
Barium hydroxide is a chemical compound with the chemical formula Ba(OH)2. The monohydrate (x = 1), known as baryta or baryta-water, is one of the principal compounds of barium. This white granular monohydrate is the usual commercial form.
An acidic oxide is an oxide that either produces an acidic solution upon addition to water, or acts as an acceptor of hydroxide ions effectively functioning as a Lewis acid. Acidic oxides will typically have a low pKa and may be inorganic or organic. A commonly encountered acidic oxide, carbon dioxide produces an acidic solution when dissolved.

Barium chloride is an inorganic compound with the formula BaCl2. It is one of the most common water-soluble salts of barium. Like most other water-soluble barium salts, it is a white powder, highly toxic, and imparts a yellow-green coloration to a flame. It is also hygroscopic, converting to the dihydrate BaCl2·2H2O, which are colourless crystals with a bitter salty taste. It has limited use in the laboratory and industry.
Classical qualitative inorganic analysis is a method of analytical chemistry which seeks to find the elemental composition of inorganic compounds. It is mainly focused on detecting ions in an aqueous solution, therefore materials in other forms may need to be brought to this state before using standard methods. The solution is then treated with various reagents to test for reactions characteristic of certain ions, which may cause color change, precipitation and other visible changes.
In chemistry, disproportionation, sometimes called dismutation, is a redox reaction in which one compound of intermediate oxidation state converts to two compounds, one of higher and one of lower oxidation states. The reverse of disproportionation, such as when a compound in an intermediate oxidation state is formed from precursors of lower and higher oxidation states, is called comproportionation, also known as synproportionation.

Phosphorous acid (or phosphonic acid) is the compound described by the formula H3PO3. This acid is diprotic (readily ionizes two protons), not triprotic as might be suggested by this formula. Phosphorous acid is an intermediate in the preparation of other phosphorus compounds. Organic derivatives of phosphorous acid, compounds with the formula RPO3H2, are called phosphonic acids.

Sodium dithiophosphate is the salt with the formula Na3PS2O2. It is usually supplied as the hydrated solid or as an aqueous solution together with other thiophosphates such as sodium monothiophosphate and sodium trithiophosphate. It is a colorless compound, but commercial samples can appear dark owing to the presence of impurities. It is used to facilitate the isolation of molybdenum from its ores.
Hypophosphorous acid (HPA), or phosphinic acid, is a phosphorus oxyacid and a powerful reducing agent with molecular formula H3PO2. It is a colorless low-melting compound, which is soluble in water, dioxane and alcohols. The formula for this acid is generally written H3PO2, but a more descriptive presentation is HOP(O)H2, which highlights its monoprotic character. Salts derived from this acid are called hypophosphites.

Sodium monofluorophosphate, commonly abbreviated SMFP, is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Na2PO3F. Typical for a salt, MFP is odourless, colourless, and water-soluble. This salt is an ingredient in some toothpastes.

Sodium thioantimoniate or sodium tetrathioantimonate(V) is an inorganic compound with the formula Na3SbS4. The nonahydrate of this chemical, Na3SbS4·9H2O, is known as Schlippe's salt, named after Johann Karl Friedrich von Schlippe (1799–1867). These compounds are examples of sulfosalts. They were once of interest as species generated in qualitative inorganic analysis.

Hexafluorosilicic acid is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula H
2SiF
6. Aqueous solutions of hexafluorosilicic acid consist of salts of the cation and hexafluorosilicate anion. These salts and their aqueous solutions are colorless.
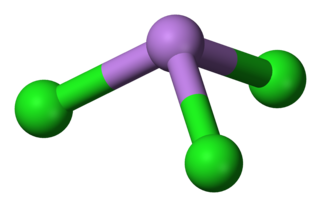
Arsenic trichloride is an inorganic compound with the formula AsCl3, also known as arsenous chloride or butter of arsenic. This poisonous oil is colourless, although impure samples may appear yellow. It is an intermediate in the manufacture of organoarsenic compounds.

Thiophosphoryl chloride is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula PSCl3. It is a colorless pungent smelling liquid that fumes in air. It is synthesized from phosphorus chloride and used to thiophosphorylate organic compounds, such as to produce insecticides.
Antimony pentasulfide is an inorganic compound of antimony and sulfur, also known as antimony red. It is a nonstoichiometric compound with a variable composition. Its structure is unknown. Commercial samples are contaminated with sulfur, which may be removed by washing with carbon disulfide in a Soxhlet extractor.

Barium bromide is the chemical compound with the formula BaBr2. It is ionic and hygroscopic in nature.
Thiophosphates (or phosphorothioates, PS) are chemical compounds and anions with the general chemical formula PS
4−xO3−
x (x = 0, 1, 2, or 3) and related derivatives where organic groups are attached to one or more O or S. Thiophosphates feature tetrahedral phosphorus(V) centers.
Thiocarbonate describes a family of anions with the general chemical formula CS
3−xO2−
x (x = 0, 1, or 2):

Arsenic pentasulfide is an inorganic compound containing arsenic and sulfur.

Thiocarbonic acid is an inorganic acid with the chemical formula H2CS3. It is an analog of carbonic acid H2CO3, in which all oxygen atoms are replaced with sulfur atoms. It is an unstable hydrophobic red oily liquid.
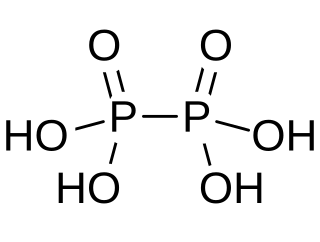
Hypophosphoric acid is a mineral acid with the formula H4P2O6, with phosphorus in a formal oxidation state of +4. In the solid state it is present as the dihydrate, H4P2O6·2H2O. In hypophosphoric acid the phosphorus atoms are identical and joined directly with a P−P bond. Isohypophosphoric acid is a structural isomer of hypophosphoric acid in which one phosphorus has a hydrogen directedly bonded to it and that phosphorus atom is linked to the other one by an oxygen bridge to give a phosphorous acid/phosphoric acid mixed anhydride. The two phosphorus atoms are in the +3 and +5 oxidation states, respectively.













