
The Apple II is a personal computer released by Apple Inc. in June 1977. It was one of the first successful mass-produced microcomputer products and is widely regarded as one of the most important personal computers of all time due to its role in popularizing home computing and influencing later software development.

The Atari 5200 SuperSystem or simply Atari 5200 is a home video game console introduced in 1982 by Atari, Inc. as a higher-end complement for the popular Atari Video Computer System. The VCS was renamed to the Atari 2600 at the time of the 5200's launch. Created to compete with Mattel's Intellivision, the 5200 wound up a direct competitor of ColecoVision shortly after its release. While the Coleco system shipped with the first home version of Nintendo's Donkey Kong, the 5200 included the 1978 arcade game Super Breakout which had already appeared on the Atari 8-bit computers and Atari VCS in 1979 and 1981 respectively.

The Commodore 64, also known as the C64, is an 8-bit home computer introduced in January 1982 by Commodore International. It has been listed in the Guinness World Records as the highest-selling single computer model of all time, with independent estimates placing the number sold between 12.5 and 17 million units. Volume production started in early 1982, marketing in August for US$595. Preceded by the VIC-20 and Commodore PET, the C64 took its name from its 64 kilobytes(65,536 bytes) of RAM. With support for multicolor sprites and a custom chip for waveform generation, the C64 could create superior visuals and audio compared to systems without such custom hardware.

The Intellivision is a home video game console released by Mattel Electronics in 1979. Development began in 1977, the same year as the launch of its main competitor, the Atari 2600. In 1984, Mattel sold its video game assets to a former Mattel Electronics executive and investors, eventually becoming INTV Corporation. Game development ran from 1978 to 1990, when the Intellivision was discontinued. From 1980 to 1983, more than 3.75 million consoles were sold. As per Intellivision Entertainment the final tally through 1990 is somewhere between 4.5 and 5 million consoles sold.

The Atari 8-bit computers, formally launched as the Atari Home Computer System, are a series of 8-bit home computers introduced by Atari, Inc. in 1979 with the Atari 400 and Atari 800. The architecture is designed around the MOS Technology 6502 CPU and three custom coprocessors which provide support for sprites, smooth multidirectional scrolling, four channels of audio, and other features. The graphics and sound are more advanced than most of its contemporaries, and video games are a key part of the software library. The 1980 first-person space combat simulator Star Raiders is considered the platform's killer app.

Zak McKracken and the Alien Mindbenders is a 1988 graphic adventure game by Lucasfilm Games. It was the second game to use the SCUMM engine, after Maniac Mansion. The project was led by David Fox, with Matthew Alan Kane as the co-designer and co-programmer.

Duckman: Private Dick/Family Man, commonly known simply as Duckman, is an American animated sitcom created and developed by Everett Peck, based on characters he created in his 1990 one-shot comic book published by Dark Horse Comics. Duckman aired on the USA Network from March 5, 1994, through September 6, 1997, for 4 seasons and 70 episodes. It follows Eric Tiberius Duckman, a private detective who lives with his family.

Arkanoid is a 1986 block breaker arcade game developed and published by Taito. In North America, it was published by Romstar. Controlling a paddle-like craft known as the Vaus, the player is tasked with clearing a formation of colorful blocks by deflecting a ball towards it without letting the ball leave the bottom edge of the playfield. Some blocks contain power-ups that have various effects, such as increasing the length of the Vaus, creating several additional balls, or equipping the Vaus with cannons. Other blocks may be indestructible or require multiple hits to break.

Deluxe Paint, often referred to as DPaint, is a bitmap graphics editor created by Dan Silva for Electronic Arts and published for the then-new Amiga 1000 in November 1985. A series of updated versions followed, some of which were ported to other platforms. An MS-DOS release with support for the 256 color VGA standard became popular for creating pixel graphics in video games in the 1990s.

MicroProse is an American video game publisher and developer founded by Bill Stealey, Sid Meier, and Andy Hollis in 1982. It developed and published numerous games, including starting the Civilization and X-COM series. Most of their internally developed titles were vehicle simulation and strategy games.

Centipede is a 1981 fixed shooter arcade video game developed and published by Atari, Inc. Designed by Dona Bailey and Ed Logg, it was one of the most commercially successful games from the golden age of arcade video games and one of the first with a significant female player base. The primary objective is to shoot all the segments of a centipede that winds down the playing field. An arcade sequel, Millipede, followed in 1982.

Dangerous Dave is a 1988 computer game by John Romero. It was developed for the Apple II and DOS as an example game to accompany his article about his GraBASIC, an Applesoft BASIC add-on, for the UpTime disk magazine.
Chessmaster is a chess-playing video game series, which is owned and developed by Ubisoft. It is the best-selling chess franchise, with more than five million units sold as of 2002. The same cover art image featuring Will Hare was used from Chessmaster 2000 to Chessmaster 9000.

Rybka is a computer chess engine designed by International Master Vasik Rajlich. Around 2011, Rybka was one of the top-rated engines on chess engine rating lists and won many computer chess tournaments.

The Casio Loopy, subtitled My Seal Computer SV-100, is a 32-bit home video game console. Released exclusively in Japan in October 1995 with a price of 25,000¥, the marketing for it was completely targeted to female gamers.
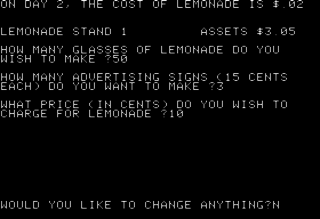
Lemonade Stand is a business simulation game created in 1973 by Bob Jamison of the Minnesota Educational Computing Consortium (MECC). In it, the player moves through several rounds of running a lemonade stand, beginning each round by making choices dependent on their current amount of money about their stock, prices, and advertising. In each round, the results are randomized based on the player's inputs, as well as affected by random events such as thunderstorms and street closures. Each round ends with a summary of the player's current status, and the game ends after 12 rounds.

Abandonware is a product, typically software, ignored by its owner and manufacturer, which can no longer be found for sale, and for which no official support is available and can't be bought.

Game-Maker is an MS-DOS-based suite of game design tools, accompanied by demonstration games, produced between 1991 and 1995 by the Amherst, New Hampshire based Recreational Software Designs and sold through direct mail in the US by KD Software. Game-Maker also was sold under various names by licensed distributors in the UK, Korea, and other territories including Captain GameMaker and Create Your Own Games With GameMaker!. Game-Maker is notable as one of the first complete game design packages for DOS-based PCs, for its fully mouse-driven graphical interface, and for its early support for VGA graphics, Sound Blaster sound, and full-screen four-way scrolling.

Gumball is a video game written for the Apple II by Veda Hlubinka-Cook and published by Broderbund in 1983. It was ported to the Atari 8-bit computers, and Commodore 64. The player controls the valves of a maze-like machine to sort gumballs by color.


















