Related Research Articles

In modern mapping, a topographic map or topographic sheet is a type of map characterized by large-scale detail and quantitative representation of relief features, usually using contour lines, but historically using a variety of methods. Traditional definitions require a topographic map to show both natural and artificial features. A topographic survey is typically based upon a systematic observation and published as a map series, made up of two or more map sheets that combine to form the whole map. A topographic map series uses a common specification that includes the range of cartographic symbols employed, as well as a standard geodetic framework that defines the map projection, coordinate system, ellipsoid and geodetic datum. Official topographic maps also adopt a national grid referencing system.

Topography is the study of the forms and features of land surfaces. The topography of an area may refer to the land forms and features themselves, or a description or depiction in maps.

The raphe nuclei are a moderate-size cluster of nuclei found in the brain stem. They have 5-HT1 receptors which are coupled with Gi/Go-protein-inhibiting adenyl cyclase. They function as autoreceptors in the brain and decrease the release of serotonin. The anxiolytic drug Buspirone acts as partial agonist against these receptors. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) antidepressants are believed to act in these nuclei, as well as at their targets.
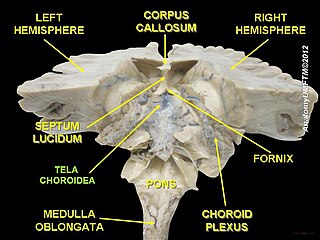
The choroid plexus, or plica choroidea, is a plexus of cells that arises from the tela choroidea in each of the ventricles of the brain. Regions of the choroid plexus produce and secrete most of the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) of the central nervous system. The choroid plexus consists of modified ependymal cells surrounding a core of capillaries and loose connective tissue. Multiple cilia on the ependymal cells move to circulate the cerebrospinal fluid.
STS-99 was a Space Shuttle mission using Endeavour, that launched on 11 February 2000 from Kennedy Space Center, Florida. The primary objective of the mission was the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM) project. This was also the last solo flight of Endeavour; all future flights for Endeavour became devoted to the International Space Station. STS-99 was also the first Shuttle mission of the 2000s.

The genitourinary system, or urogenital system, are the organs of the reproductive system and the urinary system. These are grouped together because of their proximity to each other, their common embryological origin and the use of common pathways, like the male urethra. Also, because of their proximity, the systems are sometimes imaged together.

The locus coeruleus (LC), also spelled locus caeruleus or locus ceruleus, is a nucleus in the pons of the brainstem involved with physiological responses to stress and panic. It is a part of the reticular activating system.

The elevation of a geographic location is its height above or below a fixed reference point, most commonly a reference geoid, a mathematical model of the Earth's sea level as an equipotential gravitational surface . The term elevation is mainly used when referring to points on the Earth's surface, while altitude or geopotential height is used for points above the surface, such as an aircraft in flight or a spacecraft in orbit, and depth is used for points below the surface.

The thyroid cartilage is the largest of the nine cartilages that make up the laryngeal skeleton, the cartilage structure in and around the trachea that contains the larynx. It does not completely encircle the larynx.
The Systematized Nomenclature of Medicine (SNOMED) is a systematic, computer-processable collection of medical terms, in human and veterinary medicine, to provide codes, terms, synonyms and definitions which cover anatomy, diseases, findings, procedures, microorganisms, substances, etc. It allows a consistent way to index, store, retrieve, and aggregate medical data across specialties and sites of care. Although now international, SNOMED was started in the U.S. by the College of American Pathologists (CAP) in 1973 and revised into the 1990s. In 2002 CAP's SNOMED Reference Terminology was merged with, and expanded by, the National Health Service's Clinical Terms Version 3 to produce SNOMED CT.

The iris dilator muscle, is a smooth muscle of the eye, running radially in the iris and therefore fit as a dilator. The pupillary dilator consists of a spokelike arrangement of modified contractile cells called myoepithelial cells. These cells are stimulated by the sympathetic nervous system. When stimulated, the cells contract, widening the pupil and allowing more light to enter the eye.

The ilium is the uppermost and largest part of the coxal bone, and appears in most vertebrates including mammals and birds, but not bony fish. All reptiles have an ilium except snakes, although some snake species have a tiny bone which is considered to be an ilium.
Nomina Anatomica (NA) was the international standard on human anatomic terminology from 1895 until it was replaced by Terminologia Anatomica in 1998.
Terminologia Anatomica is the international standard for human anatomical terminology. It is developed by the Federative International Programme on Anatomical Terminology, a program of the International Federation of Associations of Anatomists (IFAA).

Corneal topography, also known as photokeratoscopy or videokeratography, is a non-invasive medical imaging technique for mapping the anterior curvature of the cornea, the outer structure of the eye. Since the cornea is normally responsible for some 70% of the eye's refractive power, its topography is of critical importance in determining the quality of vision and corneal health.
A topographic map is the ordered projection of a sensory surface, like the retina or the skin, or an effector system, like the musculature, to one or more structures of the central nervous system. Topographic maps can be found in all sensory systems and in many motor systems.
Topography may refer to:
A clinical coder—also known as clinical coding officer, diagnostic coder, medical coder, or nosologist—is a health information professional whose main duties are to analyse clinical statements and assign standardized codes using a classification system. The Health data produced are an integral part of health information management, and are used by local and national governments, private healthcare organizations and international agencies for various purposes, including medical and health services research, epidemiological studies, health resource allocation, case mix management, public health programming, medical billing, and public education.

Anatomical terminology is a form of scientific terminology used by anatomists, zoologists, and health professionals such as doctors, physicians, and pharmacists.
References
- ↑ Thompson, Edward Theodore; Hayden, Adaline C. (1956). Anatomy for the Medical Record Librarian. Physicians' Record Company. Retrieved 16 May 2023.