Related Research Articles

Joel Chandler Harris was an American journalist and folklorist best known for his collection of Uncle Remus stories. Born in Eatonton, Georgia, where he served as an apprentice on a plantation during his teenage years, Harris spent most of his adult life in Atlanta working as an associate editor at The Atlanta Constitution.

Song of the South is a 1946 American live-action/animated musical comedy-drama film directed by Harve Foster and Wilfred Jackson, produced by Walt Disney, and released by RKO Radio Pictures. It is based on the Uncle Remus stories as adapted by Joel Chandler Harris, and stars James Baskett as Uncle Remus in his final film role. The film takes place in the U.S. state of Georgia during the Reconstruction era, a period of American history after the end of the American Civil War and the abolition of slavery. The story follows seven-year-old Johnny who is visiting his grandmother's plantation for an extended stay. Johnny befriends Uncle Remus, an elderly worker on the plantation, and takes joy in hearing his tales about the adventures of Br'er Rabbit, Br'er Fox, and Br'er Bear. Johnny learns from the stories how to cope with the challenges he is experiencing while living on the plantation.

Gullah is a creole language spoken by the Gullah people, an African American population living in coastal regions of South Carolina and Georgia as well as extreme northeastern Florida and the extreme southeast of North Carolina.

Uncle Remus is the fictional title character and narrator of a collection of African American folktales compiled and adapted by Joel Chandler Harris and published in book form in 1881. Harris was a journalist in post–Reconstruction era Atlanta, and he produced seven Uncle Remus books. He did so by introducing tales that he had heard and framing them in the plantation context. He wrote his stories in a dialect which was his interpretation of the Deep South African-American language of the time. For these framing and stylistic choices, Harris's collection has garnered controversy since its publication.

John the Conqueror, also known as High John de Conqueror, John, Jack, and many other folk variants, is a deity from the African-American spiritual system called hoodoo. He is associated with the roots of Ipomoea purga, the John the Conqueror root or John the Conqueroo, to which magical powers are ascribed in African-American folklore, especially among practitioners of Hoodoo. Muddy Waters mentions him as Johnny Cocheroo in the songs "Mannish Boy" and "I'm Your Hoochie Coochie Man". In "Mannish Boy", the line is "I think I'll go down/To old Kansas too/I'm gonna bring back my second cousin/That little Johnny Conqueroo". This line is borrowed from the Bo Diddley song "I'm a Man", to which "Mannish Boy" is an answer song. In "I'm Your Hoochie Coochie Man", it is called "John De Conquer Blue".

The Tar-Baby is the second of the Uncle Remus stories published in 1881; it is about a doll made of tar and turpentine used by the villainous Br'er Fox to entrap Br'er Rabbit. The more that Br'er Rabbit fights the Tar-Baby, the more entangled he becomes.
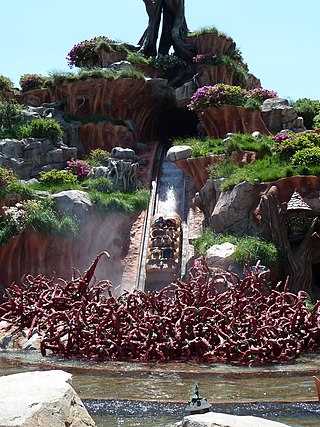
Splash Mountain is a log flume ride at Tokyo Disneyland. It was formerly located at Disneyland and Magic Kingdom. The attraction is based on the animated sequences of Disney's 1946 film Song of the South. The ride experience begins with an outdoor float-through that leads to indoor dark ride segments, with a climactic steep drop followed by an indoor finale. The drop is 52.5 feet.
"Henny Penny", more commonly known in the United States as "Chicken Little" and sometimes as "Chicken Licken", is a European folk tale with a moral in the form of a cumulative tale about a chicken who believes that the world is coming to an end. The phrase "The sky is falling!" features prominently in the story, and has passed into the English language as a common idiom indicating a hysterical or mistaken belief that disaster is imminent. Similar stories go back more than 25 centuries and "Henny Penny" continues to be referred to in a variety of media.
African-American folktales are the storytelling and oral history of enslaved African Americans during the 1700s–1900s. Prevalent themes in African-American folktales include tricksters, life lessons, heartwarming tales, and slavery. African Americans created folktales that spoke about the hardships of slavery and told stories of folk spirits that could outwit their slaveholders and defeat their enemies. These folk stories gave hope to enslaved people that folk spirits would liberate them from slavery. Folktales have been used to perpetuate negative stereotypes about the African American community, from minstrel shows to academic journals. One of these heroes that they looked up to was the charming High John the Conqueror, who was a cunning trickster against his slave masters. He often empowered newly freed slaves, saying that if they needed him, his spirit would be in a local root. Other common figures in African-American folktales include Anansi, Brer Rabbit, and Uncle Monday. Many folktales are unique to African-American culture, while others are influenced by African, European, and Native American tales. Even today in Hip-Hop, we see the effects of African American Folklore. Tropes like Badman and Trickster have influenced the characteristics and themes seen in modern-day hip hop like gangsters and pimps.

Br'er Rabbit is a central figure in an oral tradition passed down by African-Americans of the Southern United States and African descendants in the Caribbean, notably Afro-Bahamians and Turks and Caicos Islanders. He is a trickster who succeeds by his wits rather than by brawn, provoking authority figures and bending social mores as he sees fit. Popular adaptations of the character, originally recorded by Joel Chandler Harris in the 19th century, include Walt Disney Productions' Song of the South in 1946.
An animal tale or beast fable generally consists of a short story or poem in which animals talk. They may exhibit other anthropomorphic qualities as well, such as living in a human-like society. It is a traditional form of allegorical writing.

In mythology and the study of folklore and religion, a trickster is a character in a story who exhibits a great degree of intellect or secret knowledge and uses it to play tricks or otherwise disobey normal rules and defy conventional behavior.

Br'er Fox and Br'er Bear are fictional characters from African-American oral traditions popular in the Southern United States. These characters have been recorded by many different folklorists, but are most well-known from the folktales adapted and compiled by Joel Chandler Harris, featuring his character Uncle Remus.

"Br'er Rabbit Earns a Dollar a Minute" is a traditional African American folktale, featuring Br'er Rabbit, Br'er Fox and Br'er Bear. It is famous for its inclusion among Joel Chandler Harris' Uncle Remus stories. Although its folk roots most likely trace back to ancient Africa, the folktale's first written appearance was as a chapter titled "Mr. Rabbit and Mr. Bear" in Uncle Remus: His Songs and Sayings, published in 1881.

J. M. Condé was an early 20th century "golden age" book illustrator and comic strip artist best known for his ink and watercolor illustrations for books by Joel Chandler Harris and Albert Bigelow Paine. He also worked on at least two comic strips, one of which was derived from Harris's "Br'er Rabbit" stories.

The Tales of Uncle Remus: The Adventures of Brer Rabbit is a 1987 Children's book by Julius Lester and illustrator Jerry Pinkney. It is a retelling of the American Br'er Rabbit tales.
The Azalea Regional Library System (AZRLS) is a collection of ten public libraries located partially in the Atlanta metropolitan area and Central Georgia. It is headquartered in Madison, Georgia and serves the counties of Greene, Hancock, Jasper, Morgan, Putnam, and Walton, of which 32% of the population are members of the library.
Uncle Remus and His Tales of Br'er Rabbit is an American Disney comic strip that ran on Sundays from October 14, 1945, to December 31, 1972. It first appeared as a topper strip for the Mickey Mouse Sunday page, but after the first few years, almost always appeared on its own. The strip replaced the 1932-1945 Silly Symphony strip, which had spent its final year on gag strips featuring Panchito from The Three Caballeros.
References
- ↑ Opala, Joseph A. "Gullah Customs and Traditions". The Gullah: Rice, Slavery, and the Sierra Leone-American Connection. Archived from the original on 2006-05-17.
- ↑ Brasch, Walter M. (2000). Brer Rabbit, Uncle Remus, and the 'Cornfield Journalist': The Tale of Joel Chandler Harris. Mercer University Press. pp. 74, 275.