Related Research Articles
The Essenes or Essenians were a mystic Jewish sect during the Second Temple period that flourished from the 2nd century BCE to the 1st century CE.

The Hasmonean dynasty was a ruling dynasty of Judea and surrounding regions during the Hellenistic times of the Second Temple period, from c. 140 BCE to 37 BCE. Between c. 140 and c. 116 BCE the dynasty ruled Judea semi-autonomously in the Seleucid Empire, and from roughly 110 BCE, with the empire disintegrating, Judea gained further autonomy and expanded into the neighboring regions of Perea, Samaria, Idumea, Galilee, and Iturea. The Hasmonean rulers took the Greek title basileus ("king") as the kingdom became a regional power for several decades. Forces of the Roman Republic intervened in the Hasmonean Civil War in 63 BCE and made it into a client state, marking the decline of Hasmonean dynasty; Herod the Great displaced the last reigning Hasmonean client-ruler in 37 BCE.
The Sadducees were a sect of Jews active in Judea during the Second Temple period, from the second century BCE to the destruction of the Second Temple in 70 CE. The Sadducees are described in contemporary literary sources in contrast to the two other major sects at the time, the Pharisees and the Essenes.

The First Jewish–Roman War, sometimes called the Great Jewish Revolt or the Jewish War, was the first of three major rebellions by the Jews against the Roman Empire fought in the province of Judaea, resulting in the destruction of Jewish towns, the displacement of its people, and the appropriation of land for Roman military use, as well as the destruction of the Jewish Temple and polity.

Syria Palaestina was the renamed Roman province formerly known as Judaea, following the Roman suppression of the Bar Kokhba revolt, in what then became known as the Palestine region between the early 2nd and late 4th centuries AD. The provincial capital was Caesarea Maritima. It forms part of timeline of the period in the region referred to as Roman Palestine.

Pella was an ancient city in what is now northwest Jordan, and contains ruins from the Neolithic, Chalcolithic, Bronze Age, Iron Age, Canaanite, Hellenistic and Islamic periods. It is located near a rich water source within the eastern foothills of the Jordan Valley, close to the modern village of Ṭabaqat Faḥl some 27 km (17 mi) south of the Sea of Galilee. The site is situated 130 km (81 mi) north of Amman: a drive of about two hours, and an hour southwest by car from Irbid, in the north of the country. Pella's ruins – predominantly temples, churches, and housing – have been partially excavated by teams of archaeologists; they attract thousands of tourists annually but especially in spring, during which time the area is awash with spring flowers.
The region of Palestine, also known as historic Palestine, is a geographical area in West Asia. It includes modern-day Israel and the State of Palestine, as well as parts of northwestern Jordan in some definitions. Other names for the region include Canaan, the Promised Land, the Land of Israel, or the Holy Land.

The Jewish–Roman wars were a series of large-scale revolts by Jewish subjects against the Roman Empire between 66 and 135 CE. The term primarily applies to the First Jewish–Roman War (66–73) and the Bar Kokhba revolt (132–136)—nationalist rebellions striving to restore an independent Jewish state. Some sources also include the Diaspora Revolt (115–117), an ethno-religious conflict fought across the Eastern Mediterranean and including the Kitos War in Judaea.

Aristobulus II was the Jewish High Priest and King of Judea, 66 BCE to 63 BCE, from the Hasmonean dynasty.

Judaea was a Roman province from 6 to 132 CE, which at its height incorporated the Levantine regions of Judea, Idumea Samaria, and Galilee, and parts of the costal plain including Philistia, extending over the territories of the Hasmonean and Herodian kingdoms. The name Judaea was derived from the Iron Age Kingdom of Judah, that was centered predominantly in Judea.

Coele-Syria was a region of Syria in classical antiquity. The term originally referred to the "hollow" Beqaa Valley between the Lebanon and the Anti-Lebanon mountain ranges, but sometimes it was applied to a broader area of the region of Syria. The area is now part of modern-day Syria and Lebanon.

Perea or Peraea was the term used mainly during the early Roman period for part of ancient Transjordan. It lay broadly east of Judea and Samaria, which were situated on the western side of the Jordan River, and southwest of the Decapolis.

The Herodian dynasty was a royal dynasty of Idumaean (Edomite) descent, ruling the Herodian Kingdom of Judea and later the Herodian tetrarchy as a vassal state of the Roman Empire. The Herodian dynasty began with Herod the Great who assumed the throne of Judea, with Roman support, bringing down the century-old Hasmonean Kingdom. His kingdom lasted until his death in 4 BCE, when it was divided among his sons and daughter as a tetrarchy, which lasted for about 10 years. Most of those tetrarchies, including Judea proper, were incorporated into Judaea Province from 6 CE, though limited Herodian de facto kingship continued until Agrippa I's death in 44 CE and nominal title of kingship continued until c. 92 or 100 CE, when the last Herodian monarch, king Agrippa II, died and Rome assumed full power over his de jure domain.
Hellenistic Judaism was a form of Judaism in classical antiquity that combined Jewish religious tradition with elements of Hellenistic culture and religion. Until the early Muslim conquests of the eastern Mediterranean, the main centers of Hellenistic Judaism were Alexandria in Egypt and Antioch in Turkey, the two main Greek urban settlements of the Middle East and North Africa, both founded in the end of the 4th century BCE in the wake of the conquests of Alexander the Great. Hellenistic Judaism also existed in Jerusalem during the Second Temple Period, where there was a conflict between Hellenizers and traditionalists.
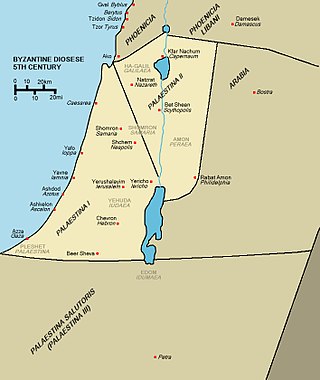
Palaestina Secunda or Palaestina II was a province of the Byzantine Empire from 390, until its conquest by the Muslim armies in 634–636. Palaestina Secunda, a part of the Diocese of the East, roughly comprised inland Galilee, the Jezreel (Yizrael) Valley, Bet Shean Valley, and the corresponding area of Transjordan, with its capital in Scythopolis. The province experienced the rise of Christianity under the Byzantines, but was also a thriving center of Judaism, after the Jews had been driven out of Judea by the Romans as a result of their 1st- and 2nd-century revolts.

The Second Temple period or post-exilic period in Jewish history denotes the approximately 600 years during which the Second Temple stood in the city of Jerusalem. It began with the return to Zion and subsequent reconstruction of the Temple in Jerusalem, and ended with the First Jewish–Roman War and the Roman siege of Jerusalem.

Judea or Judaea is a mountainous region of the Levant. Traditionally dominated by the city of Jerusalem, it is now part of Palestine and Israel. The name's usage is historic, having been used in antiquity and still into the present day; it originates from Yehudah, a Hebrew name. Yehudah was a son of Jacob, who was later given the name "Israel" and whose sons collectively headed the Twelve Tribes of Israel. Yehudah's progeny among the Israelites formed the Tribe of Judah, with whom the Kingdom of Judah is associated. Related nomenclature continued to be used under the rule of the Babylonians, the Persians, the Greeks, and the Romans. Under the Hasmoneans, the Herodians, and the Romans, the term was applied to an area larger than Judea of earlier periods. In 132 CE, the Roman province of Judaea was merged with Galilee to form the enlarged province of Syria Palaestina.

The history of the Jews in the Roman Empire traces the interaction of Jews and Romans during the period of the Roman Empire. A Jewish diaspora had migrated to Rome and to the territories of Roman Europe from the land of Israel, Anatolia, Babylon and Alexandria in response to economic hardship and incessant warfare over the land of Israel between the Ptolemaic and Seleucid empires from the 4th to the 1st centuries BCE. In Rome, Jewish communities thrived economically. Jews became a significant part of the Roman Empire's population in the first century CE, with some estimates as high as 7 million people; however, this estimation has been questioned.

This article presents a list of notable historical references to the name Palestine as a place name for the region of Palestine throughout history. This includes uses of the localized inflections in various languages, such as Arabic Filasṭīn and Latin Palaestina.
The administration of Judaea as a province of Rome from 6 to 135 was carried out primarily by a series of Roman Prefects, Procurators, and Legates pro praetore. These administrators coincided with the ostensible rule by Hasmonean and Herodian rulers of Judea. The Roman administrators were as follows:
References
- ↑ The Scroll of Antiochus (Megillath Benei Hashmonai), printed in the Yemenite Baladi-rite prayer book, Sefer Ha-Tiklāl (Tiklal Qadmonim), ed. Yosef Ḥubārah, Jerusalem 1964, pp. 75b–ff.
- ↑ Dioscorides, Materia Medica (4-160), p. 715
- ↑ Josephus, De Bello Judaico (The Jewish War) III, 51 (The Jewish War 3.3.5)
- ↑ Josephus. The Jewish War (1.6.5; 4.8.1); Antiquities (14.3.4).
- ↑ Naturalis Historia , 5:66–73
- ↑ Pliny (1947). H. Rackham (ed.). Natural History. Vol. 2. Cambridge: Harvard University Press. p. 273 (Book V, ch. XV, 70). ISBN 0674993888. OCLC 954144356.
- ↑ Josephus, Antiquities XIV.I.4. (14.14)
- ↑ Lehmann, Clayton Miles (Summer 1998). "Palestine: History: 135–337: Syria Palaestina and the Tetrarchy". The On-line Encyclopedia of the Roman Provinces. University of South Dakota. Archived from the original on 2009-08-11. Retrieved 2014-08-24.
- ↑ Rabbi Judah the Prince, The Mishnah (ed. Herbert Danby, Oxford University Press: Oxford 1933, s.v. Tractate Sheviit 9:2.
- ↑ Epiphanius’ Treatise on Weights and Measures: The Syriac Version, Studies in Ancient Oriental Civilization (SAOC), page 30, line 54c
- ↑ p. 1
- ↑ Salmon, Thomas (1744). Modern History Or the Present State of All Nations. T. Longman. p. 461.