Related Research Articles
Human teeth function to mechanically break down items of food by cutting and crushing them in preparation for swallowing and digesting. As such, they are considered part of the human digestive system. Humans have four types of teeth: incisors, canines, premolars, and molars, which each have a specific function. The incisors cut the food, the canines tear the food and the molars and premolars crush the food. The roots of teeth are embedded in the maxilla or the mandible and are covered by gums. Teeth are made of multiple tissues of varying density and hardness.

Tooth decay, also known as cavities or caries, is the breakdown of teeth due to acids produced by bacteria. The cavities may be a number of different colors from yellow to black. Symptoms may include pain and difficulty with eating. Complications may include inflammation of the tissue around the tooth, tooth loss and infection or abscess formation.

A root canal is the naturally occurring anatomic space within the root of a tooth. It consists of the pulp chamber, the main canal(s), and more intricate anatomical branches that may connect the root canals to each other or to the surface of the root.

Dental braces are devices used in orthodontics that align and straighten teeth and help position them with regard to a person's bite, while also aiming to improve dental health. They are often used to correct underbites, as well as malocclusions, overbites, open bites, gaps, deep bites, cross bites, crooked teeth, and various other flaws of the teeth and jaw. Braces can be either cosmetic or structural. Dental braces are often used in conjunction with other orthodontic appliances to help widen the palate or jaws and to otherwise assist in shaping the teeth and jaws.
Cosmetic dentistry is generally used to refer to any dental work that improves the appearance of teeth, gums and/or bite. It primarily focuses on improvement in dental aesthetics in color, position, shape, size, alignment and overall smile appearance. Many dentists refer to themselves as "cosmetic dentists" regardless of their specific education, specialty, training, and experience in this field. This has been considered unethical with a predominant objective of marketing to patients. The American Dental Association does not recognize cosmetic dentistry as a formal specialty area of dentistry. However, there are still dentists that promote themselves as cosmetic dentists.

Endodontics is the dental specialty concerned with the study and treatment of the dental pulp.
Dental restoration, dental fillings, or simply fillings are treatments used to restore the function, integrity, and morphology of missing tooth structure resulting from caries or external trauma as well as to the replacement of such structure supported by dental implants. They are of two broad types—direct and indirect—and are further classified by location and size. A root canal filling, for example, is a restorative technique used to fill the space where the dental pulp normally resides.

Toothache, also known as dental pain or tooth pain, is pain in the teeth or their supporting structures, caused by dental diseases or pain referred to the teeth by non-dental diseases. When severe it may impact sleep, eating, and other daily activities.

Deciduous teeth or primary teeth, also informally known as baby teeth, milk teeth, or temporary teeth, are the first set of teeth in the growth and development of humans and other diphyodonts, which include most mammals but not elephants, kangaroos, or manatees, which are polyphyodonts. Deciduous teeth develop during the embryonic stage of development and erupt during infancy. They are usually lost and replaced by permanent teeth, but in the absence of their permanent replacements, they can remain functional for many years into adulthood.

A dental extraction is the removal of teeth from the dental alveolus (socket) in the alveolar bone. Extractions are performed for a wide variety of reasons, but most commonly to remove teeth which have become unrestorable through tooth decay, periodontal disease, or dental trauma, especially when they are associated with toothache. Sometimes impacted wisdom teeth cause recurrent infections of the gum (pericoronitis), and may be removed when other conservative treatments have failed. In orthodontics, if the teeth are crowded, healthy teeth may be extracted to create space so the rest of the teeth can be straightened.

The maxillary first molar is the human tooth located laterally from both the maxillary second premolars of the mouth but mesial from both maxillary second molars.
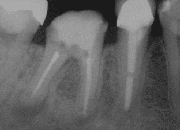
A root end surgery, also known as apicoectomy, apicectomy, retrograde root canal treatment or root-end filling, is an endodontic surgical procedure whereby a tooth's root tip is removed and a root end cavity is prepared and filled with a biocompatible material. It is an example of a periradicular surgery.

Veterinary dentistry is the field of dentistry applied to the care of animals. It is the art and science of prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of conditions, diseases, and disorders of the oral cavity, the maxillofacial region, and its associated structures as it relates to animals.
Dilaceration is a developmental disturbance in shape of teeth. It refers to an angulation, or a sharp bend or curve, in the root or crown of a formed tooth. This disturbance is more likely to affect the maxillary incisors and occurs in permanent dentition. Although this may seem more of an aesthetics issue, an impacted maxillary incisor will cause issues related to occlusion, phonetics, mastication, and psychology on young patients.

Dental instruments are tools that dental professionals use to provide dental treatment. They include tools to examine, manipulate, treat, restore, and remove teeth and surrounding oral structures.
Dental anatomy is a field of anatomy dedicated to the study of human tooth structures. The development, appearance, and classification of teeth fall within its purview. Tooth formation begins before birth, and the teeth's eventual morphology is dictated during this time. Dental anatomy is also a taxonomical science: it is concerned with the naming of teeth and the structures of which they are made, this information serving a practical purpose in dental treatment.

Root canal treatment is a treatment sequence for the infected pulp of a tooth which is intended to result in the elimination of infection and the protection of the decontaminated tooth from future microbial invasion. Root canals, and their associated pulp chamber, are the physical hollows within a tooth that are naturally inhabited by nerve tissue, blood vessels and other cellular entities. Together, these items constitute the dental pulp.

When extracting lower wisdom teeth, coronectomy is a treatment option involving removing the crown of the lower wisdom tooth, whilst keeping the roots in place in healthy patients. This option is given to patients as an alternative to extraction when the wisdom teeth are in close association with the inferior alveolar nerve, and so used to prevent damage to the nerve which may occur during extraction.
The Hall Technique is a minimally-invasive treatment for decayed baby back (molar) teeth. Decay is sealed under preformed crowns, avoiding injections and drilling. It is one of a number of biologically orientated strategies for managing dental decay.
Root resection or root amputation is a type of periradicular surgery in which an entire root of a multiroot tooth is removed. It contrasts with an apicoectomy, where only the tip of the root is removed, and hemisection, where a root and its overlying portion of the crown are separated from the rest of the tooth, and optionally removed.
References
- ↑ "Endodontists' Guide to CDT 2017" (PDF). American Association of Endodontists. 2017. pp. 13–14. Retrieved 2020-03-14.
- ↑ Organization, The Dentist Near Me (2022-12-01). "Tooth Hemisection". thedentistnearme.info.