Amicable numbers are two different natural numbers related in such a way that the sum of the proper divisors of each is equal to the other number. That is, s(a)=b and s(b)=a, where s(n)=σ(n)-n is equal to the sum of positive divisors of n except n itself (see also divisor function).

In mathematics, a conjecture is a conclusion or a proposition that is proffered on a tentative basis without proof. Some conjectures, such as the Riemann hypothesis or Fermat's Last Theorem, have shaped much of mathematical history as new areas of mathematics are developed in order to prove them.
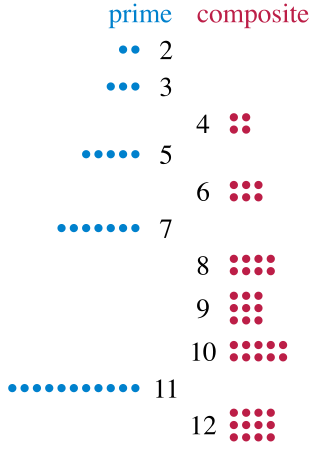
A prime number is a natural number greater than 1 that is not a product of two smaller natural numbers. A natural number greater than 1 that is not prime is called a composite number. For example, 5 is prime because the only ways of writing it as a product, 1 × 5 or 5 × 1, involve 5 itself. However, 4 is composite because it is a product (2 × 2) in which both numbers are smaller than 4. Primes are central in number theory because of the fundamental theorem of arithmetic: every natural number greater than 1 is either a prime itself or can be factorized as a product of primes that is unique up to their order.

Srinivasa Ramanujan was an Indian mathematician. Though he had almost no formal training in pure mathematics, he made substantial contributions to mathematical analysis, number theory, infinite series, and continued fractions, including solutions to mathematical problems then considered unsolvable.
Gödel's incompleteness theorems are two theorems of mathematical logic that are concerned with the limits of provability in formal axiomatic theories. These results, published by Kurt Gödel in 1931, are important both in mathematical logic and in the philosophy of mathematics. The theorems are widely, but not universally, interpreted as showing that Hilbert's program to find a complete and consistent set of axioms for all mathematics is impossible.
Catalan's conjecture (or Mihăilescu's theorem) is a theorem in number theory that was conjectured by the mathematician Eugène Charles Catalan in 1844 and proven in 2002 by Preda Mihăilescu at Paderborn University. The integers 23 and 32 are two perfect powers (that is, powers of exponent higher than one) of natural numbers whose values (8 and 9, respectively) are consecutive. The theorem states that this is the only case of two consecutive perfect powers. That is to say, that

Amalie Emmy Noether was a German mathematician who made many important contributions to abstract algebra. She proved Noether's first and second theorems, which are fundamental in mathematical physics. She was described by Pavel Alexandrov, Albert Einstein, Jean Dieudonné, Hermann Weyl and Norbert Wiener as the most important woman in the history of mathematics. As one of the leading mathematicians of her time, she developed theories of rings, fields, and algebras. In physics, Noether's theorem explains the connection between symmetry and conservation laws.

Metamathematics is the study of mathematics itself using mathematical methods. This study produces metatheories, which are mathematical theories about other mathematical theories. Emphasis on metamathematics owes itself to David Hilbert's attempt to secure the foundations of mathematics in the early part of the 20th century. Metamathematics provides "a rigorous mathematical technique for investigating a great variety of foundation problems for mathematics and logic". An important feature of metamathematics is its emphasis on differentiating between reasoning from inside a system and from outside a system. An informal illustration of this is categorizing the proposition "2+2=4" as belonging to mathematics while categorizing the proposition "'2+2=4' is valid" as belonging to metamathematics.

Shing-Tung Yau is a Chinese-American mathematician. He is the director of the Yau Mathematical Sciences Center at Tsinghua University and Professor Emeritus at Harvard University. Until 2022 he was the William Caspar Graustein Professor of Mathematics at Harvard, at which point he moved to Tsinghua.

Arthur Cayley was a prolific British mathematician who worked mostly on algebra. He helped found the modern British school of pure mathematics.

Paul Erdős was a Hungarian mathematician. He was one of the most prolific mathematicians and producers of mathematical conjectures of the 20th century. Erdős pursued and proposed problems in discrete mathematics, graph theory, number theory, mathematical analysis, approximation theory, set theory, and probability theory. Much of his work centered around discrete mathematics, cracking many previously unsolved problems in the field. He championed and contributed to Ramsey theory, which studies the conditions in which order necessarily appears. Overall, his work leaned towards solving previously open problems, rather than developing or exploring new areas of mathematics.

Richard Dagobert Brauer was a leading German and American mathematician. He worked mainly in abstract algebra, but made important contributions to number theory. He was the founder of modular representation theory.

Klaus Friedrich Roth was a German-born British mathematician who won the Fields Medal for proving Roth's theorem on the Diophantine approximation of algebraic numbers. He was also a winner of the De Morgan Medal and the Sylvester Medal, and a Fellow of the Royal Society.

The Final Solution: A Story of Detection is a 2004 novella by Michael Chabon. It is a detective story that in many ways pays homage to the writings of Sir Arthur Conan Doyle and other writers of the genre. The story, set in 1944, revolves around an unnamed 89-year-old long-retired detective, now interested mostly in beekeeping, and his quest to find a missing parrot, the only friend of a mute Jewish boy. The title of the novella references Doyle's 1893 Sherlock Holmes story "The Final Problem" and the Final Solution, as well as The Seven-Per-Cent Solution, a 1974 novel written in homage to Conan Doyle by Nicholas Meyer.

Andrew Mattei Gleason (1921–2008) was an American mathematician who made fundamental contributions to widely varied areas of mathematics, including the solution of Hilbert's fifth problem, and was a leader in reform and innovation in mathematics teaching at all levels. Gleason's theorem in quantum logic and the Greenwood–Gleason graph, an important example in Ramsey theory, are named for him.

The Last Theorem is a 2008 science fiction novel by Arthur C. Clarke and Frederik Pohl. It was first published in the United Kingdom by HarperVoyager in July 2008, and in the United States by Del Rey Books in August 2008. The book is about a young Sri Lankan mathematician who finds a short proof of Fermat's Last Theorem, while an alien invasion of Earth is in progress.

Pierre de Fermat was a French mathematician who is given credit for early developments that led to infinitesimal calculus, including his technique of adequality. In particular, he is recognized for his discovery of an original method of finding the greatest and the smallest ordinates of curved lines, which is analogous to that of differential calculus, then unknown, and his research into number theory. He made notable contributions to analytic geometry, probability, and optics. He is best known for his Fermat's principle for light propagation and his Fermat's Last Theorem in number theory, which he described in a note at the margin of a copy of Diophantus' Arithmetica. He was also a lawyer at the Parlement of Toulouse, France.

The mutilated chessboard problem is a tiling puzzle posed by Max Black in 1946 that asks:
Suppose a standard 8×8 chessboard has two diagonally opposite corners removed, leaving 62 squares. Is it possible to place 31 dominoes of size 2×1 so as to cover all of these squares?

In number theory, Fermat's Last Theorem states that no three positive integers a, b, and c satisfy the equation an + bn = cn for any integer value of n greater than 2. The cases n = 1 and n = 2 have been known since antiquity to have infinitely many solutions.
Math Girls is the first in a series of math-themed young adult novels of the same name by Japanese author Hiroshi Yuki. It was published by SoftBank Creative in 2007, followed by Math Girls: Fermat's Last Theorem in 2008, Math Girls: Gödel's Incompleteness Theorems in 2009, and Math Girls: Randomized Algorithms in 2011. As of December 2010, the series had sold over 100,000 books in Japan. On November 23, 2011, an English translation of the book was released by Bento Books, who subsequently released translations of Fermat's Last Theorem (ISBN 978-0983951339) and Gödel's Incompleteness Theorems (ISBN 978-1939326294) on December 5, 2012, and April 25, 2016, respectively.