
Marfan syndrome (MFS) is a multi-systemic genetic disorder that affects the connective tissue. Those with the condition tend to be tall and thin, with long arms, legs, fingers, and toes. They also typically have exceptionally flexible joints and abnormally curved spines. The most serious complications involve the heart and aorta, with an increased risk of mitral valve prolapse and aortic aneurysm. The lungs, eyes, bones, and the covering of the spinal cord are also commonly affected. The severity of the symptoms is variable.

Aortic dissection (AD) occurs when an injury to the innermost layer of the aorta allows blood to flow between the layers of the aortic wall, forcing the layers apart. In most cases, this is associated with a sudden onset of agonizing chest or back pain, often described as "tearing" in character. Vomiting, sweating, and lightheadedness may also occur. Damage to other organs may result from the decreased blood supply, such as stroke, lower extremity ischemia, or mesenteric ischemia. Aortic dissection can quickly lead to death from insufficient blood flow to the heart or complete rupture of the aorta.
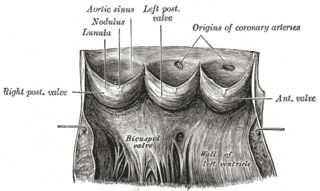
Aneurysm of the aortic sinus, also known as the sinus of Valsalva, is a rare abnormality of the aorta, the largest artery in the body. The aorta normally has three small pouches that sit directly above the aortic valve, and an aneurysm of one of these sinuses is a thin-walled swelling. Aneurysms may affect the right (65–85%), non-coronary (10–30%), or rarely the left coronary sinus. These aneurysms may not cause any symptoms but if large can cause shortness of breath, palpitations or blackouts. Aortic sinus aneurysms can burst or rupture into adjacent cardiac chambers, which can lead to heart failure if untreated.

A thoracic aortic aneurysm is an aortic aneurysm that presents primarily in the thorax.
Aortic valve replacement is a cardiac surgery procedure whereby a failing aortic valve is replaced with an artificial heart valve. The aortic valve may need to be replaced because of aortic regurgitation, or if the valve is narrowed by stenosis.

The Toronto General Hospital (TGH) is a major teaching hospital in Toronto, Ontario, Canada and the flagship campus of University Health Network (UHN). It is located in the Discovery District of Downtown Toronto along University Avenue's Hospital Row; it is directly north of The Hospital for Sick Children, across Gerrard Street West, and east of Princess Margaret Cancer Centre and Mount Sinai Hospital. The hospital serves as a teaching hospital for the University of Toronto Faculty of Medicine. In 2019, the hospital was ranked first for research in Canada by Research Infosource for the ninth consecutive year.
Valve-sparing aortic root replacement is a cardiac surgery procedure which is used to treat Aortic aneurysms and to prevent Aortic dissection. It involves replacement of the aortic root without replacement of the aortic valve. Two similar procedures were developed, one by Sir Magdi Yacoub, and another by Tirone David.
The Bentall procedure is a type of cardiac surgery involving composite graft replacement of the aortic valve, aortic root, and ascending aorta, with re-implantation of the coronary arteries into the graft. This operation is used to treat combined disease of the aortic valve and ascending aorta, including lesions associated with Marfan syndrome. The Bentall procedure was first described in 1968 by Hugh Bentall and Antony De Bono. It is considered a standard for individuals who require aortic root replacement, and the vast majority of individuals who undergo the surgery receive mechanical valves.

Annuloaortic ectasia is characterized by pure aortic valve regurgitation and aneurysmal dilatation of the ascending aorta. Men are more likely than women to develop idiopathic annuloaortic ectasia, which usually manifests in the fourth or sixth decades of life. Additional factors that contribute to this condition include osteogenesis imperfecta, inflammatory aortic diseases, intrinsic valve disease, Loeys-Dietz syndrome, Marfan syndrome, and operated congenital heart disease.
Duke E. Cameron is an American cardiac surgeon. Formerly Chief of Cardiac Surgery at Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine; the James T. Dresher Sr. Professor of Surgery; Director of Pediatric Cardiac Surgery; and Director of The Dana and Albert "Cubby" Broccoli Center for Aortic Diseases , at the Johns Hopkins Hospital, he returned to Hopkins in 2023. His clinical interests include:

Randall Bertram Griepp was an American cardiothoracic surgeon who collaborated with Norman Shumway in the development of the first successful heart transplant procedures in the U.S. He had an international reputation for contributions to the surgical treatment of aortic aneurysms and aortic dissection and in heart and lung transplantations. He received nearly $8 million in grants from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute.
Lars Georg Svensson is a cardiac surgeon and the chairman of the heart and vascular institute at Cleveland Clinic. He is the Director of the Aorta Center, Director of the Marfan Syndrome and Connective Tissue Disorder Clinic, and is a professor of surgery at Cleveland Clinic Lerner College of Medicine and Case Western Reserve University. He is also the Director of Quality Outcomes and Process Improvement for the Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery and Affiliate Cardiac Surgery Program at Cleveland Clinic.
Hugh Bentall FRCS was a British surgeon who pioneered open-heart surgery.
Giuseppe Di Benedetto is an Italian cardiac surgeon born in Eboli on 8 January 1946, He holds the Italian national record for the use of carbon dioxide laser to perform revascularization trans-myocardial otherwise inoperable; specialized in congenital diseases of cardiovascular system, is one of the few surgeons in the world that practice successfully the surgery of aortic arch.
Michael J. Reardon is an American cardiac surgeon and medical researcher. He is known for his work in heart autotransplantation for malignant heart tumors, an operation in which the surgeon removes the patient's heart, cuts out the malignant tumor, and reimplants the heart back in the patient's chest. He performed the first successful heart autotransplantation for a cancerous heart tumor in 1998.

Hans-Joachim Schäfers is a German surgeon, as well as cardiac, thoracic, and vascular surgeon and university professor. He is director of the department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery at the Saarland University Medical Center in Homburg/Saar, Germany. He is known for his activities in aortic valve repair, aortic surgery, and pulmonary endarterectomy.

Christoph Huber MD, FMH, FECTS is a Swiss cardiac surgeon who is a professor and the head of the Division of Cardiac and Vascular Surgery at the University Hospital Geneva, Switzerland.
Marjan Jahangiri FRCS, FRCS (CTh) is Professor of Cardiac Surgery at St. George's Hospital, University of London. She was the first woman to be appointed professor of cardiac surgery in the United Kingdom and Europe.
John D. Puskas is an American researcher, author, inventor and cardiovascular surgeon. As of 2022, he is Professor, Cardiovascular Surgery, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, and chairman, Department of Cardiovascular Surgery at Mount Sinai Morningside, Mount Sinai Beth Israel and Mount Sinai West. He holds 11 U.S. patents and co-founded the International Coronary Congress and the International Society for Coronary Artery Surgery. He is credited by ResearchGate with 330 publications and 15,234 citations and as of 2022 Scopus reports an h-index of 62. Puskas is known for advancing coronary artery bypass (CABG) surgery by refining surgical techniques for all-arterial, off-pump CABG and inventing finer instruments to be used for advanced coronary bypass surgical procedures. He is credited with performing the first totally thoracoscopic bilateral pulmonary vein isolation procedure. He is the co-editor of State of the Art Surgical Coronary Revascularization, the first textbook solely devoted to coronary artery surgery.
Joseph E. Bavaria, M.D., FACS, FRCS (Edin) ad hom, is an American cardiothoracic surgeon a professor of surgery at the University of Pennsylvania and Director of its Thoracic Aortic Surgery Program. Bavaria is known as a leading figure in clinical trials for catheter-based aortic valve replacement (TAVR), thoracic aortic surgery, and aortic endograft procedures (TEVAR). He wrote more than 600 research papers and founded the Penn Aortic Center. Bavaria served as the 52nd president of the Society of Thoracic Surgeons (STS) from 2016 to 2017, the 3rd President of the Thoracic Surgery Foundation (TSF) (2019-2022), the Chairman of The Society of Thoracic Surgeons/ACC TVT Registry Steering Committee (2017-2020) and an International Councilor of the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS) (2021-2024) Bavaria has performed more than 9,000 surgeries throughout his career as of 2019.








