the Canton of Trois-Rivières and is divided into two communes: Terre-de-Haut and Terre-de-Bas. It is in the arrondissement of Basse-Terre and also in Guadeloupe's 4th constituency.
Exile One is a cadence musical group founded by Gordon Henderson in the 1970s with musicians invited over from Dominica, to be based in Guadeloupe. The band was influential in the development of Caribbean music. It became famous throughout the Caribbean, Europe, Africa and the Indian Ocean. Exile One opened the way for numerous Cadence-Lypso artists as well as for Zouk.
John Kenneth Holt OD was a Jamaican reggae singer who first found fame as a member of The Paragons, before establishing himself as a solo artist.

As an overseas department of France, Martinique's culture is French, African and Caribbean. Its former capital, Saint-Pierre, was often referred to as the Paris of the Lesser Antilles. The official language is French, although many Martinicans speak a Creole patois. Based in French, Martinique's Creole also incorporates elements of English, Spanish, Portuguese, and African languages. Originally passed down through oral storytelling traditions, it continues to be used more often in speech than in writing.

Dominica, officially the Commonwealth of Dominica, is an island country in the Caribbean. It is part of the Windward Islands chain in the Lesser Antilles archipelago in the Caribbean Sea. The capital, Roseau, is located on the western side of the island. Dominica's closest neighbours are two constituent territories of the European Union, the overseas departments of France, Guadeloupe to the northwest and Martinique to the south-southeast. Dominica comprises a land area of 750 km2 (290 sq mi), and the highest point is Morne Diablotins, at 1,447 m (4,747 ft) in elevation. The population was 71,293 at the 2011 census.
The term Caribbean culture summarizes the artistic, musical, literary, culinary, political and social elements that are representative of Caribbean people all over the world.
References
- Guilbault, Jocelyne (1999). "Dominica". Garland Encyclopedia of World Music. Vol. 2. Routledge. pp. 840–844. ISBN 0-8153-1865-0.
- "Mas Domnik: A History of Dominica's Carnival". A Virtual Dominica. Retrieved May 27, 2006.