
Ingrid van Houten-Groeneveld was a Dutch astronomer.

1604 Tombaugh, provisional designation 1931 FH, is a rare-type Eos asteroid from the outer region of the asteroid belt, approximately 32 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 24 March 1931, by American astronomer Carl Otto Lampland at Lowell Observatory in Flagstaff, Arizona, in the United States. It was named after the discoverer of Pluto, Clyde Tombaugh.
688 Melanie is a dark background asteroid from the central regions of the asteroid belt. It was discovered by Austrian astronomer Johann Palisa at the Vienna Observatory on 25 August 1909. The carbonaceous C-type asteroid has a rotation period of 18.9 hours and measures approximately 42 kilometers in diameter. Any reference to the origin of the asteroid's name is unknown.
774 Armor is a minor planet orbiting in the main belt. It was discovered on 13 December 1913, in Paris by French astronomer Charles le Morvan and was named after the Celtic region of Armorica. The asteroid is orbiting at a distance of 3.05 AU with a period of 5.32 yr and an eccentricity of 0.169. The orbital plane is inclined by an angle of 5.56° to the plane of the ecliptic.
814 Tauris is a dark and very large background asteroid, approximately 109 kilometers in diameter, located the outer regions of the asteroid belt. It was discovered on 2 January 1916, by astronomer Russian Grigory Neujmin at the Simeiz Observatory on Crimea. The carbonaceous C-type asteroid has a longer-than average rotation period of 35.8 hours. It was named after the ancient name of the Crimean peninsula where the discovering observatory is located.
827 Wolfiana, provisional designation 1916 ZW, is a Florian asteroid from the inner regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 8 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered at Vienna Observatory on 29 August 1916, by Austrian astronomer Johann Palisa, who named it after German astronomer Max Wolf. The assumed stony asteroid has a rotation period of 4.0654 hours.

856 Backlunda is a dark background asteroid from the inner region of the asteroid belt. It was discovered on 3 April 1916, by Russian astronomer Sergey Belyavsky at the Simeiz Observatory on the Crimean peninsula. The carbonaceous C-type asteroid has a rotation period of 12.1 hours and measures approximately 45 kilometers in diameter. It was named after Swedish-Russian astronomer Oskar Backlund (1846–1916).
1024 Hale, provisional designation A923 YO13, is a carbonaceous background asteroid from the outer regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 45 kilometers (28 miles) in diameter. The asteroid was discovered on 2 December 1923, by Belgian–American astronomer George Van Biesbroeck at the Yerkes Observatory in Wisconsin, United States. It was named for American astronomer George Ellery Hale. The dark C-type asteroid may have a rotation period of 16 hours.
1060 Magnolia, provisional designation 1925 PA, is a stony Florian asteroid from the inner regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 7 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 13 August 1925, by German astronomer Karl Reinmuth at the Heidelberg-Königstuhl State Observatory. The asteroid was named after the flowering plant magnolia.
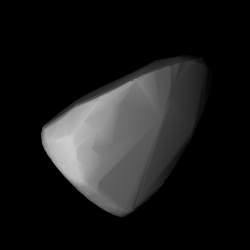
1554 Yugoslavia, provisional designation 1940 RE, is a stony Eunomian asteroid from the middle region of the asteroid belt, approximately 16 kilometres (9.9 mi) in diameter. It was discovered by Serbian astronomer Milorad Protić at Belgrade Astronomical Observatory, Serbia, on 6 September 1940. It was named for the former country of Yugoslavia.
June U. Gunter, better known as Jay U. Gunter or J. U. Gunter, was an American pathologist and amateur astronomer.

1404 Ajax is a carbonaceous Jupiter trojan from the Greek camp, approximately 83 kilometers kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 17 August 1936, by German astronomer Karl Reinmuth at Heidelberg Observatory in southern Germany, and named after the legendary warrior Ajax from Greek mythology. The assumed C-type asteroid belongs to the 40 largest Jupiter trojans and has a longer than average rotation period of 29.4 hours.
2797 Teucer is a large Jupiter trojan from the Greek camp, approximately 110 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 4 June 1981, by American astronomer Edward Bowell at the Anderson Mesa Station near Flagstaff, Arizona, in the United States. The dark D-type asteroid belongs to the 20 largest Jupiter trojans and has a rotation period of 10.15 hours. It was named after the Greek hero and great archer, Teucer.
3063 Makhaon is a large Jupiter trojan from the Greek camp, approximately 114 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 4 August 1983, by Soviet astronomer Lyudmila Karachkina at the Crimean Astrophysical Observatory in Nauchnij, on the Crimean peninsula. The dark D-type asteroid is the principal body of the proposed Makhaon family and belongs to the 20 largest Jupiter trojans having a rotation period of 8.6 hours. It was named after the legendary healer Machaon from Greek mythology.
4068 Menestheus is a dark Jupiter trojan from the Greek camp, approximately 67 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 19 September 1973, by Dutch astronomers Ingrid and Cornelis van Houten at Leiden, on photographic plates taken by Tom Gehrels at the Palomar Observatory in California, United States. The D-type asteroid belongs to the 60 largest Jupiter trojans and has a rotation period of 14.4 hours. It was named after the Athen leader Menestheus from Greek mythology.
1928 Summa, provisional designation 1938 SO, is a stony asteroid from the inner regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 9 kilometers in diameter.
4902 Thessandrus is a Jupiter trojan from the Greek camp, approximately 60 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 9 January 1989, by American astronomer Carolyn Shoemaker at the Palomar Observatory in California, and later named after Thessander (Thessandrus) from Greek mythology. The dark D-type asteroid is an exceptionally slow rotator and tumbler. It belongs to the 70 largest Jupiter trojans.
6545 Leitus, provisional designation:1986 TR6, is a Jupiter trojan from the Greek camp, approximately 53 kilometers (33 miles) in diameter. It was discovered on 5 October 1986, by Slovak astronomer Milan Antal at the Piwnice Astronomical Observatory in Poland. The dark D-type asteroid has a rotation period of 16.3 hours and belongs to the 90 largest Jupiter trojans. Numbered in 1995, it was named in 2021, after the Argonaut Leitus from Greek mythology, who fought in the Trojan War.
15436 Dexius, provisional designation: 1998 VU30, is a large Jupiter trojan from the Greek camp, approximately 86 kilometers (53 miles) in diameter. It was discovered on 10 November 1998, by astronomers of the Lincoln Near-Earth Asteroid Research at the Lincoln Laboratory's Experimental Test Site near Socorro, New Mexico. The presumed C-type asteroid has a rotation period of 8.97 hours. It is one of the 50 largest Jupiter trojans and was named after Dexius, father of Iphinous from Greek mythology.
(15502) 1999 NV27 (provisional designation 1999 NV27) is a Jupiter trojan from the Trojan camp, approximately 53 kilometers (33 miles) in diameter. It was discovered on 14 July 1999, by astronomers with the Lincoln Near-Earth Asteroid Research at the Lincoln Lab's ETS near Socorro, New Mexico, in the United States. The dark Jovian asteroid has a rotation period of 15.1 hours and belongs to the 90 largest Jupiter trojans. It has not been named since its numbering in June 2000.




