
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the evolution of dinosaurs is a subject of active research. They became the dominant terrestrial vertebrates after the Triassic–Jurassic extinction event 201.3 mya and their dominance continued throughout the Jurassic and Cretaceous periods. The fossil record shows that birds are feathered dinosaurs, having evolved from earlier theropods during the Late Jurassic epoch, and are the only dinosaur lineage known to have survived the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event approximately 66 mya. Dinosaurs can therefore be divided into avian dinosaurs—birds—and the extinct non-avian dinosaurs, which are all dinosaurs other than birds.

Pterosaurs are an extinct clade of flying reptiles in the order Pterosauria. They existed during most of the Mesozoic: from the Late Triassic to the end of the Cretaceous. Pterosaurs are the earliest vertebrates known to have evolved powered flight. Their wings were formed by a membrane of skin, muscle, and other tissues stretching from the ankles to a dramatically lengthened fourth finger.

A skeleton is the structural frame that supports the body of most animals. There are several types of skeletons, including the exoskeleton, which is a rigid outer shell that holds up an organism's shape; the endoskeleton, a rigid internal frame to which the organs and soft tissues attach; and the hydroskeleton, a flexible internal structure supported by the hydrostatic pressure of body fluids.

The skull is a bone protective cavity for the brain. The skull is composed of four types of bone i.e., cranial bones, facial bones, ear ossicles and hyoid bone, however two parts are more prominent: the cranium and the mandible. In humans, these two parts are the neurocranium (braincase) and the viscerocranium that includes the mandible as its largest bone. The skull forms the anterior-most portion of the skeleton and is a product of cephalisation—housing the brain, and several sensory structures such as the eyes, ears, nose, and mouth. In humans, these sensory structures are part of the facial skeleton.
The beak, bill, or rostrum is an external anatomical structure found mostly in birds, but also in turtles, non-avian dinosaurs and a few mammals. A beak is used for pecking, grasping, and holding, preening, courtship, and feeding young. The terms beak and rostrum are also used to refer to a similar mouth part in some ornithischians, pterosaurs, cetaceans, dicynodonts, anuran tadpoles, monotremes, sirens, pufferfish, billfishes and cephalopods.

Woodpeckers are part of the bird family Picidae, which also includes the piculets, wrynecks and sapsuckers. Members of this family are found worldwide, except for Australia, New Guinea, New Zealand, Madagascar and the extreme polar regions. Most species live in forests or woodland habitats, although a few species are known that live in treeless areas, such as rocky hillsides and deserts, and the Gila woodpecker specialises in exploiting cacti.

Gallimimus is a genus of theropod dinosaur that lived in what is now Mongolia during the Late Cretaceous period, about seventy million years ago (mya). Several fossils in various stages of growth were discovered by Polish-Mongolian expeditions in the Gobi Desert of Mongolia during the 1960s; a large skeleton discovered in this region was made the holotype specimen of the new genus and species Gallimimus bullatus in 1972. The generic name means "chicken mimic", referring to the similarities between its neck vertebrae and those of the Galliformes. The specific name is derived from bulla, a golden capsule worn by Roman youth, in reference to a bulbous structure at the base of the skull of Gallimimus. At the time it was named, the fossils of Gallimimus represented the most complete and best preserved ornithomimid material yet discovered, and the genus remains one of the best known members of the group.

The jugal is a skull bone found in most reptiles, amphibians and birds. In mammals, the jugal is often called the malar or zygomatic. It is connected to the quadratojugal and maxilla, as well as other bones, which may vary by species.

A trabecula is a small, often microscopic, tissue element in the form of a small beam, strut or rod that supports or anchors a framework of parts within a body or organ. A trabecula generally has a mechanical function, and is usually composed of dense collagenous tissue. It can be composed of other material such as muscle and bone. In the heart, muscles form trabeculae carneae and septomarginal trabeculae. Cancellous bone is formed from groupings of trabeculated bone tissue.
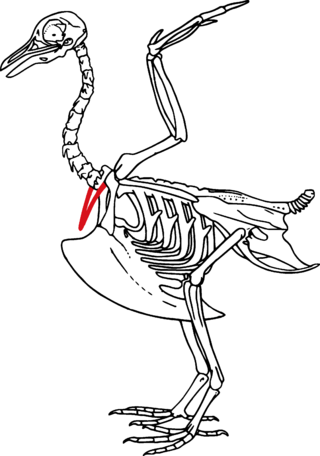
The furcula or wishbone is a forked bone found in most birds and some species of non-avian dinosaurs, and is formed by the fusion of the two clavicles. In birds, its primary function is in the strengthening of the thoracic skeleton to withstand the rigors of flight.

Vegavis is a genus of extinct bird that lived during the Late Cretaceous of Antarctica, some 68 to 66 mya. Among modern birds, most studies show that Vegavis is most closely related to ducks and geese (Anatidae), but it is not considered to be a direct ancestor of them, although other studies question these results.

The crown is the top portion of the head behind the vertex. The anatomy of the crown varies between different organisms. The human crown is made of three layers of the scalp above the skull. The crown also covers a range of bone sutures, and contains blood vessels and branches of the trigeminal nerve.
Bird anatomy, or the physiological structure of birds' bodies, shows many unique adaptations, mostly aiding flight. Birds have a light skeletal system and light but powerful musculature which, along with circulatory and respiratory systems capable of very high metabolic rates and oxygen supply, permit the bird to fly. The development of a beak has led to evolution of a specially adapted digestive system.

Lectavis is a genus of enantiornithine birds. Their fossil bones have been recovered from the Late Cretaceous Lecho Formation at estancia El Brete, Argentina. The genus contains a single species, Lectavis bretincola.
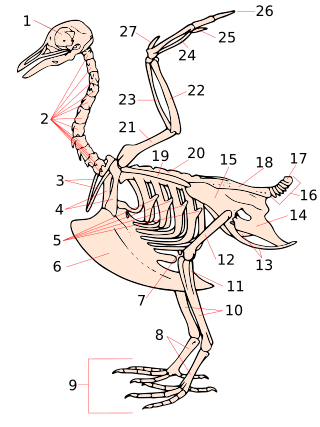
The tarsometatarsus is a bone that is only found in the lower leg of birds and some non-avian dinosaurs. It is formed from the fusion of several bones found in other types of animals, and homologous to the mammalian tarsus and metatarsal bones (foot). Despite this, the tarsometatarsus of birds is often referred to as just the shank, tarsus or metatarsus.
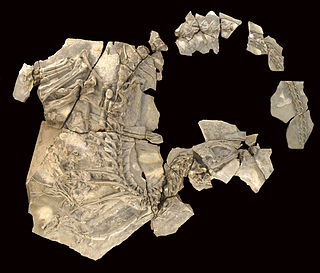
Concavenator is an extinct carcharodontosaurid theropod dinosaur that lived approximately 130 million years ago during the Early Cretaceous period. The type species is C. corcovatus. Concavenator corcovatus means "Cuenca hunter with a hump". The fossil was discovered in the Las Hoyas fossil site of Spain by paleontologists José Luis Sanz, Francisco Ortega, and Fernando Escaso from the Autonomous University of Madrid and the National University of Distance Education.

The vertebral column, also known as the spinal column, spine or backbone, is the core part of the axial skeleton in vertebrate animals. The vertebral column is the defining and eponymous characteristic of the vertebrate endoskeleton, where the notochord found in all chordates has been replaced by a segmented series of mineralized irregular bones called vertebrae, separated by fibrocartilaginous intervertebral discs. The dorsal portion of the vertebral column houses the spinal canal, an elongated cavity formed by alignment of the vertebral neural arches that encloses and protects the spinal cord, with spinal nerves exiting via the intervertebral foramina to innervate each body segments.
Cerebavis is an extinct genus of ornithurine dinosaurs that lived during the middle Cenomanian of the Late Cretaceous period, and is known from a single partial skull found in the Melovatskaya Formation of Volgograd Region in Russia. The skull was initially described as the fossilised brain of an enantiornithean by Russian palaeornithologist Evgeny Kurochkin and colleagues in 2006. Kurochkin and colleagues described Cerebavis as having a notable mixture of ancestral traits, such as a well-developed olfactory system, with derived traits of modern birds like a large cerebrum. At the same time, they identified various unusual and unique features not seen in the brains of reptiles or birds. These include well-developed auditory tubercles on the midbrain, as well as a prominent parietal organ compared to living birds or Archaeopteryx between them.

Mirarce is a genus of enantornithe bird from the Late Cretaceous of Utah. It contains a single species, M. eatoni. It was similar in size to modern turkeys.

Fukuipteryx is an extinct genus of basal avialan dinosaurs found in Early Cretaceous deposits from Japan's Kitadani Formation. It contains one species, Fukuipteryx prima.


















