
Panama, officially the Republic of Panama, is a country in Latin America at the southern end of Central America, bordering South America. It is bordered by Costa Rica to the west, Colombia to the southeast, the Caribbean Sea to the north, and the Pacific Ocean to the south. Its capital and largest city is Panama City, whose metropolitan area is home to nearly half of the country's over 4 million inhabitants.

The history of Panama includes the history of the Isthmus of Panama prior to European colonization.

The economy of Panama is based mainly on the tourism and services sector, which accounts for nearly 80% of its GDP and accounts for most of its foreign income. Services include banking, commerce, insurance, container ports, and flagship registry, medical and health and tourism. Historically, the Panama Canal was the key source of Panama's income, but its importance has been displaced by the services sector.

The Panama Canal is an artificial 82-kilometer (51-mile) waterway in Panama that connects the Caribbean Sea with the Pacific Ocean. It cuts across the narrowest point of the Isthmus of Panama, and is a conduit for maritime trade between the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans. Locks at each end lift ships up to Gatun Lake, an artificial fresh water lake 26 meters (85 ft) above sea level, created by damming the Chagres River and Lake Alajuela to reduce the amount of excavation work required for the canal. Locks then lower the ships at the other end. An average of 200 ML (52,000,000 US gal) of fresh water is used in a single passing of a ship. The canal is threatened by low water levels during droughts.

Manuel Antonio Noriega Moreno was a Panamanian dictator and military officer who was the de facto ruler of Panama from 1983 to 1989. He never officially served as president of Panama, instead ruling as an unelected military dictator through puppet presidents. Amassing a personal fortune through drug trafficking operations by the Panamanian military, Noriega had longstanding ties with American intelligence agencies before the U.S. invasion of Panama removed him from power.

Omar Efraín Torrijos Herrera was a Panamanian dictator and military leader of Panama, as well as the Commander of the Panamanian National Guard from 1968 to his death in 1981. Torrijos was never officially the president of Panama, but instead held self-imposed and all-encompassing titles including "Maximum Leader of the Panamanian Revolution". Torrijos took power in a coup d'état and instituted a number of social reforms.

The Hay–Bunau-Varilla Treaty was a treaty signed on November 18, 1903, by the United States and Panama, which established the Panama Canal Zone and the subsequent construction of the Panama Canal. It was named after its two primary negotiators, Philippe-Jean Bunau-Varilla, the French diplomatic representative of Panama, and United States Secretary of State John Hay.

The United States invaded Panama in mid-December 1989 during the presidency of George H. W. Bush. The purpose of the invasion was to depose the de facto ruler of Panama, General Manuel Noriega, who was wanted by U.S. authorities for racketeering and drug trafficking. The operation, codenamed Operation Just Cause, concluded in late January 1990 with the surrender of Noriega. The Panama Defense Forces (PDF) were dissolved, and President-elect Guillermo Endara was sworn into office.
Balboa is a district of Panama City, located at the Pacific entrance to the Panama Canal. It was the former capital of the Panama Canal Zone under American administration.

The Torrijos–Carter Treaties are two treaties signed by the United States and Panama in Washington, D.C., on September 7, 1977, which superseded the Hay–Bunau-Varilla Treaty of 1903. The treaties guaranteed that Panama would gain control of the Panama Canal after 1999, ending the control of the canal that the U.S. had exercised since 1903. The treaties are named after the two signatories, U.S. President Jimmy Carter and the Commander of Panama's National Guard, General Omar Torrijos.

Ancón is a corregimiento in Panamá District, Panamá Province, Panama with a population of 29,761 as of 2010. Its population as of 1990 was 11,518; its population as of 2000 was 11,169. It is sometimes considered a suburb or small town within Panama City, northeast of the limits of the town of Balboa. Ancon Hill is also the name of a large hill that overlooks Panama City and once served as a form of protection from pirates and sea invasion. The township was originally located around this hill, and was created to house employees of the Panama Canal during its construction. As part of the construction effort, the historic Gorgas Army Hospital was founded and built on the hillside. The first ship to officially transit the canal, SS Ancon, was named after the district. The community continued to serve as housing for employees of the Panama Canal Company until 1980, when parts of it began to be turned over to the Panamanian government under the 1977 Torrijos-Carter Treaties. Modern-day Ancón is a corregimiento of Panama City, serving mainly as a residential area. The Gorgas Army Hospital building is now the Panamanian Oncology Hospital, primarily used for cancer research. The area also houses Panama's Supreme Court, just a few feet away from the Gorgas Army Hospital building, and several Smithsonian Tropical Research Institute buildings for research into tropical biology. Ancón is also a parish (parroquia) of the District of Panama, located in the Panama Canal adjacent area.

Gorgas Hospital was a U.S. Army hospital in Panama City, Panama, named for Army Surgeon General William C. Gorgas (1854—1920).
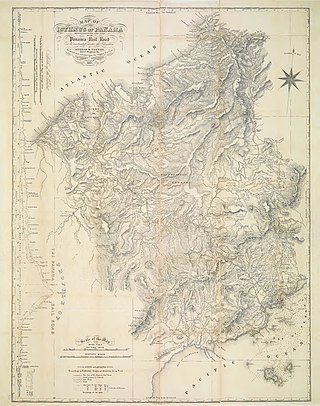
The Panama Canal fence is a term used for a variety of barriers built by the United States in the Panama Canal Zone to control movement in the zone for a variety of enforcement purposes. The Canal Zone, primarily consisting of the Panama Canal, a strip of land running from the Pacific Ocean to the Caribbean that was administered by the United States to various degrees until 1999. The fence was occasionally dubbed a “fence of shame” and "another Berlin Wall” by those opposed to continued United States presence and control of the Canal Zone.

The Panama Defense Forces (Spanish: Fuerzas de Defensa de Panamá; FFDD), formerly the National Guard (of Panama) (Spanish: Guardia Nacional), were the armed forces of the Republic of Panama.
Panama is a transcontinental country spanning the southern part of North America and the northern part of South America.
Panama is a transcontinental country spanning the southern part of North America and the northern part of South America
Title 35 of the Code of Federal Regulations was a United States federal government regulation on the Panama Canal. The U.S. controlled the Panama Canal Zone from 1904 to 1999. The Torrijos–Carter Treaties provided for handover to Panama. After a period of joint American–Panamanian control, the canal was taken over by the Panamanian government in 1999, and is now operated by the Panama Canal Authority, a Panamanian government agency.
The nations of Mexico and Panama established diplomatic relations in 1904. Both nations are mutual members of the Association of Caribbean States, Community of Latin American and Caribbean States, Latin American Integration Association, Organization of Ibero-American States and the Organization of American States.
The Panama Truth Commission was appointed by Panamanian president Mireya Moscoso in 2000 to investigate crimes committed under the military rule of Omar Torrijos and Manuel Noriega.














